by
Andrei
Conovaloff —
Draft In-Progress:
(Started: 2012; last updated 22 March 2025)
Comments, corrections welcome — Administrator @ Molokane. org — Link: goo.gl/oGJX0U Some parts of this long text are duplicated, and being edited as time permits. Changes mainly in Malakan places, animals and foods Contents
The purpose of this simple Taxonomy (classification system) is to
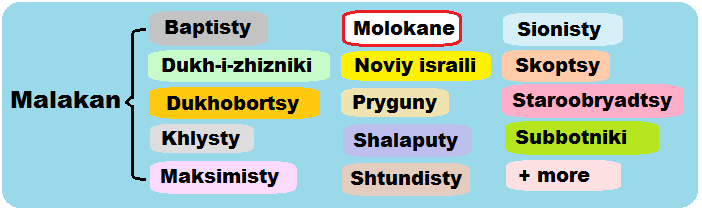
Please properly use these 3 transliterated Russian terms in honest respect, to set the record straight. Avoid confusing English labels, except to define the original labels in the Russian language. Avoid extensive misinformation and disinformation published after 1900. Though all of these 3 groups, and sub-groups, use the Russian Synodal Bible ritually opened on their meeting tables, only Dukh-i-zhizniki require it, without a cross embossed on the cover. Molokane and Pryguny can use any Russian Bible. Molokane have the least ritual. Dukh-i-zhizniki impose the most ritual rules, insist on their own religious texts and songs, and typically avoid other faiths and some Dukh-i-zhiznik tribes. Other Spiritual Christian (non-Orthodox, folk-Protestant, sectarian) groups with origins in Old Russia that resettled in North America (Adventisty, Baptisti, Dukhobortsy,*** Evangeliki, Pyatidesyatniki, Shalaputi, Subbotniki, Svobodniki, Shtundisty, etc.) are not the focus of this taxonomy, though they were all often called malakan, and Molokan in error. Old Orthodox faiths (Old Ritualists, staroobryadtsy, Old Believers, staroverie) are raskolniki, not Spiritual Christians, and are also confused as malakan. And Molokane have mistakenly been called "old believers" probably because their faiths are "old". Too many journalists and scholars confuse the various groups of Spiritual Christians from Russia because they are somewhat historically related but extensively divided and evolved over time into many distinct groupings. The Summary Charts below will help one to easily identify these 3 major groups. * Etymology of Tambov is from tomba, a Mordovian Moksha term for "deep pool of water," referring to the vast wetlands in the province. A myth among American Dukh-i-zhizniki is the origin of their faiths is from the phrase tam Bog (там Бог : God is there), falsely implying that their religions and prophet M.G. Rudomyotkin are from a place with a holy name. Spelling and Pronunciation Guide, and Relative Distribution
** U.M.C.A. : United Molokan Christian Association, a misnamed Sunday School and youth social organization, that published booklets of transliterated songs. *** For Spiritual Christians who retained their ancestral Ukrainian and/or Southern Russian dialects, Prygun/ Pryguny must be pronounced as Prihun/ Prihuny (Pree-hoon/ Pree-hoo-NEE).(6) ^ Contents
^
Summary Charts in 4 Languages — English, Russian Русский , Spanish Español, Turkish Türkçe —————————————————— ENGLISH These 3 Spiritual Christian groups are easily identified by their characteristic liturgies used during prayer-worship services.
1.
Founded in America. All
Maksimisty are Dukh-i-zhizniki, but
not all Dukh-i-zhizniki are Maksimisty.
2. Most songs are adapted from Russian folk songs, and borrowed from German Protestants in Russia. 3. Not during worship service, but often during meals at weddings, funerals, child dedication, holidays 4. Open canon, a sacred text that can be modified by continuous revelation through their prophets. 5. Each congregation has 1 or more prophets. There have been at least 200 prophets since 1928 in all congregations around the world. Prophecies of only 4 prophets were published in their Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' (1928 religious text in Los Angeles). Over 100 prophesies are written in secret notebooks shown only to trusted believers. 6. In Taurida Governorate in 1833 they organized. But the "Pryguny" label first appeared in 1856 to describe these tribes in Caucasus.(84) And in 1897, Pryguny were counted in the census of the Russian Empire separate from Molokane, and other Spiritual Christians. RUSSIAN Эти три группы духовных христиан можно легко определить по их различним характеристикам.
1. Основанная в
Америке. Все максимисты – дух-и-жизники, но не все
дух-и-жизники максимисты.
2. Большинство взято из русских народных песен и заимствовано от немецких протестантов в России.. 3. Поют во время обеда на свадьбах, похоронах, кстинах и праздниках.. 4. Священный текст который может быть непрерывно изменен через откровения пророков. 5. Каждое собрание имеет по меньшей мере одного пророка. С 1928 года во всех общинах по всему миру было по меньшей мере 200 пророков. Пророчества только 4 пророков были опубликованы в их Книге солнца, дух и жизнь (священная книга от 1928 г.). Более чем 100 пророчеств были записаны в секретных тетрадях и только иногда эти пророчества показаны самым надежным верующим. ^ Contents ^
SPANISH Estos 3 grupos cristianos espirituales son fácilmente identificados por sus liturgias característicos usados durante los servicios de oración de adoración.
1.
Fundada en los Estados Unidos. Todos los Maksimisty
son Dukh-i-zhizniki, pero no todos los Dukh-i-zhizniki
son Maksimisty.
2. La mayoría fueron tomadas de canciones populares rusas y tomadas de los protestantes alemanes en Rusia.. 3. No durante el servicio, pero a menudo durante las comidas en las bodas, funerales, dedicación niño, días de fiesta. 4. Abra canon, un texto sagrado que puede ser modificado por la revelación continua, algo similar a cánones de los Santos de los Últimos Días. 5. Cada congregación tiene uno o más profetas. Ha habido por lo menos 200 profetas desde 1928 en todas las congregaciones de todo el mundo. Profecías de sólo 4 profetas fueron publicados en su Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' (Libro del Sol, Espíritu y Vida, 1928 libro sagrado). Más de 100 profecías están escritas en cuadernos secretos, que se muestran sólo a los miembros que creen en el espíritu. TURKISH Bu 3 Manevi Hıristiyan gruplar kolayca dua-ibadet sırasında kullanılan karakteristik ayinlerinde tarafından tespit edilir.
1.
Amerika Birleşik
Devletleri'nde kurulmuştur. Her Maksimist bir Dukh-i-zhizniki
olan; bazı Dukh-i-zhizniki Maksimisty olan.
2. Şarkıların çoğu Rus halk şarkılarından uyarlanmış olup, ve Rusya'daki Alman Protestanlardan ödünç alınmıştır. 3. Değil hizmeti sırasında, ama çoğu zaman düğün, cenaze, çocuk özveri ve dini yemekler sırasında.. 4. Onların peygamberler aracılığıyla sürekli vahiy tarafından değiştirilebilir bir kutsal metin. 5. Her topluluk, bir ya da daha fazla peygamber vardır. Ddünyadaki tüm cemaatlerin içinde 1928'den beri en az 200 peygamberler olmuştur. Sadece 4 peygamberler kitapta yayınlandı, Kniga solnste dukh i zhizn' (Güneşin Kitabı, Ruh ve Hayat, 1928 kutsal kitabı). 100'den fazla kehanetleri gizli dizüstü yazılır, sadece kendi kutsal ruhuna inanan üyelere gösterilen. ^ Contents ^
1. Introduction This Taxonomy answers 3 questions :
^ Contents ^
———————————Short answer to question 1: Why do so many falsely call themselves "Molokan"?
Captain P. A. Demens and P. V. Young, independently and sequentially intervened to help diverse groups of economic immigrants from Russia who resettled in the United States and Mexico. Both Demens and Young also immigrated from Slavic countries to the United States with family, spoke Russian, quickly learned English, and established high profile professions in America. I present evidence that they intentionally confusingly mislabeled all Spiritual Christians from Russia in Southern California as "Molokans" for different altruistic reasons. Below I show that both Demens and Young were powerful vectors for propagating the mythical identity of these immigrants from Russia.
Short answer to question 2: What and who are they? They are many different Spiritual Christian faiths. About 1% migrated to North America. After 1928 many fake Molokane became Dukh-i-zhizniki, some remained Pryguny, and with other Spiritual Christian faiths, continued to use the simple malakan label imported from South Russia, but wrongly misspelled as Molokan.(57) Most descendants in North America have assimilated into the "melting pot", some in Australia. ——————————— Short answer to question 3: Where are they now — the active congregations?
^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Why should you, a reader, care about this simple Taxonomy? Do you feel like:
Today you have no worries mates, but you need to know who you are now, and compare yourself to who your ancestors were in their own place and time. They did not carry a telephone-TV-computer in their pocket, and those before them did not have a telephone (some believed it was an evil thing), and before immigration most could not imagine such devices, or steam powered trains and boats. Most could not read or write. They knew how to spin thread, weave cloth and make cloths, grind grain and bake bread, build wagons and houses, which most of you do not know how to do. Those with a desire for knowledge may binge read this to the end and want more, and check periodically for updates. Dukh-i-zhizniki set in their zealous beliefs will ignore this for various personal reasons. They don't need it, and it is too much to read. It is religiously false to them. I am trying to apply hard science methods to soft science. In other words, I'm trying to use what I learn from developed natural sciences to social sciences, and present it to you in a way that you might understand. If you are an educated person, you can skip this section. If you barely finished high school and believe education "robs the spirit"(91) then you are probably not reading this. But, if you have read this far, I commend you for seeking knowledge. I don't expect you to accept my explanations here, but ask you to please continue with an open mind. Maybe you will check my references, go to libraries, travel to the F S U and do your own field research. Warning: this will be a lot of reading, surprises, travel and thinking. I've been doing this research since about 1970. Selling Dukh-i-zhizniki or Pryguny as Molokane is false advertising. Dukhobortsy in Canada have a similar problem.(28) ——————————————————————————— Can you imagine working with someone who has very little vocabulary and refuses to learn any new words? For many people, education is such an uncomfortable burden that they avoid learning. Many Dukh-i-zhizniki oppose education, especially for girls. Can you imagine someone who calls everyone "dude," never learning peoples' real names? Wouldn't life be so much simpler if we just all call everyone "dude"? That's so much easier than remembering Vassili Ivanovich, Mikhail Kondratich, Parasha Petrovna, ... It's even easier than "dude dudovich". Imagine a dude who doesn't know many words and always calls a #2 Phillips screwdriver a "stick," a shop broom a "stick," or a 15" pipe-wrench a "stick"? How can you work with him? Every tool with a handle he calls "stick." Would you get the tools yourself, or teach him a few new words? I have a Russia-born neighbor friend in Arizona who once said in Russian: "Я забыл мой ключ" (Ya zabyl moy kliuch), literally: "I forgot my key", and had to go home to get it. Later we figured out what he meant when we asked about his key. In Russia slang "key" also means "wrench". He was telling us he forgot his tools, and had to go home. Imagine that your spiritual friends hear that "yellow-tail tuna are running at Long Beach." They chartered a boat and invited you. You take your gear, pay, ride out into the ocean. The boat captain stops at a school of barracuda claiming they are tuna. "They are all the same," he says. "They swim, have a head and tail." Would you complain? Call him stupid? Demand your money back? What? Is borshch really cabbage soup, beet soup, tomato soup, potato soup, carrot soup, or something else? Broth, salt, pepper? Why call it borshch? If you did not know what borshch is, how can you ask for it?
* 7,500 varieties of apples are grown throughout the world, and 2,500 varieties are grown in the United States, 100 commercially.The table above shows examples of 4 classification analogies for the categories : Borshch, Spiritual Christians, Fruit and Rubbish Dumpsters. Each category term represents or contains many items (ingredients), and neither Borshch, Spiritual Christians nor Fruit are homogeneous. In Borshch one can easily recognize most of the separate vegetables, and taste the salt and pepper. I forgot about sour cream. Similarly, one can easily discern among various branches of the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians, even if they live in the same or adjacent villages, or neighborhoods. Though each tribe performs similar rituals during their meetings, they have different books, holidays, positions, songs, prayers, etc; and, they have different attitudes, beliefs and behaviors among and between tribes. Today the authentic Molokane are a fairly specific faith with some variations mainly due to geography (location, host country and language). Molokane are identified by their holidays, songs, and books, distinct from Pryguny and Dukh-i-zhizniki. They are as distinct as apples and oranges. For a simple analogy, one usually does not confuse, for example, Southern Baptists, The Church of Christ of Later Day Saints (LDS), and the Russian Orthodox Church(77) because each of these faiths recites the Lord's Prayer and baptizes in water. You know they are not the same for other reasons, and neither are Molokane, Pryguny or Dukh-i-zhiznki the same, nor are the many different tribes of Dukh-i-zhiznki. Upon immigration to Los Angeles, many Spiritual Christians called all the other Protestant faiths "baptisty", probably because they did water baptism. Even in the 2000s some Maksimisty still use the word "baptist" to refer to the "666 false faiths" scorned by Rudomyotkin in the Kniga Solnste dukh i zhizn'. Similarly I have heard the word Catholic (katoliki) used by Dukh-i-zhiznik elders to refer to all Orthodox and Roman Catholic people. Among the first generation of immigrant Spiritual Christians from Russia in Los Angeles, the words "baptist" and 'katolik" specified what kind of outsider (ne nash, them, out-group) they meant. Unfortunately an outsider, even those fluent in Russian, cannot easily determine who is of what faith or tribe by appearance from a distance, or up close, unless they know what to look for and ask. All the tribes from Russia may dress about the same, speak similar dialects, eat similar foods, perform similar rituals, etc. There is no way to categorize them until they conduct a religious service, or are quizzed about their liturgy, and checked against the Summary Charts above. Then they can be quickly identified using this taxonomy. Most outsiders cannot do such fact checking, even university-trained specialists, PhDs. Most do not meet the various Spiritual Christians during their religious service. The outsiders rely on and are misled by erroneous published literature and informants who do not know how to define their own faiths, and/or are hiding their faiths. I grew up among Dukh-i-zhiniki and visited Molokane in San Francisco many times, yet it took me from about 1960 to the 2000s (more than 40 years) to firmly decide a key word was missing — Dukh-i-zhizniki. ———————————————————————————— Dukh-i-zhiznik refused a Subbotnik elder In 2019, a Dukh-i-zhiznik named Ivan from Southern California, a truck driver delivering cars, met the Subbotnik presbyter Mihael Morozov in Portland, Oregon. I had met Morozov in Portland when I surveyed all the five Subbotniki congregations there (1 in Vancouver, WA) in 2018. I told thousands of these recent chain immigrants from Ukraine, Moldova, and Central Asia, about Subbotniki who came to Los Angeles 100 hears ago with other Spiritual Christians from Russia like my family. The first Subbotnik meeting hall was on Clarence street between First Street and the podval meeting hall and Klubnikin's Market, across the street from my mother's family Shubin's Bakery. The meeting hall moved to Breed Street, near the Armenian Prygun sobranie, and 1974 when they no longer had a . Morozov phoned me to tell me this story after they met. The Dukh-i-zh-i-znik had a beard, spoke some Russian and was friendly with the Russian speaking Morozov. Ivan bragged that he was a "Molokan", and his "church in Los Angeles" has "2000 members". Morozov was interested to meet these alleged Russian-speaking Christians, and got Ivan's phone number, later called and asked when could he visit. Ivan immediately changed his story claiming he actually attended a small "church" and I would have to ask his "preacher" for "permission" to invite a guest. Morozov called Ivan several times with no answer. Perturbed, Morozov phoned me in Arizona to ask what happened. I met Morozov several times while researching the Subbotniki of Portland, Oregon, and Vancouver, Washington. When we first met at his Saturday evening meeting, Morozov chose to interview me and my Russian Molokan wife before his congregation, with many questions. During that one week trip in August 2018, we met most of the 10,000 Subbotniki who immigrated to Oregon and Washington within the past 10 years. They sing several Bible verses similar to Dukh-i-zhizniki and Dukhobortsy. Some of the presvitery raise their hands during prayer at the end of the evening meeting, ending Sabbath. Morozov had no problem inviting an unexpected guest to the front of his Saturday night meeting, and he comfortably cancelled his regular service to use all their time to conduct an educational interview. He heard a couple of historians were touring their congregations and he wanted to make the most of our short time together. We both learned a lot about each other's history and faiths, as did his congregation. His congregation embraced interfaith Christian fellowship. So, how should I answer presbyter Mihael Morozov about why the "Christian" truck driver, Ivan, from Southern California bragged, acted friendly, then hid? I had to explain that Dukh-i-zhizniki are not Molokane, and they do not behave like other Christians. The number 2000 probably refers to all Dukh-i-zhznik congregations in the U.S.A. and Australia who attend during holidays. Why did Ivan not call back, or answer the phone? He was embarrassed, ashamed that he lied, and did not ask for permission to bring in a ne nash Spiritual Christian guest from Russia who speaks fluent Russian and knows the Bible well. ———————————————————————————— Readers should explore:
Many people habitually continue a mistake to be consistent with previous mistakes, to not confuse the listener-reader. "Don't rock the boat." What if Aristotle lied and said the earth is flat, because that's what most people believed in his time, and he did not want to upset or confuse them. But, Aristotle knew they were wrong and told them the truth. About 100 years later (240 B.C.), Eratosthenes estimated the circumference of the earth with perhaps less than 10% error. Many refused to believe the facts. Even today, there are a few flat earth societies. Another common example is people who continue to say that Aboriginal Indigenous Peoples, Native North Americans and First Nations, and over 200 named tribes/bands in North America are from India — Indians or West Indians. Many journalists now try to avoid this offensive mistake when possible and use terms like Native Americans, Indigenous people, tribal, etc., except when "Indian" happens to be part of an official agency name. Not knowing the right words is silly, like calling all animals with 4 feet and a tail "cats" because you don't know the other names (dog, horse, mouse, sheep, wolf, etc.); or, a dude not knowing the names of their tools, calling everything "hammer" that has a stick handle. Not knowing alternatives is dangerous in professions where we expect expertise. Would you trust a doctor who did not know the difference between carcinoma, sarcoma, lymphoma and blastoma? What if the doctor did not know the difference between arms and legs, or left and right? Would you trust a pharmacist who gave you any pill no matter what your prescription said? If not, then why trust the religious elders, journalists and professors who only know one term and definition for .... the reason I present this Taxonomy — to make sense out of non-sense. A simple historical classification system (below) accurately defines confused sub-groups of non-dukhobor Spiritual Christians, who, a century ago were told by Demens and Young and I. G. Samarin in Los Angeles that they should all falsely claim to be "Molokans" in America no matter what or who they were in Russia, or became in America. Though many resisted this name hijacking, the false identity transformation was gradually adopted until it passed a tipping-point after W.W.II, probably because:
In 1956, the first edition of the "Molokan Directory,"
which was distributed more than the Review,
contained a false title and a short false history on the
last page, which was reproduced on every update of the Directory
for the next 20 years. I was born in 1948 and was deceived by the false
"Molokan" label most of my life. But over time, as I
visited various congregations of Spiritual Christians
from Russia in North America, I could see the distinct
divisions between various Spiritual Christians in Canada
and the USA, and between Northern California and
Southern California, and among many of the congregations
and within congregations in Southern California and
Arizona. After 1992, during my 5 trips to Russia, I got
to know my relatives (father's first cousins) who sat on
the front rows of 3 different congregations in Pyatigorst,
Stavropol, Russia — Molokan, Prygun (dukhovniye)
and Maksimist (which uses their 1934 Kniga
solntse, dukh i zhin' in place of the Bible). The
Pyatigorst Prygun congregation, with some of my
Molokan relatives as guests, performed my
marriage ceremony in 1997. Many were excellent singers.
I am fortunate to have known many in my parent's
generation in Russia well before they died. Some may think I am wrong for revealing, even challenging, my own heritage tribes about facts they never heard before from "the elders." Some may see and/or call me a bad person, an agitator, a heathen, and/or a heretic. I see myself as a researcher, a scientist seeking truth and facts. I hope to help heal fear, lies, and shame. I seek factual reporting and media transparency. The false label(s) confuses histories of diverse faiths which are not Molokan. The solution is simple — learn your actual histories and correctly use a few new words. Can you say Dukh-i-zhizniki? ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Who are Spiritual Christian Dairy-eaters? Dukhovnye khristiane-molokane (Духовные христиане-молокане : Spiritual Christian Dairy-eaters) is a registered religion with an international organization and headquarters in south Russia, North Caucasus. Members of this organization are officially internationally recognized as "Molokan." Descendants of real Molokane, especially those who have not joined another faith and remain close to practicing relatives, also use the term.
Molokane (named about 1765 in Central Russia) are the oldest, largest and the most documented and organized today of these 3 confused Spiritual Christian groups. Before the term Molokane, many were often called ikonobortsy. The few you immigrated to America were called Russian Quakers. Molokane today have a central hierarchy (a bureaucracy, religious/spiritual and temporal), published contacts and content on the Internet, meetings, conventions, buildings, museums, interfaith representation, and a long a history of publications in Russia. They are Bible-centered folk Protestant Christians in Russia, not Orthodox.(57) A more accurate label from the perspective of the Old Russian Orthodox Church for this faith is Ne-postniki (Non-Fasters), because they are folk-protestants in Russia who do not comply with the approximately 180-200 fasting days required by the Russian Orthodox Church. Their label originated from their heresy of not fasting (ne-postniki, нe-постники) especially during Lent (Great Fast). Instead of fasting they were seen consuming their normal diet which included dairy (molochnye) products, like milk (moloko : молоко), sir (сир : cheese), brynza (брынза : cheese), tvorog (творог : like cottage cheese), kefir (кефир), ryazhenka (ряженка), toplyonoe (топлёное молоко : baked milk), prostokvasha (простокваша : soured milk). A peasant with one cow and a large family will not let food spoil. The only people in the Russian Empire exempt from obeying the Russian Orthodox Church fasting laws were registered Jews, Muslims, Buddhists, indigenous tribes and foreigners. Other citizens by default were required to obey the religious-state laws. By not obeying the fasting laws they became outlaws, criminals, heretics, sectarians (sektanty). Russians were either Orthodox (correct belief) or heathens. Unfortunately most descriptions of folk-protestants stress what they objected to — icons, priests, candles, wine, Saint days, about 200 fasting days, etc.— but not listing what they retained. Spiritual Christian Molokane retained about 10% of the Orthodox rituals (prayers, psalms, holidays, tapestry, rug, etc.). Dukhoborsty in Russia retained more Orthodox holidays (Calendar of Doukhobor Holidays in the Caucasus, by Jonathan Kalmakoff.), most of which were abandoned by the third who moved to Canada, in preference for Peace/Love Day, remembering the burning of arms in 1895. Much misunderstanding results from erroneous newspaper news and publications about migration of Spiritual Christians from Russia to North America around 1900. Too often Molokane are confused with Dukhobortsy and many other sects (or "malakan") that pretended to be Molokane when they fled from Russia, and/or arrived in California. Only about 500 Molokane (100 families) migrated to California in the early 1900s, where most settled in San Francisco and Northern California. After February 1906, there was never an organized Molokan congregation in North America except in San Francisco (meeting hall established in 1928) and later in Sheridan colony (north of Sacramento). Numerous old reports of organized Molokan congregations in North America outside of Northern California are false, though small clusters of Molokan families temporarily lived in Oregon, Northern California, New Mexico, and Baja California. In the 1930s to 1940s, a congregation of diaspora Molokane existed in the Russian section of Harbin, Manchuria. I met one family that moved to San Francisco. In Fresno, I was introduced to a woman who lived in Harbin who told me she had childhood friends there who were Molokane and Dukhobortsy and that many moved to Japan. In the 1980s, when I asked Ethel Dunn, who lived near Berkeley, California, how she learned of Molokane in San Francisco, she said that a friend of hers introduced her to a Molokan man living in nearby Oakland, who then indroduced the Dunns to the congregation in San Francisco. I met this man, named Nozhen, who told me that in the 1950's about 50 Molokan families from Harbin, China migrated to Perth, Australia, where they assimilated.(63) His brother was the presbyter in Australia. I recall that Nozhen told me his brother's last congregation was in Sidney. Coincidentally, also in the 1980s, I learned from American Maksimist William W. Prohoroff that in 1964 when his family flew to Australia to live, they were met at the airport a group Australian Molokane who read in their newspapers about "Molokans" (Dukh-i-zhizniki) moving to Australia from America. The Australian Molokane and Maksimisty from American soon realized they were completely different faiths and never kept contact.(64) Years later, Paulina (Bahgdanov) Slivkoff met an Australian Molokan who came to the University of West Australia to hear her speak about her master's thesis which was mistitled to be about "Molokane". ——————————————————————————— The Russian term molokan(1) unfortunately has too often been confusingly, falsely and vaguely misused when referring to diverse non-homogeneous religious Christian groups or sects, any dissident in Russia, any old faith, or any migrant from Russia to the Caucasus and their descendants —
For clarity and historic accuracy, the umbrella terms for "folk-Protestants in Russia" — dukhovnye khristiane, Spiritual Christians* — or sectarians** in or from Russia should be used when generally referring to an unknown or mixed religious group(s) of non-Orthodox, non-Jewish, non-Muslim and similar folk Protestant faiths and/or groups in, or from, Old Russia, and/ or their descendants. Their ancestry can be a mixture of Caucasian and Asiatic people; including Armenian, Chuvash, Finn, German, Mordvin, Russian, Tatar, Ukrainian, etc.(71) * The term "Spiritual Christianity" (Russian: dukhovnoe khristianstvo : духовное христиаство) specifically refers to "folk protestantism in Russia," referring to 100+ types (many named) of sectarians (Russian: sektanty : сектанты). "Spiritual Christianity" was used by Molokane (молокане) and other Orthodox heretics to describe themselves, and was popularized in scientific literature by Moscow Professor Alexander Ilyich Klibanov (1910-1994), a historian, religious scholar, and pioneering researcher of religious and social movements in Russia. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Who are Dukh-i-zhizniki and Pryguny? By definition all Dukh-i-zhizniki use the religious text: Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn', prayer book of Maksim G. Rudomyotkin, and Sionskiy pesennik (Songbook of Zion). No other faiths in the world used these religious texts. Use of these 3 books is the easiest way to identify Dukh-i-zhizniki. Dukh-i-zhizniki were named in 2007 though formerly founded about 1928 in the U.S. by a variety of zealous Spiritual Christian tribes who immigrated from Russia to Arizona and California, including all Maksimisty, Novo Israili, Sionisty, Klubnikinisty, many Pivovarovsty, many Pryguny, and a few converted former Subbotniki and Molokane. At that time, some could claim affiliation to multiple tribes due to intermarriage and ambiguous knowledge of the origins of their heritage and faiths, which continues today (in the 2000s, 21st Century). Most Dukh-i-zhizniki to not call themselves by that term, but they all know that their congregation, or family's faith, uses the essential book, in short called: Dukhi i zhizn' (Spirit and Life). I have witnessed differences and clashes between Dukh-i-zhizniki and Pryguny my entire life. I grew up attending the Dukh-i-zhiznik congregation in Arizona, among zealous jumping Maksimisty, and among their congregations in Southern California. Though my parents could not explain why we were treated as 2nd class members, my relatives in Russia explained that my Conovaloff family were Pryguny in Saratov Oblast, Central Russia, before resettling in Selim village, Kars Oblast (now in Turkiye). My Prygun heritage did not originate in Novorossiya. My grandfather's New Salem colony in Arizona was Prygun, and was continuously criticized by some of the Maksimist congregates as being an inferior separate faith for not embracing their prophet M. G. Rudomyotkin. When he visited Los Angeles, my grandfather Jake D. (Yakov Danilich) Conovaloff attended the Aktinsky sobranie (Samarin's, Percy Street) with about 5 Prygun skazatel'i (talkers, speakers) who ignored the text of M. G. Rudomyotkin and did not jump. In Arizona the separation between Dukh-i-zhizniki and Pryguny continued after the 2 congregations merged about 1947.(83) Discrimination became acute in the 1960s after a Maksimist prophet, Fred "Stretch" Slivkoff, anointed my father to be the next presbyter, a position which the son (David William Tolmachoff) of the standing elder presbyter believed he should inherit. Due to the volatility of these Maksimisty, my dad waited, serving as assistant presviter* for more than a decade before the position was opened by the death of D.W. Tolmachoff and no one else wanted to "inherit" it. The real reason was lack of education, and willingness to attend every meeting because he rarely traveled, and no one else could recite most of the prayers.och * In America, Dukh-i-zhizniki used the Russian word pomoshnik (помошник), "helper", for the English word "assistant", but in Russia Dukh-i-zhizniki use the Russian word zamestitel' (заместитель), replacement, deputy.For several years prior to 2007, I variously called the faiths that used the book, called in short, "Spirit and Life" as: "Spirit and Life users", "S&L-users" and "Spirit and Lifers." I knew from my many meetings with Molokane and Pryguny around the world that they did not use the Kniga sontse, dukh i -zhizn'. Most had never heard of it. The very few Molokane who ever examined the book said it has nothing to do with Molokane, nor was it of interest to Pryguny who remained steadfast (postoyannie) to their faiths. About 2005, I realized a Russian word for "Spirit and Lifers" was needed and asked several Russian immigrants in Arizona for a translation, or a word that describes these faiths. After years of discussion, my wife Tatiana Nikolaeyevna one day said дух и жизники — the perfect word for "people who use the Dukh i zhizn'." Of course! Russians make chai in a chainik. The companion that orbits earth's path (put') is a sputnik. And the Saturday people are Subbotniki. This new word must be transcribed with hyphens — as dukh-i-zhiznziki — for clarity in Russian. Without the hyphens, it could be misunderstood as 2 words, representing 2 things, rather than one thing and the name of one book. Discussions with several colleagues who are still in the habit of using the wrong word, finalized this new term. The term is not capitalized in Russian, but capitalized in English as a proper label. Since about 1915, the new ritual sacred texts of future Dukh-i-zhiznziki, which, with the aid of Dr. P. V. Young, transformed through as many as 7 draft versions (106) and was finalized in 1928 as a Russian language religious text : Книга солнце, дух и жизнь (Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' : Book of the Sun Spirit and Life). The short form — Dukh i zhizn' — is a draft title from an early print version with a leather cover, which resembled a leather covered Bible. This book never satisfied all the various tribes, and was intensely contested by Mike P. Pivovaroff for omitting his writings.(65) This book defined the beginnings of new religious movements because the Los Angeles prophet Afonasay T. Bezayeff, while filled with the Holy Spirit declared that it must be placed on their altar tables next to the Russian Bible, as a third testament in addition to the Bible, not to replace the Bible. He thus canonized the new text. When each congregation placed the book on their table was not recorded. It was never uniformly accepted by all members as canon law. Some believed it replaced the Bible, some rejected it, while most accepted it somewhere in between those extremes while not being literate enough in Russian to understand it. In the 1960s and 1970s, when I or my peers questioned various elders about the role, meaning or content of the Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn', I recall that those who tried to answer typically replied something like: one "must be "in the Spirit" to understand it. No interpretation was given. Among Dukh-i-zhiznziki, a fourth testament for a congregation, or for at least the most zealous believers, consists of their collection and recollection of prophesies, include today's prophecy. In this way, the word of God was written and revealed many times in the past, and is being revealed today for those chosen to listen and obey. The Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' was slightly modified about 1934 by the zealous Molodoe sobranie (young people's gathering) and exported to Spiritual Christians remaining in Kars province, Eastern Türkiye, and Soviet Armenia. The new book converted most all the Maksimisty in those areas and the most zealous Pryguny and a few similar faiths to form their own Dukh-i-zhiznik tribes. Though these various zealot faiths adopted the new 1928 ritual book sent from Los Angeles (customized for them in 1934), they mostly remained separate tribal faiths, and sub-faiths, to this day because each congregation has its own historic geographic territory, oral history, lead elders, prophets, singers, band societies and clans. Similarly the Dukh-i-zhinzik tribes in the United States, Australia, and Uruguay have maintained cordial separation. Dukh-i-zhizniki were officially founded about 1928 in the U.S.A. (Arizona and California, not in Russia), as new religious movements which use the Russian language religious text in addition to the Old Russian Bible with Apocrypha. The Dukh i zhizn' (short title) defines and separates Dukh-i-zhizniki from all other faiths in the world, which many believers demonize as the "666 false faiths." Congregations that use the Dukh i zhizn' are mostly loosely networked and transformed Spiritual Christian faiths not in koinonia (unity, fellowship, brotherhood, partnership, full communion : единство, братство, товарищество, полное общение) with any other faiths, nor Molokane nor Pryguny, and many not with each other. They have no uniform liturgy, no central office, no hierarchy, no public phone number, no annual meetings nor general meetings, no meeting minutes or records (births, marriages, deaths), no official representatives or central organization,(7) no official website or centralized world-wide network, no holy objects or artifacts or relics, no logo or flag, and no representative journal or newsletter.(40) They have no missions or missionaries, do not recruit non-heritage members, and forbid interfaith contact. There are no paid religious positions, nor pastor's allowance. There is no water baptism, only dry baptism by the Holy Spirit. They serve kosher-like killed meat during feasts, and a few are lacto-ovo vegetarian. Many tribes are closed secretive societies. Though each Dukh-i-zhiznik congregation has one or more prophets, only the writings of 4 prophets (+1 added in an optional supplement) born in Russia are published in their religious text: Kniga solnste, dukh i zhin' (Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life, 1928). Oral and written notebook prophecies of perhaps 100 other prophets exist, and about 200 prophets have been active since 1900 around the world. Since no inter-congregational congresses are held, leadership is often entrenched and authoritarian by geographic location and congregation. Separate congregations often have autonomous meeting halls near each other, even across the street from each other. Intermarriage, if allowed, among Dukh-i-zhizniki is scrutinized; and brides typically must join the groom's congregation. To contact them, one must approach each congregation, organization and group separately and preferably verbally in person, because they typically will not respond in writing, even if they they personally know you. Few have easy-to-find agents or addresses. About the best contact an outsider can get is with one, or a few individuals, who may only speak unofficially and/or in secret. Outsiders, even members of other Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations and organizations, may be immediately turned away, treated like an intruder at a private or secret meeting for members only. Dukh-i-zhizniki in the U.S.A. and Australia formally prohibit (scorn) inter-faith and public exchanges by members, while those in the Northern Caucasus typically welcome a guest and participate in events organized by regional government.(8) Some of the most zealous practicing Dukh-i-zhizniki today have preserved their oral history of oppression since the 1600s by the Russian Orthodox Church, and hatred of it. Many express group behavior similar to a selfish herd and an "introversionist sect."(9) to maintain a spiritual presence "in the world, but not of the world," somewhat like "old order" Anabaptist faiths. What became the Prygun (jumping) movement heresy is rooted in in Central Russia. Some influencers may have been called Skakuny in North Russia, perhaps due to contact with visiting enthusiastic Protestants from Europe and/or from indigenous shamanism. In the late 1700s in Russia, Ivan Vladimirovich Lopukhin a printer, statesman and Martinist, was appointed to xxxxxx In the early 1800s, many non-Orthodox Russian heretics were exiled, and/or voluntary migrated, to the Molochnaya River area, Taurida Governorate (south Ukraine), with other mixed tribes of indigenous Spiritual Christians from Russia and Protestants from Germany. By 1833, during a drought and unrest, some zealous people from different tribal faiths (German and Russian) cross-fertilized (shared) spiritual enthusiasm and some aggregated into new faiths during and after "an outpouring of the Holy Spirit" reported in oral histories. By 1840 many were offered land in the newly acquired Transcaucasia, where the term Pryguny (jumpers) was first used in print about 1856.(84) Pryguny are historically a somewhat intermediary weak evolutionary link between many sectarian groups and Dukh-i-zhizniki who reformed in America 100 years later. The Prygun faiths were further influenced by preceptors of millennialism and pietism from a variety of foreign (mostly German) faiths in south Russia. The complex origins of these multi-hybrid tribal faiths are much less documented than other Spiritual Christians because tribes, groups and adherents were were isolated, migratory, fragmented, illegal and hid. Russian reports variously described heretics as beguny, pryguny, shalaputy, sionisty, skakuny, stranniki, stundisty, vedentsy, among other terms; and in English as jumpers, holy jumpers, leapers, noisy-nose-breathers, knowers, hoppers, bouncers and dancers. These terms attempt to describe their fluid ecstatic religious enthusiasm. Many voluntarily migrated to the Southern Caucasus after 1840 with other Spiritual Christian faiths as colonizers, and/or to live near Mt. Ararat, and/or to get to Mt. Zion, Palestine (Israel). In the Caucasus they got a warmer climate, more land, religious freedom, and about a decade of exemptions from military duty and taxes. Those in the Caucasus grew in numbers and continued to unite and divide into various tribes while incorporating new beliefs, songs and rituals from other faiths, mostly from neighboring Anabaptists and descendants of Pietists who migrated from Europe to South Ukraine and the Caucasus, and from local Protestants, and perhaps Jewish-like Krymchaks and Crimean Karaites. From Liudi Bozhe (God's people), and German heupferde (hoppers) and tanzende brüder (brother dancers), some probably retained, or learned, variations of heavy rapid breathing while jumping and jerking in the spirit, and roaring and ranting, sometimes "half-naked" (without shirts?). Each congregation typically has one (leader) or more prophets. From German Protestants (Duchy of Württemburg) and missionaries, and Novo Israili (New Israelites), they apparently adapted and borrowed songs and millennialism, which continues today in year 2022. From Subbotniki (Saturday people) and Readers (Karaites) they added holidays and Old Testament customs. Some appear to have adapted song melodies from neighboring Muslims. In the late 1800s, the Maksimist tribes discarded nearly all of the holidays retained from Orthodoxy (Christ's holidays), maintained today by Molokane and Pryguny and transformed to new faiths. In general today, Pryguny are somewhat similar to Pentecostals, but not evangelical — no missionaries. Those who migrated to North America after 1900 were converted to Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths after 1928, or forced to abandoned their heritage faiths. ^ Contents ^
Today, Prygun congregations only exist in the Northern Caucasus of the Russian Federation. Diaspora congregations persisted in the U.S.A. in Arizona and San Francisco, California, up to 1950; among immigrants from Iran (Persia) in Los Angeles up to 1958; and in Mexico up to the early 1960s. The last active congregation in Los Angeles migrated to Adelaide, South Australia, in the 1960s, where it persists today with no contact with any congregation currently in the Russian Federation. In the 1970-1980s in Woodburn, Oregon, a congregation of 5 Dukh-i-zhiznik families "reformed" to a Prygun faith and published a newsletter (Besednyik, discontinued); and stopped meeting about 2013 after their presbyter Kapsof had a stroke. Congregations in the Republics of Georgia and Azerbaijan resettled to the Russian Federation due to the the Nagorno-Karabakh War (1988-1994) and ethnic cleansing. I have personally visited most of the active Pryguny in the world, and my Prygun and Molokan relatives from Pyatigorsk, Stavropol province, conducted my wedding in Yessentuki, at my Molokan wife's family apartment. Using the 1997 Johnstone definitions for sect and cult, Molokane and Pryguny are sects, and Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations are many cults. All 3 groups are heterodox, not-orthodox, and many Dukh-i-zhizniki venerate and/ or revere select prophets and historic relics. Analysis with other classifications systems of religious movements is in-progress. Common to all 3 groups All 3 groups have retained about 10% of their heritage from old Russian Orthodox rituals and folklore (select beliefs, prayers, prayer rug, hymns, melodies, food, dress) and discarded 90% of which the most emphasized are: icons, candles, priests, saints, most holidays and nearly all fasting holidays. Less noted is how much non-Christian (pagan) folklore was retained by Spiritual Christians from their old Russian heritage.( XXX ) To an outsider or a non-Russian speaking heritage member, the differences between these 3 religious groups may seem minor, if at all detected, which is why so many have been fooled into thinking they are all "essentially the same".(Dunn 1972 xxx) I have attended and participated in services with many congregations of these 3 faith groups in the United States and Former Soviet Union. All were similar enough for me to easily know what to do, how to act, where to stand or sit, to sing along, and speak as a guest. I recognized similar prayers, songs and melodies, dress and rituals in all 3 types of faiths. I am sure any of the congregants I met could do the same if they visit other tribes, but they rarely do because they know the differences. All 3 groups use a Russian Synodal Bible during meetings (sobranie) from which they read aloud and sing Psalms and verses (hymns). The lead elder men sit on 1 to 3 sides of an altar table either in the corner or center mid-wall of the meeting room (depending on room size and congregation custom), with the religious texts on the table, laid open in a row before the presbyter (presviter) and other elders at the table (prestol). The arrangement of books and ritual format is most specific among Dukh-i-zhizniki. Women and men sit separate on back-less benches (which are easy to move and stack), either face-to-face or at right angles if the meeting room size permits and that is their custom. Meetings can be in private homes, communal halls, or outdoors. Women wear a head covering, with long sleeved full length dress, some with aprons. All services around the world begin with The Lord's Prayer in Russian, singing Bible Psalms and verses in Russian, and speaking in the language of the majority of the elders of the congregation. When members approach a meeting hall entrance, they wait for a group to accumulate where they may greet each other, then elder men proceed first, followed by younger men, then the women, all in age and gender order. Typically deference is given to the oldest or dominant male in each entering group, as they arrive. They may greet outside, or in a coat hanging hall entry corridor, a vestigial narthex, vestibule. Upon entering the main meeting hall, the lead elder recites a short prayer and all proceed to sit on benches in their position, men around the table (choir, speakers, readers, presbyters, prophets), and women in their position or section. Later, as more members enter, depending on the congregation and what they are doing, all seated may stand in common prayer with the entering people, or pause until the newly arrive are seated. None of these 3 religious groups have missionaries, or paid religious positions or staff, probably because they did not have these illegal positions in Old Russia and continued the behavior as traditions. All religious work is voluntarily and self-learned, by laypeople. In the Former Soviet Union, congregations with a separate prayer house often have a resident security/property guard, often a pensioner who gets rent in exchange for guarding the prayer hall. In the U.S.A., coreligionists are hired for meeting hall janitorial services. In the U.S.A., only the Dukh-i-zhiznik elementary school, Hacienda Heights CA, has paid staff; and their cemeteries mostly hire non-white laborers because many believers obey a commandment in their Dukh i zhizn' to hire "Arabs" (people of color) to become wealthy, and to touch a dead body is considered "unclean." Therefore, zealous adherents refuse to volunteer to perform community service manual labor. Zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki forbid their members from aiding members of other faiths whom they believe to be "non-believers" or heretics of their particular Dukh-i-zhiznik faith. By 1960, all Prygun congregations in the U.S., except one in San Francisco which merged with local Molokane, were extinguished or converted to a Dukh-i-zhiznik faith, while the majority who did not conform to their rules and rituals were rejected, and/or harassed to extinction. Though a congregation may be coerced into placing these sacred texts on their alter table, not all congregants personally accepted the books as divine, yet many maintained paid Dukh-i-zhiznik membership for family tradition, cultural and social reasons. In the 1970s, 5 heritage Dukh-i-zhiznik families in Oregon, who had no personal knowledge of Pryguny in the Soviet Union, and 2 were Pryguny from Iran, united to "re-form" their own version of a Prygun faith by (1) rejecting the divinity of the book Kniga solnste dukh i zhizn'; (2) performing their service in English (Russian optional), using selected translated songs and prayers formerly learned while Dukh-i-zhizniki; and (3) somewhat recognizing the former abandoned Americanized Christ's holidays. After meeting house-to-house for about a decade, they bought a meeting house at 995 Belle Passi Road NE, in Woodburn, Oregon. Their self-reversion to Pryguny was severely scorned by zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki as heresy and apostasy which was inflamed when they mailed a free newsletter, Besednyik (sic: Besednik), for more than a decade (1980-1990s) to over 4,500 households listed in the mislabeled 1980 Молокан Directory (better title: 1980 Directory of the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians from Russia: Comprising many faiths), of mostly American Dukh-i-zhizniki. Intense verbal attacks and lack of leadership talent deterred much wanted similar English Prygun or English Molokan congregations from forming in Southern California. In the early 2000s they started a website, which was online for a few years. The Pryguny of Woodburn discontinued meetings about 2013 after their presbyter Kapsof had a stroke. I also visited congregations of Spiritual Christians from Russia not in this taxonomy — Dukhobory in Canada and Republic of Georgia, Subbotniki in Oregon and Washington, and Baptisti in Arizona and Russia — and found many of the similarities among these very different faiths common with the 3 groups of this taxonomy. Are they all "essentially the same." A simple analogy about how Spiritual Christians are similar and different is driving a car. Most readers have driven many different cars in their lives. After you first learned to drive one car, how much trouble was it to learn to drive a different make and model car? Most people would say that all cars are pretty much the same, yet they are distinctly different, and given different names, and numbers to identify them, especially when you need to buy a replacement part. Most cars have 4 wheels, an engine in the front, storage in the back, seats, windows, steering wheel, lights, etc. Remember cars first started with a crank, then a floor button, then keys, and now dashboard buttons. Are they the same, or different? ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Who/what are malakan? This phonetically transliterated term was used in English as early as 1819 by William Allen, who visited sectarians in Saratov, Central Russia. In September 1821 Ebenezer Henderson met 3 "Malakans" in Mozdok, South Russia. In Old Russia, and continuing in the Former Soviet Union and now the Russian Federation, the term malakan has 2 general meanings, depending on context.
Characters in several Russian novels and short stories were labeled "molokan" or "malakan" to infer pacifism, morals, cowardliness, dissidence, etc. Other meanings for the spelling of malakan occur in the Middle East and Asia, and it is a surname in several nationalities. Research in-progress. malakan places, animals and foods Many places and things in the Caucasus are named "malakan" (molokan, malokan, ...) for the malakan people who created them.
The general use of malakan is as broad and non-specific as the general use of jew, asian, indian, or colored people — each term attempts to cluster huge populations to separate them from other populations, while a multitude of divisions exist and evolve over place and time within the populations.
Due to globilization of the Internet on personal
computers and mobile phones siince 2000, the words malakan
and molokan appear to be more often
alternately spelled and colloquilly used as equivalent,
when they are not equal. Journalists, academics and
governemt workers should be diligent in their use of
these deceptionally similar terms with different
meanings. In the southern Caucasus one can say my
ancestors were "Molokan", but not know specifically if
they were dukhobortsy, Estontsy,
khlysty, Klubnikinisty, pryguny, Maksimisty,
Mordovski, Mennonity, molokane, noviye
israili, pravaslavnie (Orthodox), Popovtsy,
stundisty, subbotniki, etc. Most of these
sectarian groups were illegal heritics and could not
document their fiaths, rituals, canon, litergy, etc,
until after 1905 . Malakan markets (рынки : rynki ; базары : bazary) existed north of the Caucasus mountains in the Russian Empire, later called the Former Soviet Union (Post Soviet States); and now Vladikavkaz, North Ossetia-Alania, and south of the mountains in what is now Tbilisi, Georgia; and Baku, Azerbaijan. Now there's a market and soccer team in Vladikavkaz, and in Baku 2 restaurants and a hotel with the label.  Click on image to ENLARGE. "Malakanksiy" Market, 9 Gertsena street, Vladikavkaz, Russia. The photo-enhanced sign says: "Products, Ready Kitchen, Household Chemicals (cleaners); and telephone number". See the store on Google Street View 2021.
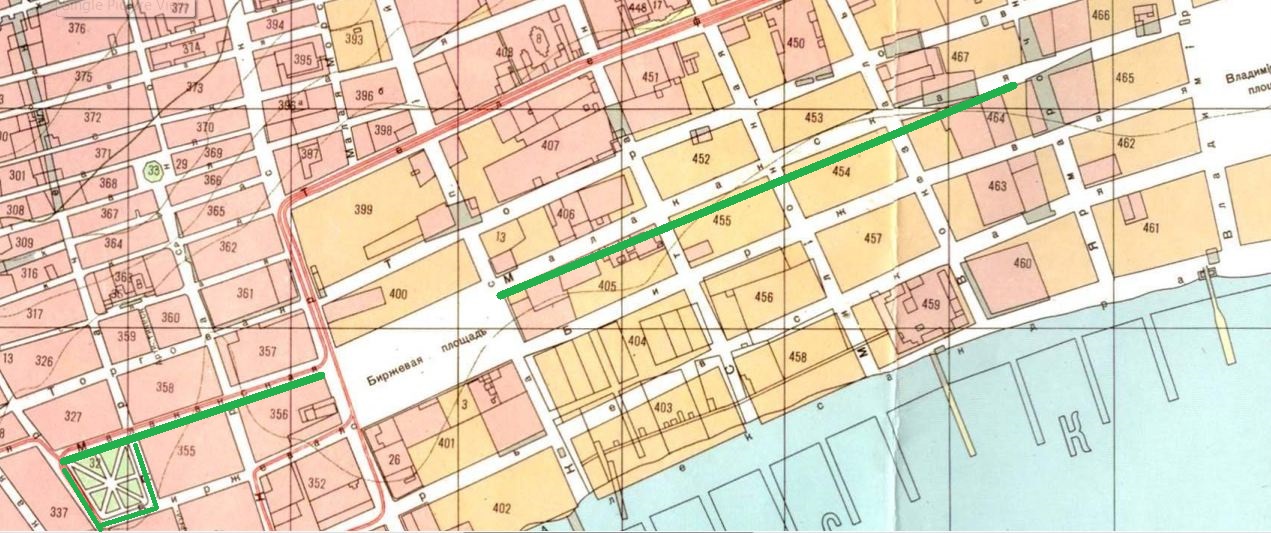 Click on map to ENLARGE. In Baku, Azerbaijan, Malakanskaya street (green line) ran east from the north side of the Molokan/ Malakan Garden. The name was changed by the Soviets in 1923 to "January 9" street in memory of the 1905 "Bloody Sunday" protests in Moscow, and in 1946 to the current name of Khagani Alley/Street.(104)
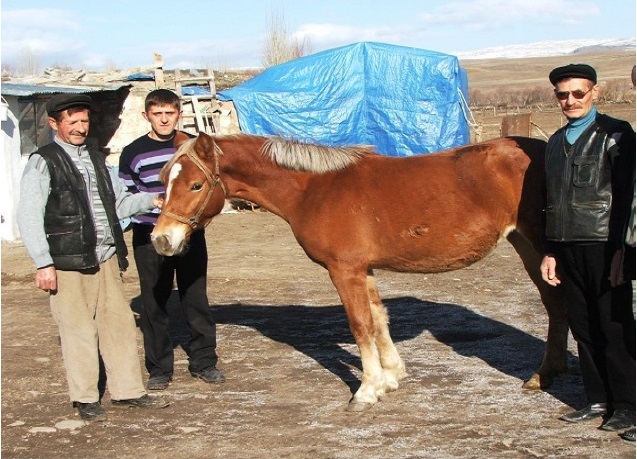
Beginning in 1926, after the 1921 Treaty of Kars, the Soviet Union (Russia) voluntarily repatriated thousands from abroad, including most Molokane, Dukhobortsy and Novyy israili and some Pryguny from Türkiye, leaving all the Staroobryadtsy and more than a thousand of the most zealous Spiritual Christians from Russia in Türkiye, many of whom were converted to Dukh-i-zhizniki after 1930. Most of the repatriated Molokane, Pryguny and Dukhobortsy were given adjacent tracts of barren land in east Rostov oblast, Russia, where they established communal farms and produced dairy products before being stopped by Soviet collectivization in the early 1930s for being too successful. I visited this area in 1992 and found one Prygun congregation, the rest were Molokane, no Dukh-i-zhizniki. — malakan Animals — The Spiritual Christian tribes who remained in Turkey (properly spelled Türkiye after May 2022) were offered land to continue breeding their outstanding horses and cows, and to manage the state agricultural experimental farm just outside the capital of Ankara.(82) That farmland is now the Atatürk Forest Farm and Zoo. Had these tribes taken the Ankara offer, they could have remained in Türkiye near the capital, some as respected agriculturalists and most in their urban enclaves. They may have refused for any or all of these reasons:
The migrations of segments of several different Spiritual Christian tribes from Kars to North America (1889-1930) and to the Soviet Union in the 1920s, left most all Spiritual Christian villages around Kars partially vacant. Young Spiritual Christian couples (non-Dukhobors) could have their own used house, and some homeless Kurds moved in. When Dukhobortsy abandoned their houses they typically left khleb-sol for the next occupant — a loaf of bread, small dish of salt and a container of water — as an offering (zhertva) of hospitality. Starting in 1923, Atatürk's reforms to modernize and unify the country, continued into the 1950s. The next generation of descendants of Spiritual Christians from Russsia had to adapt to their Turkish culture outside their villages and attend Turkish schools. The government changed many Russian surnames to Turkish. Many men served in the military. Some intermarried. The government offered the most talented animal breeders jobs managing the government livestock grounds in Ankara and others city jobs. The majority of Spiritual Christians refused to move, preferring to stay in Kars province in their heritage rural villages, so the government concentrated them into 3 clusters in and near the 3 villages of:
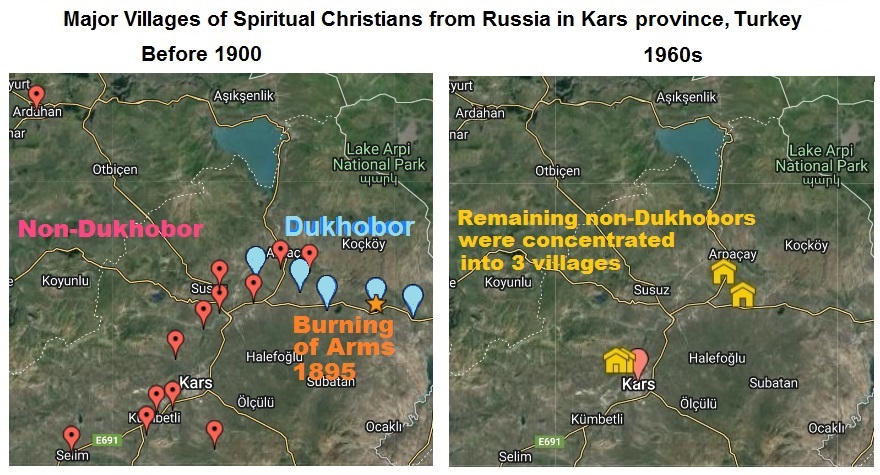 The majority of non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians — Molokane, Pryguny, and Dukh-i-zhizniki, etc. — in Kars province, Türkiye, in the 1960s who chose to repatriate to the Soviet Union, were already resettled in 3 villages (above right) with which their descendant Dukh-i-zhziniki mostly identified upon arrival in Russia, and continuing into the 2000s. For example, if your family was raised in Atchilar, you most likely will associate with congregations of people from Atchilar in Stavropol province, Russia, and less with others who did not come from Atchilar. This immigration group behavior is similar to how the Spiritual Christians from Iran (Persia) in the 1950s behaved when about 200 were sponsored to Los Angeles. For more than 50 years many of these "Persians" were socially tolerated as sub-group because they did not immediately convert to the Maksimist faiths and embrace the Kniga sontsa dukh i zhizn'. Knowing these 3 villages is essential to understanding the social structure of Dukh-i-zhizniki in Stavropol'skiy krai because descendants from any one of the 3 villages typically will not formally mix with descendants of the other 2 villages. They will not tell you which of the 3 Kars villages they came from unless you ask. This 3-way division is hidden from outsiders, like tourist Dukh-i-zhizniki from America and Australia. To understand their divisions you must consistently ask: Are you Atchilar, Chalkavur, or Yalinchayir? Only then you can see that most of their relatives, friends and associates are also from the same village. This 3-village division greatly hampered how American Dukh-i-zhizniki distributed charity to whom they believed were their co-religounists in the Former Soviet Union in the lat 1980s. Example: In the 1980s, presviter John Kochergen, Kerman CA, was saddened during a trip to Russia when he saw that all congregations he visited were using worn 100+-year-old Bibles. The Psalms pages were brown from finger priints, and torn from more than a century of use. He wanted to give his Russian brethren new Bibles but their vintage Synodal Bibles used the pre-revolution Russian alphabet, and was out of print. He found a publisher in Moscow who would reprint the books for $5 each. To raise money from the stingy Dukh-i-zhizniki in America, he offered a copy for $15 (cheap in America) with the bonus that 2 Bibles will be go congregations and people in Russia. With several thousand printed he went back to Russia to deliver the Bible to "all Molokans in Russia." But how? He was introduced to a presbyter Shitinin in the village of Novomar'evskaya, 10 miles north west of Stavropol city. went to Stavropol'skii krai in the 1990s to distribute new Russian Bibles he raised money for. If you are a member of "Big Church" in Los Angeles County, California, your ancestors may be from Ol'shanka (#1 above, as is my wife's family). The most zealous tribes will not attend another tribes events, nor permit outsiders in, and avoid other tribes while walking on the street. I've seen this behavior in Stavropol'skiy krai. Many do not know the location of the meeting places of the other branches, and they not be familiar with those people, therefore avoid them. Similar behavior exists among Dukh-i-zhiznik tribes in America and Australia. When American Dukh-i-zhizniki visited their coreligionists (our people) in Russia, and they are hosted by a member of one of the 3 branches, they will only be taken to congregations of their hosts branch,ignoring all Molokane, Pryguny and about two-thirds of the Dukh-i-zhizniki. This happened with John Alex Kochergin, from Kerman CA, in the 1980s when he raised money in the USA to donate Bibles to all Malakan congregations in Russia. His escort was an Atchilar presbyter who claimed to know everybody, all Malakane in Russia, but drove Kochergen past most of the congregations. (Told by my relatives in 1992.) In 2007, I was in Levokumko, Stavropolskiy krai, for a week and was hosted by Olga Samarin, director of the museum in the next town with a large Malakan display. Her family was Yalinchayir, and her husband Molokan, and the town attorney. They were the most educated couple in town. As her husband was driving me around town, he heard that someone from America was visiting. Within a few minutes he learned that Morrie Pivovaroff, from Kerman CA, and and Peter Partnoff, from Fresno CA, spent the night, visited many people, and already left, being driven by the same Atchilar guy who drove Kochergen 20 years earlier. Some time later I visited Morrie an told him what he missed and why. Most of the Molokane, Pryguny, and Yalinchayir-Dukh-i-zhizniki knew I was in town, but not the Atchilar-Dukh-i-zhizniki. These branches and denominations have different channels of communication as those in America and Australia. In Türkiye a huge population of Old Orthodox (Old Ritualist) Staroobryadtsy remained at Lake Manyas in western Türkiye who did not repatriate to Russia in the 1920s. In the 1960s most were lured to the Soviet Union to some of the same rural districts in northeastern Stavropol krai as the Spiritual Christians from Russia in Kars Province. Because they formed costumed choirs and folk dance clubs willing to perform in public, they have become more well known in Russia and abroad under different names, sometimes confused with Malakan — Nekrasov Cossacks, Cossacks, staroobryadtsy, Old Ritualists, Old Believers, Staro very, etc. After 1930, most of the Spiritual Christians from Russia who remained around Kars were Pryguny and Maksimisty, the minority were Molokane and other faiths. Most all of the most zealous tribes of Spiritual Christians from Russia transformed into separate tribes of Dukh-i-zhizniki in the mid-1930s after shipments of a revised Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' arrived from Los Angeles, California, sent by the "Molodoi sobranie" (young people's congregation) in the Flats area. Many Pryguny and all Molokane who remained in Türkiye rejected the new book as a religious text; and, after moving to the Soviet Union in the 1960s, they were continually insulted by the most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki for not converting. The most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki in Russia also condemn those who moved to North America for abandoning their spiritual homeland.(82) Spiritual Christians from Russia, particularly the most zealous tribes are very divided around the world, but the term malakan is attached to legacy products and places, as if produced by one unified population and faith. The names of those individuals who did the first animal breeding and first cheese making was never recorded for history, as far as I know. Malakan horses are descended from draft (work) horses, some brought from Ukraine, and local draft horses in the Caucasus. They are one of the 14 major horse breeds indigenous to Türkiye and now protected by law. — malakan Food — Cheese and honey Spiritual Christians from Russia are credited with popularizing cheese and beekeeping in the Kars area, north eastern Anatolia. In the 1960s, before the last (2nd) repatriation of Spiritual Christians back to Russia, they were known for their malakan cheese, described as similar to Gruyère cheese. Malakan cheese is now labeled "Kars peynir" (Kars cheese) to promote the local cheese industry. In July 2015, I walked into one of more than 60 cheese and honey specialty shops in Kars — some across the street from each other — and asked for malakan peynir (malakan cheese). The Turkish clerk immediately pointed to the refrigerated dairy case. There it was — a large round flat roll, about 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds). The taste is mild, and texture firm when cold, soft at room temperature, somewhat similar to low-moisture, whole-milk, mozzarella cheese. Some batches of malakan cheese have holes (photo above) due to dust contamination which does not occur with cheese made from pasteurized milk. [Insert Photo] The clerk then showed me a large Turkish book about malakane in Kars. I was surprised to see this book on display and pointed to my name and photo in the credits.(49) The clerk made a phone call, and the co-author soon walked in, introduced himself. We took a photo together, and walked about 2 blocks to meet the author Vedat Akçayöz. See more about these men and book in Spiritual Christians from Russia in Türkiye. The original Kars dairy and cheese factory was established next to what became the village of Novo-Vorontsovka (now Boğatepe), Kars Oblast. The village was founded by Spiritual Christians resettled from Voronstovka, Tiflis guberniya (now Tashir, Armenia). Their large village in Armenia was known for its voronstovka potatoes. In 1905 Voronstovka (Tiflis) hosted the the All-Russian Congress of Spiritual Christian Molokans,(110) celebrating 100 years of religious freedom since 1805, which thousands attended and a group photo was made.(48) At least one former Spiritual Christian house remains inhabited in Boğatepe, Türkiye, and is a monument to the builder. In the late 1880s-1890s the Kars cheese factory, established by Swedish investors, was conscripted to teach cheese making to locals, including resettled Spiritual Chrstians. Those selected to be trained at the factory were to return to their respective villages and teach the skill to others. Probably because the communal immigrants from Russia, the malakane, could work communally as a village, they were the most successful at producing the most cheese. Hence, the legacy of malakan peynir. ^ Contents ^
In the 2010s, the cheese factory was conserved and converted to the Cheese Eco-Museum Factory for tourists and students, with a working dairy and cheese factory to train industry workers. 50 miles northeast of the Factory, across the border in Georgia, Spiritual Christian Dukhoborsty are still milking their own cows for 2 cheese factories (42) they have operated since Soviet times, a skill they also acquired 200+ years ago. During Soviet times, after Kars was returned to Türkiye, Dukhobor-made cheese was shipped to Moscow.(35) It is my observation that among Spiritual Christians in North America today, more Dukhobortsy eat their own home-made cheese than Dukh-i-zhizniki and Molokane combined. Only a few rural Spiritual Christian families who migrated from Russia to the USA established dairy and cheese operations using skills that may have been learned in Kars. The largest was the Shakarians Dairy, Downey CA, (3,000 cows in 1943) then the Ivan Treguboff dairy west of Glendale AZ (on 75th Ave, between Camelback Road and Bethany Home Road). In the 1920s a commercial cheese factory was established by Ivan Alek. Tolmachoff, west of Glendale AZ, who supplied Safeway markets; and his family and kids were nick-named "cheese" — "John cheese", "Bill cheese", etc. There were at least 3 smaller family dairies. Chernabaeffs near Shafter-Wasco CA also made cheese, mainly for family and relatives, not sold commercially. In Arizona, my grandfather Jake (Yabov) Dan Conovaloff had a small heard up to about 1950 and a dairy barn; and our neighbor Pete Ivan Treguboff had more than 100 cows which he milked most of his life near near Tolleson AZ (Thomas Road, west of 91st Ave). After the 1960s there was a large dairy in Tulare County California owned by John Fred Valov (1926-2013); two dairies were started and failed, by the sons of Jack and Doris Tolmachoff, the first with stolen goods animals, feed and medicine, and the other rented.(52) Potatoes In the Republic of Georgia, a variety, or varieties, of potato grown and sold by Spiritual Christians was/were called malakanskaya (малаканская) and vorontsovka (воронцовка), from the name of their village. These potatoes from Russia were also called, and still called, ruskartoe (a contraction of the Russian words for "Russian potato" — russkaya kartorshka) and “kartoli” (slang). The village of Voronstovka (now Tashir, north Armenia) was founded in 1844 by settlers from the Molochna River district of Novorossiya who were given about 35 square miles (22,400 acres) by a Georgian prince. It may have been the largest Spiritual Christian village in the Caucasus and was located between the cities of Erevan and Tiflis, now on the south side of the Georgia-Armenia border. The 100-year anniversary celebration of religious freedom for Molokane was held here in 1905. Some Spiritual Christians moved from Voronstovka to Novo-Voronstovka, which became the cheese center for Kars Oblast (described above). Turkish historians document that their potatoes most likely were introduced from Russia, probably by Spiritual Christians from Russia (malakan — Dukhobory, Molokane, Subbotniki, Pryguny), because both (immigrants and potatoes) arrived about 1878 across the eastern border in Kars Oblast, and one variety was called by the Russian term: kartoli. The Russian word for potato is kartofil. Close enough. Though potatoes were promoted across Asia Minor (Anatolia) in the 1880s as a "bread substitute and as animal feed" they did not arrive in Istanbul until about 1900 after a 5-year drought and famine.(79) Pickled cabbage Malakan pickled/ salted cabbage (solyonaya kapusta : солëная капуста) is the specialty product of Fioletovo village, Armenia, collective farm (kolkhoz), hometown of the Dukh-i-zhiznik saint-prophet-presviter M. G. Rudomyotkin (1818~1877). During Soviet times, the village (named Nikitino before 1936) branded their pickled cabbage in large (~500 liter) wood barrels painted burnt-orange. Vendors sold salted-cabbage fresh scooped from their painted barrels in many bazaars (markets). Barrels were painted burnt-orange to deter barrel theft and it became a brand identity, a logo, one could easily see from a distance. Truck caravans with barrels stacked 2-high formed a convoy that drove from Armenia, north through Georgia, into Stavropol territory and the Northern Caucasus, where the orange barrels were widely distributed to bazaar vendors, and empties brought back. The orange barrel brand of Malakan solonye kapusta is still widely known in South Russia. An Armenian diplomat working in the U.S. and visiting Arizona, told me that he savors for Malakan solonye kapusta every time he visits Armenia. He said: "It's so delicious. At the rinok (market), when you go down the line of babushki selling pickled cabbage and sample taste each one, then you get to the Malakan — ahh-hh — nothing compares" he exclaimed. For younger readers: He was like, "Ahh-hh — nothing compares." After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Georgia restricted commercial trade from Armenia to Russia, which devastated the cabbage business in Fioletovo. In 2007 I witnessed 2 Dukh-i-zhiznik families, who resettled in Stavropol, Russia, from Armenia, complete within 50 feet of each other in the huge "Ludmilla" bazaar complex in Pyatigorsk, Stavropol territory, each with an orange barrel; while other families from Fioletovo sell in Stavropol and Kislovodsk cities. The largest operation outside of Armenia is by a family from Fioletovo, resettled in Stavropol city, who told me the crispy type of cabbage grown in Armenia cannot be grown north of the mountains. Because local pickled cabbage is tougher and not sweet, they had to diversify to appeal to more customers. So they grow and sell mushrooms, cucumber pickles, carrots, and other vegetables which they ferment and store in a refrigerated building. Farmers in Fioletovo will appreciate the economic and brotherhood support if Dukh-i-zhizniki in the USA and Australia would import pickled cabbage (no export duty) to be served as a stable during communal meals and at home. But, Dukh-i-zhizniki outside of the Former Soviet Union believe only they are saved, and their congregations will probably attack or insult any congregation to tries to do business with those left behind, and will not financially support them due to differences among the various Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths and non-Christian behavior among assimilated families. They are like: "Why bother", or "I don't have time for that." These malakan places, animals and foods were named after the malakan peoples. All Spiritual Christians in/from Russia are malakane, but not all malakane are Spiritual Christians in/from Russia ^ Contents ^
malakan Peoples In 2000 perhaps 13,000 malakan peoples (Spiritual Christians from Russia) and their descendants were in the South Caucasus of the former Soviet Union. Estimated populations, year 2000
Another estimated 100,000 Spiritual Christians from Russia resettled from the South Caucasus to the Northern Caucasus, most to Stavropol and Krasnodar territories, some to Rostov oblast and Central Russia. Many joined or revitalized indigenous congregations that never migrated to the Caucasus. The 2022 Russia attack on Ukraine probably dispersed Spiritual Christians from Russia back to the Southern Caucasus, and affected all Molokane and their descendants in Ukraine, thousands at least. Who are they? The ancestors of malakan people were orthodox heretics, who called themselves Spiritual Christians in Russia. Many were moved from Novorossiya and Central Russia after Russia began colonizing the Caucasus, after 1840, to get more economic benefits (more land, no taxes) and religious freedom offered for colonizing the new territory. They are neither creeds, nor sub-creeds of one faith or religion. They are many faiths of mostly heterodox (non-Orthodox), mostly White people intermixed with other peoples (Asiatic, Northern Europe, Germanic) from many places in the Russian Empire who were mostly collected in Novorossiya, then migrated to the Caucasus. The exception to non-Orthodox are the old rite Orthodox, Old Ritualists, who are also considered heretics to the New Orthodox. Most malakane lived in groups or clans, often in their own villages, or sharing a village with other heterodox people from Russia who met for the first time in the Caucasus, often clashing, some inter-marrying. Malakan is an etic term used by indigenous Caucasian peoples referring to the "new invasive settlers from Russia" — a foreign group, "them" (chuzhikh grupp), "outsiders,"outgroup, ne nashi, aliens. In a similar xenophobic manner, before 1700 in the Russian Empire, all western foreigners in Russia were called Nemtsy (dumb, those who can't speak our language), no matter what their actual nationality; and this term meant both Germans and stupid, because few could understand them. It was more insulting than Americans today who say: "It's Greek to me" when they don't understand something. In a similar fashion, a single derogatory term is used in the American Southwest "... to refer to (any) foreign citizens living in the U.S." — "wetback" (morjado). Do not confuse the general category malakan with the Spiritual Christian Molokan faith. These 2 words sound alike, appear to be cognates, and are too often confused. The origin of Molokan is from the heresy of eating dairy (molochnye) products, probably morphed into a pun about nursing infants (molokane) who are too immature to understand religion. The origin of malakan is probably from a geographic river area in South Ukraine, northeast of Crimea, the Molochnaya (German spelling: Molotchnaya). Malakan originally was a demonym (gentilic) for "people from the Molochnaya (river area)" who were moved to the Caucasus(30) by the thousands. Molochnaya (German: Molotschna) is the river delta and territory in south Ukraine northeast of Crimea. Molochnaya means "milky" in Russian, which referred to the abundant dairy grazing land. In the native language Cuman (Polovtsy), the area was called syutana, meaning "nurse, mother."(31) For most of a century, many descendants of Spiritual Christians in the southern republics of the Soviet Union and who migrated to the U.S.A. from the Caucasus, retained an oral history that their label (malakan) came from ancestors who lived in "Milky-waters."(32) I was told by Molokane who remained in Central Russia that they never heard this rumor until they met Molokan refugees from the Caucasus and South Ukraine who were repatriated to Central Russia after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Most settlers in the Caucasus from Russia called malakan were illiterate and did not know much of their history, nor how to define their faiths. They probably accepted the default geographic label, emic, from within their groups, like I did when some people who did not know, or could not remember my name, nicknamed me "Arizona" from my 1952 Ford car license plate, when I moved from Arizona to Los Angeles in 1966. The old car and my country manners excluded me from most of LA-UMCA parking lotters who socially valued sporty cars and surfers. For years a few guys in Los Angeles would only call me "Arizona" to probably impress among their peers that I was an outsider in their Los Angeles territory, and that my name was not important. To them I represented a different tribe. Also, the Los Angeles presbyter George Samarin stated to me several times that, although I attend his Aktinsky congregation on Percy Street along with my grandparents (father's and mother's), and his congregation married my parents, he considered me a member of the Arizona congregation. After my grandparents died, Samarin's assistant presviter Harry Shubin differed with Samarin and repeated invited me into his kitchen work brigade (parti). After Harry Shubin died, I lost my contact. 30 years later, Samarin's congregation refused to bury my parents who were married by their original congregation, declaring simply they were not "dues-paying" members. See more egregious shunning behavior reported by Paul J. Orloff in the section below: Variety of Dukh-i-zhizniki. In the late 1700s after Russia conquered the south Ukraine, called New Russia (Novorossiya), incentives were given to state serfs (controlled by the Tsar) to settle the area. In 1789, Anabaptists (mostly varieties of Mennonites and Lutherans) from Germany were given huge priority settlement sites, military and tax exemptions, their own German-language schools, and allowed to live as they wished. Much is documented about the Molotschna Mennonites and their neighbors from Germany. Similarly, incentives and invitations were then given to the state serfs across Russia (about half the rural population of peasants in Russia). Many state serfs were also Spiritual Christians, many in secret, and welcomed being removed from central Orthodox areas, and thousands voluntarily accepted the offer, particularly the extra land and temporary military exception. The resettlement policy was somewhat similar in intention to the Homestead Act of 1862 in the U.S.A. and in Canada, The Free Grants and Homestead Act in 1868 to disperse colonizers into territory being taken from indigenous tribes. MAPS In 1802, Dukhoborsty were given land on the west side of the Molochna River, then Molokane and other heretics were given land mostly on the east side, south of the Anabaptists from Germany. Part of the origins of what became Pryguny probably occurred south of the Molochna Colony, northeast of Crimea. In the area were Subbotniki, Shalaputy, Shtundisty, Novoskopsty, some newly arrived, and other non-Orthodox indigenous faiths (probably including Khlysty), descendants of Bogomils, Apocalyptic Anabaptists from Germany, and Jewish-like Krymchaks and Karaites; the most zealous of whom probably contributed to what would later become the Prygun faiths. Today only Molokane continue to maintain their heritage faith in the Molochnaya area, Ukraine, were I visited 3 active (of 15 former) meeting halls in 1992, during the International Conference of Spiritual Christian Molokane. ^ Contents ^
By the mid-1900s, the easy to pronounce term — malakan — expanded into common usage in South Caucasus languages (Turkish, Azeri, Armenian, etc.) to refer to any peoples similar to malakan, any indigenous non-Orthodox faith (heresy, sekt) from Russia, and later into a general term for all Russian-speaking settlers from anywhere in Russia, including staroobryadsty (Old Ritualists), all Spiritual Christians and their descendants. Most of these malakan peoples were resettled by the Russian government, lived in their assigned villages, exhibited non-Caucasus cultures from Russia (dress, food, language, lifestyle, housing, etc.), practiced their own faiths and were prohibited from proselytizing, though some outsiders joined and intermarried. Like white (72) European settlers in the American West, they were distinctly lighter-skinned, some with brown or blond straight hair; and grey, hazel and blue eyes, in contrast to the dark complected indigenous tribes who dressed and spoke different languages, had different faiths and ate different foods. For more than 175 years in the Caucasus, the definition and use of the word malakan has evolved and broadened over time and place to a vague and fuzzy term meaning most any old Christian faith group from Russia in the Caucasus, not native to the Caucasus. Many malakan peoples in the Caucasus today falsely believe they are not Russian, rather a unique race, because they have their own label and heterodox (non-Orthodox, implying non-Russian) faiths. Beginning in 1880, for 30 years, news articles and books in the U.S.A. began to report about persecution of indigenous protestant-like faiths in Russia which became well-known in the West, particularly the Stundisty — "... the Stundists regarded themselves as the Society of Friends (Quakers) of Russia, as men who truly believed that all violence, nay all assertion of power, is inherently evil." In March 1905 non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians (Pryguny, Molokane, Subbotniki, ...) were called "Stundists" in the Canadian press which announced that 200,000 were coming from Russia to Canada; but they were diverted to Los Angeles by Demens. In May 1905, Los Angeles Presbyterian church leaders assumed the arriving Spiritual Christians from Russia were the Stundists (Stundisty) affiliated with Presbyterian missionaries whom they read about in Molochna (sometimes called neo-molokane). To help with the Russian settlement process the Presbyterian church assigned their Russian-speaking Rev. Teichrieb to minister "to their spiritual needs as far as possible."(99) On Sundays at the Bethlehem Stimpson-Lafayette Industrial School, which served as the first main meeting house for Spiritual Christians from Russia in Los Angeles, Rev. Teichrieb conducted services in Russian for about 5 years, and may have converted some to the Russian-speaking Presbyterian church in Los Angeles. When the first group of real Molokane arrived in Los Angeles, their presbyter was Rev. Teichrieb, until January 1906 when about 34 Molokane left Los Angeles with 86 other Spiritual Christians, mostly Pryguny, to Hawaii. By August 1906, most all the Molokane returned to San Francisco from Hawai'i, where they stayed. Up to about 1910, Rev. Teichrieb only referred to the Spiritual Christian faiths remaining in Los Angeles as Stundists. He was reassigned to another foreign parish at the north edge of Chinatown probably because the most zealous Spiritual Christian tribes from Russia (a) viewed Teichrieb as an outsider, (b) each tribal faith cluster, mostly based on their village of origin, insisted on conducting their own rituals with their own anointed or appointed leaders, and (c) by 1910 most Spiritual Christians from Russia were living on the east side of the Los Angeles river which was less crowded and new homes were being build. All of the general faiths terms shown in the chart below and more were probably called malakan at some time and place. Also many of these faiths in Central Russia were called Quaker and/or Mormon, because authorities suspected such "infectious" heresies were imported from foreign countries. ^ Contents ^
Malakan Definition Changes Over 3 Centuries.
* After 1928 in the United States and Caucasus, many Pryguny, Sionisty, Noviy israili, Maksimisty, and other immigrant faiths from Russia transformed or converted to new Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths, or abandoned their heritage faiths. ^ Contents ^
Each general faith group in the chart above has a different history by time and place, some with many factions. Many interacted with each other forming hybrids and new faiths; even with Russian Orthodox. Some moved back and forth between faiths several times, mostly to get privileges. They all changed over time, mostly synchronous with their surrounding cultures and government policies. Today, most are extinct, and their descendants assimilated, so few vestiges of practicing members remain. Compare to the United Society of Believers in Christ's Second Appearing (Shakers), 2 remained in January 15, 2017. Below is a Venn diagram (not to scale) showing how Molokan is a subset of malakan. All Molokane are malakane, but not all malakane are Molokane. Because the term malakan is phonetically similar to Molokan, the 2 terms are too often confused, thousands of times. See Wikipedia examples in Turkish, Azeri, Armenian (Մոլոկան), ... For one example, in 2011, English-language journalists began to falsely report that the ancestors of celebrity personality Kim Kardashian were "Molokans" or "Molokan Jumpers," implying the same for her. Actually her folk-Protestant Armenian grandparents joined the Spiritual Christian Pryguny faiths (not Molokane) while in Kars oblast, Russia (now in Türkiye) and some of her relatives who migrated to Los Angeles converted, after 1928, to their own Dukh-i-zhiznik faith tribe, but were shunned by more zealous and racist non-Armenian Dukh-i-zhiznik faith tribes. Several of Kim Kardashians relatives are buried in the Spiritual Christian "Old Cemetery", East Los Angeles; and a few intermarried with non-Armenian Pryguny and may be buried in the cemetery on Slauson Ave. However, Kim Kardashian was raised in private Catholic Schools (Orthodox). Her erroneous false history stories are copied, recopied, blogged and edited many times with mis-information, partially fake news to sell pay-per-click advertising. While it was correct in the Türk language to report her ancestors were malakan from Kars, reports in English and other languages failed to accurately translate and define the religious history of her ancestors (sloppy journalism). It is correct to say that her great-grand-parents were Armenian folk-protestants who left the Armenian Apostolic Church, some of whom joined a branch of the Spiritual Christian Prygun faiths in Kars Oblast. Her grand-parents migrated to Los Angeles with other non-Orthodox Spiritual Christians from Russia and continued their version of a Prygun faith, which eventually divided into about 3 congregations in the Armenian and Russian languages, and one or two congregations used the Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn'. Her father did not remain in any Prygun or Dukh-i-zhiznik faith for his family, married out, and raised his his kids as Americans. Up to 2019, Kim Kardashian professed to be Christian with no membership in any congregation. In 2015, she and her husband took her oldest daughter to Jerusalem to be baptized at the Armenian Cathedral of Saint James. In October 2019 her sister Cloe, Kim and 3 younger kids were all baptised in Etchmiadzin Cathedral, the main Armenian Apostolic Church (30 miles north of Mt. Ararat, 10 miles west of Erevan). Drawings of this ancient Armenian cathedral by "boy prophet" E. G. Klubnikin appear in the Kniga sontse, duk i zhizn' on page 702, illustrating the furture kingdom of believers. ^ Contents ^
Characteristics of Indigenous Faith Groups in Russia Confused as malakan, 1700-1900.
^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Dialects Spiritual Christians speak a variety of Slavic Tongues (dialects) and their own dialects, and sing in a variety of styles, depending on the origin of their ancestors and the geographic path of their migrations. Most studied and documented dialects are among branches of Dukhoborsty in Canada. An extensive long-term study of dialects of the staroobryadtsy has been conducted by Drs. Richars and Tamara Morris in Woodburn, Oregon.  Diagram from: Dillingham, William Paul. "Immigrant Races or Peoples: Slav (Slave), Slavic, or Slavonic ," Reports of the Immigration Commission, United States Immigration Commission (1907-1910), page 274. Nearly all of the Spiritual Christians who migrated to North America came from the Caucasus and brought with them the Southern Russian dialects, like Don Kossack Balachka. Some, including all Dukhoborstsy and many Pryguny came to the Caucasus via the South Ukraine, carried Ukrainian dialects, and their descendants brought those dialects to North america.(34) Not shown in the diagram above are the Old Church Slavonic dialects often preserved as special religious terms among some Spiritual Christians, and especially among Staroobryadtsy. who did not arrive in North America until the 1960s. The language and dialect preservation is more prevalent in diaspora populations who were removed from Russia about 1900. Use of Old Slavonic has caused divisions among some Molokan and several Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations. ^ Contents ^
Spoken Languages Spiritual Christians who immigrated to North America around 1900 mainly spoke Southern Russian dialects of limited vocabulary, sometimes mixed with Old Slavonic and Ukrainian words and phrases. Some were also fluent in Armenian, Moravian, Georgian, Azeri, Turkish, Farsi and other languages common in South Russia in 1900. Baja Californian Spanish is spoken by all raised in Mexico since 1905, and some raised in Arizona since 1911. Farsi is also spoken by those raised in Persia (Iran) after the 1917 Revolution, and immigrated to the USA around 1950. A few individuals learned other languages in school, the military, and while working in foreign countries. Many born in Russia subscribed to and bought Russian language literature. When it opened in the 1920s, about 25% of the holdings in the new Boyle Heights Branch of the Los Angeles Public Library were Russian-language books and periodicals, and the library hired Russian-speaking staff. Parental support for Russian language literacy nearly vanished during the Cold War (1940+) when it was considered unpatriotic, especially during the 2nd Red Scare and McCarthyism (1947-1956). Spoken Russian was primarily limited to people raised by Russian-born parents, and not passed on to the grandchildren to facilitate their prosperity and assimilation. In contrast, the most zealous Dukh-i-zhiznik families indoctrinated their children by rote memorizing songs, prayers and verses, with no formal grammar instruction. The Russian-literate immigrant society had by the 1960s transformed into a few who recited Russian to perform religious rituals. In Canada, retention of Russian literacy has been a goal mostly achieved by Community Dukhobortsy in British Columbia, Canada. For decades "Russian School" was held after elementary classes, and in secondary schools where Dukhobortsy were teachers or on the school board. A few school districts in the Kootenay area of British Columbia offer immersion K-12 Russian classes to serve children of U.S.C.C. Dukhobortsy, Sons of Freedom, and recent immigrants. Also groups of about a dozen college students every year were given stipends by Obshistvo Rodina, Moscow, to attend university in Russia.(66) In the U.S.A., it was common for descendants of assimilated Spiritual Christians in college to enroll in at least beginning Russian, and several managed to complete advanced Russian, while a few were Russian majors. I know of only 3 descendants of Dukh-i-zhizniki, all girls, who attended Soviet universities. All were on stipend, the same program offered to Canadian Dukhobortsy.(50) After 1980, the Hacienda Heights U.M.C.A. incorporated a non-profit Dukh-i-zhiznik "Molokan Elementary School" (M.E.S.) that still teaches their Dukh-i-zhiznik ritual songs and prayers in Russian, but very little, if any, Russian grammar. Major goals of the M.E.S. was to indoctrinate kids in the Dukh-i-zhiznik rituals, and isolate them from contact from outsiders ( ne nashi). In the 1990s, since perestroika, about 50 Spiritual Christian immigrants, mostly Dukh-i-zhizniki, have been sponsored from the Former Soviet Union, most from Armenia, and divided between the U.S.A. and Australia. The goal seemed to be more to import Russian-speakers than pure humanitarian altruism. Several came as families, more as brides, and very few men came to marry. Due to their modern Russian language lacking of Old Slavonic terms, and moderate religious stances, they initially were not moved into many "front row" positions. About 2010, most of the "front row" (pristol) of the Samarin-Percy street-Pioneer street" congregation is dominated by immigrants from Armenia. Most in from Armenia in Australia have split into their own congregation, due to religious and language differences. Those in the U.S.A. are not fully accepted in all congregations. Some are insulted by native zealots, like my wife, probably because she is of educated and integrated Molokan origin, though she has many Dukh-i-zhiznik relatives in Southern California and in Russia. In late 2017, the most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki were purging their newly conquered Hacienda Heights-U.M.C.A. territory of ne nash literature, including Russian language books not published by them, and other items, following a decade of reckless attacking and shunning perceived ne nash and "unclean" people and objects. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Migration About 30% of all Mennonites in Russia migrated out from 1870 to 1880 due to new requirements for military service which was not mentioned when they first arrived. "There were two waves of emigration from Russia to North America: the first, in 1873, saw ~18,000 Mennonites arrive in Canada and the American Midwest. The second wave occurred in the 1920s. Of the 25,000 who left Russia during the second wave, ~21,000 ended up in Canada."(97)In comparison, about 1% of all Spiritual Christians (sectarians, sectanty) in Old Russia migrated to North America from 1899 to 1930. Most came from the western Southern Caucasus, location of perhaps one-tenth of their total populations in 1900. See: Reasons for migration, Dukh-i-zhizniki in America, Chapter 1. The first migration wave was large and quick due to the intervention of Lev. N. Tolstoy and leadership of The Society of Friends, London UK. In 1889-1899 on 7 ships about 7,400 (1/3) of the most zealous and persecuted Dukhobortsy (spirit-wrestlers, Doukhobors), mainly followers of P. V. Verigin, (Veriginisty) migrated to central Canada from the Southern Caucasus; and, by 1930 about of 8,700 had arrived in Canada on 79 ships. The majority 2/3 of all Dukhobortsy remained in Russia. Dukhobor Migration to Canada (60) 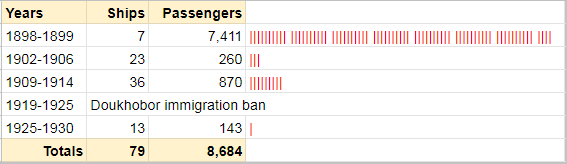  In 1899, about 85% of the Verigin Dukhobortsy (about 1/3 of all Dukhobortsy) left South Russia in one year. Five years later beginning in 1904, another smaller wave of non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians began to leave Russia because in 1901 they petitioned the Canadian government and got the "same deal as Doukhobors" to move to central Canada with the same military exemption, to live on block grant farm and range land in their own villages with freedoms of religion and education. But, P. A. Demens who had been critical of Dukhobortsy migrating to Canada instead of the United States, intervened and diverted nearly all of the arriving non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians to Los Angeles, except for a few who intermarried with Dukhobortsy, and others who stayed on the east coast of America. Only about 1% of the non-dukhobor sectarians (Spiritual Christians) fled to America, and many of the most zealous intended their migration to be temporary, until political unrest settled in Russia. Compared to the approximately 8,700 Dukhobortsy, probably less than 2,500 (~30% of the Dukhobor count) of non-Dukhbortsy arrived in groups over a 7+-year period (1904-1912). (See: Dukh-i-zhizniki in America, Chapter I: The Migration.) The migration of non-dukhobor Spiritual Christians was much smaller, and more fragmented, chaotic and uncoordinated than the migration of the Verigin Dukhobortsy. Every clan had their own oral history of how their ancestors arrived. Most landed at Ellis Island New York, and took a train directly to Los Angeles, the first groups were led by Demens. Some ships landed at Galveston, Texas, while other ships delivered immigrants to Angel Island, San Francisco Bay. Some ships took passengers directly to the Panama Canal zone, perhaps to sell them as laborers if they could not pay their fare, and many of those managed to travel north to settle in Mexico. Some were offered communal farm land in Panama, which they rejected. Some went to Brazil, where some stayed in South America, while others crossed the continent, climbed the Andes mountains to the Pacific ocean where they got a ship to America. Some arrived in Canada, then crossed at Winnipeg south into the U.S.A. to Los Angeles.(111) After 1906, most Molokane clustered in or near San Francisco, and most of the other Spiritual Christian tribes from Russia clustered in or near Los Angeles, or Ensenada, Baja California, Mexico. [MAP] Spiritual Christian Migration to America (chart in-progress) During these migrations to North America, most Spiritual Christians were called "Russian Quakers" in the press, and often "Mennonites." Sometimes Spiritual Christian Dukhobortsy were called Molokans, and sometimes Spiritual Christian Pryguny and other faiths were called Dukhobortsy. At first the terms did not seem to matter, as long as the readers generally understood they were dissident immigrants from Russia, sort of like Protestants (folk protestants). In Canada the collective term for Spiritual Christian was simplified by outsiders to 45+ various spellings of "Doukhobor". In the U.S.A. the term for "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians" was falsely simplified to "Molokan," causing international confusion for more than a century, which this Taxonomy corrects. Note that the term "Molokan" has been misspelled more than 60 ways in English print. 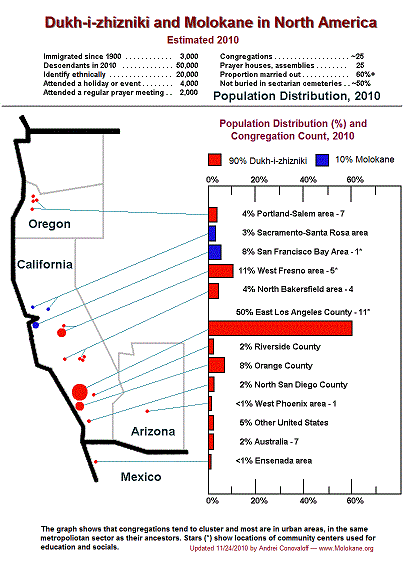 During the second wave of immigration of the "Brotherhood
of Spiritual Christians" to the U.S.A., all were
mistakenly announced and promoted simply as Molokane,
though most were varieties of Pryguny and other non-Molokan faiths, including Dukhobortsy.
Reasons for fewer Molokane emigrating are listed
in Dukh-i-zhizniki
in America, Introduction. Though some resisted
this false identity and tried to correct the mistake, they
were repeatedly conditioned by advisers and agents to only
use the short false collective name of "Molokan," probably
to simplify their complicated identities and hide their
actual faiths, to counter discrimination and avoid
deportation during decades of nationalism, religious bias
and bigotry, and later anti-communist sentiment in North
America.
During the second wave of immigration of the "Brotherhood
of Spiritual Christians" to the U.S.A., all were
mistakenly announced and promoted simply as Molokane,
though most were varieties of Pryguny and other non-Molokan faiths, including Dukhobortsy.
Reasons for fewer Molokane emigrating are listed
in Dukh-i-zhizniki
in America, Introduction. Though some resisted
this false identity and tried to correct the mistake, they
were repeatedly conditioned by advisers and agents to only
use the short false collective name of "Molokan," probably
to simplify their complicated identities and hide their
actual faiths, to counter discrimination and avoid
deportation during decades of nationalism, religious bias
and bigotry, and later anti-communist sentiment in North
America.In the 1950s, when I attended elementary school in Arizona, all our parents told us to report that our religion was "protestant" on government forms. They were ashamed of the connotation of the words "Russian" and "Molokan," and more so if they had to explain Pryguny, Skakuny, Jumper, Davidisty, Maksimisty or the Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn'. These post-WW2 families contrasted with the immigrants who, during WW1, summarized the Maksimist and Davidist faiths and books in English for the local school and government officials. Later John K. Berekoff in Los Angeles edited and published this summary to explain this new religious movement to the generation born in America. See: Berekoff, John K. Book of Prayers and Songs, 1944. Overcast in fear, the false Molokan label became ingrained throughout the 1900s into the collective memory of Dukh-i-zhizniki who forgot and/or censored their embarrassing oral histories and identities to their descendants and surrounding public. The cover-up was exposed after the breakup of the Soviet Union and reorganization of the Molokane faith internationally in the 1990s. Only then would the numerous Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths began to realize they could no longer falsely claim the Molokan faith label forever in public, though the false term persists among themselves and on recorded documents, deeds, signs, etc, and they continue to fool naive journalists and scholars, including themselves with deceptive advertising. In North America, the single label "Molokan" was first naively internationally popularized in 19051 by journalists in St. Petersburg, Russia, that that 200,000 Molokane will all migrate to North America, due to petitions received, following Dukhoborsty. Then Russian agents in Los Angeles (Demens and Cherbak, 1905-1910), and professors (Young, U.S.C. 1926-1932+) primarily used the single simple term to promote, document and shelter immigrating mixed tribes of immigrants from Russia as a valuable breed of safe White Protestant Christian immigrants (72) — tall, healthy, strong, honest, intelligent, literate, sane, sober; but not criminals, not anarchists, not Bolsheviks, not communists, not socialists, not traitors, not Jews (Hebrews), not Pentecostal Holy Jumpers/Rollers, nor fanatic pagan religious cults — a false history. ^ Contents ^
The false single simple label probably allowed the advisers and agents:
Similarly in Russia, being classified as Molokan qualified a non-Orthodox sect for privileges under the new evolving 1905 ukaz for religious and civil freedom, which was denied to "perverse" zealot groups similar to khlysty, like the Pryguny and Maksimisty. Therefore on both continents, non-Molokane simultaneously hijacked a false Molokan identity to get privileges, hide and continue the camouflage today. Unfortunately today, many of the most zealous and vocally aggressive Dukh-i-zhizniki stubbornly falsely retain a belief that they actually ARE Molokane, even boasting they are the "true" authentic version of Molokane. How did this happen? First marketing, then generations of inbred fear and shame to reveal the truth. If you are one of those people, you better quit reading this now, because you are probably afraid of the facts. Caution: Continued reading will upset you, and/or upset zealots with whom you discuss this new information. So if you continue reading, don't tell any one who might insult you for knowing more than what you are supposed to know. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Naming Old Russian sects Since all Russian sectarians are ethnic "Russian" they have no ethnic group name — no ethnonym. Russian scholars often refer to them as ethno-confessional faiths (ethnic religions), but without a specific ethnic identity. In the 1980s historian Ethel Dunn told me in the that she thought "Molokans" in the United States should be designated an official ethnic group, but I never learned if or how she would cause that to happen. Exonym versus endonym xxxxx In the Russian Empire since the 1400s, many ethnic Russians (those not Jewish, Muslim, or Buddhist) who refused the mandatory Orthodox faith for ethnic Russians called themselves and/or were called dukhovnye khristiane (Spiritual Christians)(12) or other terms. The Russian Orthodox Church, government, historians and journalists called them sektanti (sectarians) and described them by various alleged characteristic heresies (eresi) and traits —
More than a 100 descriptive labels were used for these non-Orthodox faiths, which should not be confused with the Old Orthodox faiths of staroobryadtsy (Old Ritualists) which refused to modernize, or reform to new Orthodox rituals ordered in the 1600s, yet remained Orthodox. They are unfortunately commonly called Old Believers, a term sometimes mistakenly applied to dukhovnye khristiane, which is also an old belief (100s of years old). Some dukhovnye khristiane adapted their exonym by combining terms, like dukhovnye khristiane-molokane, dukhovnye khristiane-dukhobortsy, dukhovnye khristiane-pryguny. Some of the alleged labels were not correct, rather referred to Western sects, like kvarkeri (Quakers) and mormoni (Mormons), and many were misclassified or had no label. Many changed labels to get privileges. Many did not know what to call their illegal faith(s). Combining labels is like saying: "fruit-apple-Red Delicious", "fruit-apple-Granny Smith", "fruit-apple-Gala", etc. By 1900 there may have been as many as a million followers of such non-Orthodox protestant-like faiths in the Russian Empire, about 1% of the population. A major problem for the census managers was how to label them, if and when they were identified in a location. They were a huge administrative problem. Official committees were assigned to investigate, report and propose remedies to save their souls, resulting in guidebooks for converting them to Orthodoxy, and conflicting changing regional policies for governing heretics which varied by time and place. xxxxx something to be added The sectarian problem in Old Russia was legally somewhat similar to the drug problem in the U.S.A. today. About 10% of the population in Old Russia resisted the Orthodox reformation (raskol), and about 1% were sectarians (sektanty). About 10% of the U.S.A. population had a drug use disorder, and about 1% used crack cocaine in 2016. All of these are illegal offenses subject to arrest and jail, but too big for government to solve, or cure; and policies differ over time and place. If people hid in Old Russia they could worship in non-Orthodox ways, but if caught they were punished with a misdemeanor (like possessing a small amount of marijuana for personal use). If they openly proselytized or recruited new members, they were charged with a felony (like a drug dealer who sells or gives drugs to others). If people hide in the U.S.A., they can use drugs. Would a drug dealer or user immediately trust anyone, or allow photos of their illegal activity? This analogy may help the reader understand why some Dukh-i-zhizniki are so aggressive to uninvited outsiders attending a service, or anyone taking photos. They retain oral histories of government abuse minus the context of why their ancestors were arrested in Old Russia. If one zealot convinces his congregation to be secretive, he can incite others to attack other congregations to obey his zealous standards, while allegedly attributing his fears to the Holy Spirit. ^ Contents ^
Adding to the confusion in Old Russia, many exonym terms like molokan, kwaker (Quaker), Stundist were often interchangeably used to describe any religious dissident, as synonyms. The term zamolokanil (замолоканил : molokanized) was ".. a common reference to a group that was getting disenchanted with the Greek Orthodox church, and in a manner similar to that of the Dukhobortsy was waging a struggle against the Church and therefore called 'Molokans' for lack of another term."(10) The most famous writers in Old Russia popularized the word "molokan" in their works when generally referring to pacifists, wimps, heretics, law-biding citizens (do-gooders), dissidents, etc.; and different readers and translators would interpret the usage of the blanket term "molokan" in Russian prose context differently. [Examples in-progress.] In 1805 the original Spiritual Christian Molokane were given religious freedom in a decree (order, Russian: ukaz) — Petition to the Tsar Aleksander Pavlovich, July 12, 1805. In 18__ Dukhobortsi got a different decree. Other smaller Spiritual Christian faiths were not named in these decrees. Pryguny were not named in the 1805. Pryguny were named more than 50 years later, about 1856, although they began to aggregate about 1833. Freedoms for Subbotniki were given in a separate decree, and Dukhobortsy and Molokane each got separate degrees for settlement territories. [Research in-progress.] The Spiritual Christian Pryguny-Skakuny (Jumpers-Leapers), a new heresy faith movement, allegedly founded about 1833 (perhaps also called shalaputy) was variously labeled about 1856, about 90 years after the Molokan label appeared (~1765). Members often lived near and were known to aggressively recruit among other Spiritual Christians and faiths, and probably also wanted the 1805 freedom of religion for themselves. Some falsely claimed the label "Molokan." Many may not have realized they changed faiths or could accurately label their own faith. Pryguny evolved from a zealous union of several faiths, tribes and nationalities in Central Russia, later concentrated in New Russia in the Jewish Pale of Settlement, now the South Ukraine, Zaporizhia oblast, during the famine of 1833, with a focus on the Apocalypse in the "South," Palestine.(13), while neighboring Pietists from Germany choose an Apocalypse location in the East.(23) It was common for exiled Orthodox sectarians and Jews in the Russian Empire to change faiths to get a privilege, often declaring conversion to the Orthodox faith to get a work or travel permit. Some sectarians changed faiths several times before arrest, which recorded their identity-changing practice.(14) The 1897 Russian census counted Pryguny as a separate group. Many times Pryguny testified to the government and reporters that they were not Molokane. [Examples in-progress.] Some Dukh-i-zhizniki today hate Molokane for whistle-blowing, reporting that their Prygun ancestors impersonated Molokane. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————"Molokan" misnomer spread in America, by Demens and Young Demens  The generic
non-specific Molokan misnomer
was first popularized in the United States beginning in
January 1905, apparently solely due to Captain
Peter A. Demens
(1850-1919). As a respected authority on Russia,
correspondent for the Los Angeles Times, and
organizer of an informal committee in Los Angeles to
settle immigrants from Russia, he simply promoted them all
as "Molokans ... The cream of the Russian people."
He was anxious to bring them all to Southern California,
and invested about 15 years of effort and a lot of money.
To "sell" these peasants to city officials he whitewashed
them(25)(72), apparently to
protect them from white
Christian nationalism. Within 2 years of their mass
arrival, by the end of 1906, they failed as a group to
deliver as Demens bragged they would. Many Molokane moved
to San Francisco. Many Pryguny and some Molokane
went to Mexico, but and most of the various tribes
of Spiritual Christians from Russia stayed in Los Angeles
and nearby. The generic
non-specific Molokan misnomer
was first popularized in the United States beginning in
January 1905, apparently solely due to Captain
Peter A. Demens
(1850-1919). As a respected authority on Russia,
correspondent for the Los Angeles Times, and
organizer of an informal committee in Los Angeles to
settle immigrants from Russia, he simply promoted them all
as "Molokans ... The cream of the Russian people."
He was anxious to bring them all to Southern California,
and invested about 15 years of effort and a lot of money.
To "sell" these peasants to city officials he whitewashed
them(25)(72), apparently to
protect them from white
Christian nationalism. Within 2 years of their mass
arrival, by the end of 1906, they failed as a group to
deliver as Demens bragged they would. Many Molokane moved
to San Francisco. Many Pryguny and some Molokane
went to Mexico, but and most of the various tribes
of Spiritual Christians from Russia stayed in Los Angeles
and nearby. In 1910, after interviewing many who returned from Hawaii, Demens published his analysis in the Russian newspaper Tikhi Okean as to why the Hawaii experiment failed, and gave up on them to spent more time with his family and business. In December 1910, the editor of Tikhi Okean, Anton Cherbak, apparently with help from Demens, widely promoted a report that all Spiritual Christians from Russia then in Canada, Mexico, and Los Angeles had agreed to relocate to land near Santa Barbara, California. Huge stories with pictures appeared in the New York Times, Los Angeles Times, Los Angeles Herald and many newspapers, but the event never happened. Demens was probably most impressed with the real Molokane who may have come in early 1905 from Harbin, China, during the Russo-Japanese War. They were much more educated and better dressed than the other faith tribes. The first real Molokane to arrive did not look like peasants; the men did not have beards, and dressed in suit and tie. Their leader John Kurbatoff had a camera. The first Molokan women did not wear peasant clothes, nor did they constantly cover their heads with a scarf unless needed. They appeared like Europeans, very different than the Russian peasant Pryguny and others from the Caucasus. [Photo of first 34 Molokane, probably from Manchuria.] Demens was probably afraid the most zealous non-Molokan Spiritual Christian faiths could be discriminated against or attacked by racist Americans, as the Svobodniki (after 1920 called Freedomites and Sons of Freedom) were in Canada who marched in protest in 1902, sometimes naked. He knew first-hand that many American whites (72) hated colored people and foreigners, and many people hated Catholics and emerging Pentecostals (Holy Jumpers/ Rollers). For simplicity, Demens promoted them using the single, easy to pronounce, unique word "Molokan", rather than their 1904 official label: "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians." White Anglo-Saxon Protestant (WASP) Americans would be confused to hear the complicated truth, that they were mixed dukhovnye khristiane (Spiritual Christians) from Russia, mostly Pryguny, Klubnikinisty, Maksimisty, with minor groups of Molokane, Subbotniki, Stundisti, Sionisty and Noviy israili, and others, from about 2 dozen villages in 5 districts in Transcaucasia, Russia, and most never met until they arrived to Los Angeles. Demens marketed them with a simple one-word, easy to pronounce brand identity; and he told W.A.S.P. American business men and politicians exactly what they wanted to hear. These immigrants from Russia were all one homogenous group of "Molokans," Russian for "milk-drinkers" not alcohol-drinkers, new law-abiding citizens, cheap White labor and ideal Bible-believing Protestant colonists, to deter objections and attract charity. It worked. Everyone believed his story, at first. Demens devoted more than a decade inviting fellow countrymen to California and personally trying to help them get settled. He traveled across the U.S.A. several times, inspected Dukhobor settlements in Canada, scouted and negotiated land in Hawaii, wrote letters, published articles, hosting groups at his houses, contacted the President who appointed him an agent, traveled with them, negotiated with fellow railroad tycoon H.E. Huntington who offered 30,000 acres north of Los Angeles, volunteered 1000s of hours. No matter what he did, many immigrants were not satisfied and fought among themselves. After about 15 years Demens and his colleagues gave up trying to further help these diverse dukhovnye khristiane (Spiritual Christians) from Russia who eventually erased Demens and his friends from their oral history, which is now being restored here. Demens died in 1919. ^ Contents ^
Young In the mid-1920s, sociology student Pauline V. Young (1886-1977) an immigrant Jew from Russian Poland who graduated from the University of Chicago and had worked for several social service agencies in Chicago helping Slavic immigrants, moved to Los Angeles with her American Jewish husband, sociologist Dr. Erle F. Young, also from the University Chicago. He got a teaching job in the Sociology Department at the University of Southern California (U.S.C.), where she enrolled in the graduate program. At the time U.S.C. had the most robust sociology program on the west coast. Pauline spoke Russian, had experience working with immigrant Slavic populations, and chose to continue the research begun by Lillian Sokoloff a decade earlier, and Wycliffe a year before, on the fragmented population of folk-Protestants from Russia in East Los Angeles (today called Boyle Heights). Her refugee Russian-Jewish background probably appealed to those Spiritual Christians who favored Old Testament laws, and her husband needed data on this cohort of juvenile delinquents. Though she was not hated or feared by zealots as a "pork-eater," and understood many of their holidays, facts published in her 1932 book angered many. Why Switch Pryguny to Molokane? Though Young correctly defines her subjects as immigrants from Russia who call themselves Spiritual Christian Pryguny and use a new ritual book called Dukh i zhizn' (in short), she strangely overwhelmingly mistakenly, or on purpose, calls them "Molokans" in all her publications and lectures. She never met Molokane in Northern California. Her mislabeling extensively spread the misnomer initiated by Demens 2 decades earlier, and continues today as a false history. Careful study of her text reveals that she found no history of Pryguny to fill her thesis with background information. Since her thesis committee would have critically commented about a huge gap in her research, I suspect that in despertion, she added the history of Molokane to the Pryguny, Maksimisty, Klubnikinisty, Sionisty, etc.who had no written history, and claimed they were all the same people because some of her informants testified they were "Molokane", which she extrapolated to the entire population. Her graduate committee did not speak Russian, could not have double checked her facts, and naively assumed she was completely honest. This deception greatly simplified her work with many citations of Molokane, not Pryguny. Ivan G. Samarin apparently trusted her scholarship and copied much of her false history into the 1928 Kniga solntse, dukhi i zhizn', with some protests at the time. (61) Today we know much more about the fragmented and little documented zealous tribes of Spiritual Christians in Russia, like Pryguny, and that they are definitely not the same as Molokane. The history deception that Pauline Young committed in her thesis, book and papers is like one claiming that members of the Church of Jesus Christs of Later Day Saints "won" the label Baptist because they perform total imersion in a tub of water, therefore we should from now on only call them Baptists, not Mormon, not L.D.S; and their history is the same as all Baptists, except they have a few extra religous texts and their own prophets. "... and if you believe that, I have a bridge to sell you," Upon learning English, many immigrants who lived in their ethnic enclave in Los Angeles probably became afraid and ashamed to be known by their actual Russian faiths — such as Pryguny or “Jumpers” in English, Sionisty and Noviy israili about which local Jews protested in court, or by any other term except “Molokan,” though their religions were not Molokan and the most zealous despised Molokane. Unfortunately their originally preferred correct general term "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians" faded from popular usage by WWII, perhaps sounding too common or American for those who chose to live in America, and/or to vague, and/or to long to say. In contrast, the most zealous Russian-born Maksimisty who believed they will return to Mt. Ararat before the Apocalypse, and planned to leave soon, falsely called themselves Pryguny, and were not concerned with establishing themselves in America nor hiding their faiths and ritual books. Most of the assimilating youth were occupied with school, sports and socializing in a metropolis, were not taught Russian, were excluded from sobranie politics because they were not married, and most were not interested in memorizing and performing mystical rituals in a foreign language. Young predicted the immigrant cultures from Russia would fully assimilate by 1960, 25 years after publishing her book in 1932. By 1960, more than half were fully assimilated, and by 1980 more than 90% were not easily distinguishable from middle-America. By 2000, the relatively few who continued to learn and perform Dukh-i-zhiznik rituals closed their congregations and societies from outsiders (ne nashi) and non-dues-paying members whom they often scrutinize, sometimes with harrasment. Read much more about Pauline Young below. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Resurrection of Molokane in Russia In 1991 during perestroika, Molokane in the Former Soviet Union (F.S.U.) resurrected as a legally registered faith. Some Prygun congregations in the F.S.U. registered with the Molokane to gain official status, but Dukh-i-zhizniki did not, and have not as of 2024 while falsely claiming to be Molokane. (Researchers and journalists, beware of this deception.) Diaspora Molokane in San Francisco and Sheridan, California, joined the international organization and held international visits. Though all Dukh-i-zhizniki were curious about news about real Molokane, none joined the international Molokan organization because they knew they were not Molokane, and the most zealous obeyed a Maksimist creed which opposed the Molokan faith. By 2000, about 90% of the descendants of Spiritual Christians around the world had abandoned practicing their heritage faiths. In the west (USA and Australia) many joined (or attended) local Protestant denominations, especially megachurches, which offered trained clergy, free literature, broadcast lessons, child care, youth groups, comfortable seating and educational services in English. In 2005, not one Dukh-i-zhiznik attended the 200th Anniversary of Religious Freedom communal meeting in Stavropol' province, Russian Federation, hosted by the Molokane, though many Pryguny attended and also attended the previous celebration in 1905. In 2007, most Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations in Russia agreed that the easiest way to differentiate themselves from the organized Molokane is to honestly identify their faiths with their common ritual book (short name: Dukh i zhizn') despite the many differences among themselves. The meaning of this new label was clear to them when shown a list of all congregations in the world being compiled. If they wanted to be published in a world directory of Spiritual Christian congregations, they did not want to be shown in print as Molokan, Prygun, Dukhovniye, Subbotnik, or Dukhobor, rather as Dukh-i-zhiznik. No other identity label was suggested, nor has been submitted (as of October 2016). But, orally, mostly among members, they call themselves Molokane, because it is In America, extensive repetition of the "Molokan" misnomer for a century has unfortunately semantically changed, or brand-jacked, the original meaning into a broad erroneous generic term, which if used, will always need an awkward and confusing explanation, presented as a compound term: Original Molokan, Jumper-Molokan, Russian-Molokan-Jumper, Charismatic Molokan, Molokan-Prygun, Constant-Molokan, Maksimist-Molokan, … Molokan-Molokan. It is ridiculous to use false variable compound terminology when one exact word will do. Imagine you only know the word "cat" for a 4-legged mammal, because you don't know the other names (dog, horse, mouse, sheep, wolf, etc.). To label different animals you might say: "cat-cat", "cat that barks", "big cat, run fast", "small cat, hide in holes", "fuzzy cat, say baah", "cat cry at night". This is similar to pidgin English, and Native American expressions like "iron horse" for a steam locomotive. The "Molokan" term is so widely abused that some scholars, and many reporters and government officials, falsely think Molokans are a type of Orthodox or Old Believer faith (misnomer for Old Ritualists : staroobryadsty). Occasionally the term is mistaken as a non-Russian nationality. No wonder many authentic Molokane feel they are misrepresented in the press, by historians and zealous impersonators. Their confused identity has hindered the Molokane from getting recognized for their actual faith, and from getting land in the F.S.U. to build meeting halls. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Use correct labels It's much simpler, honest, informed and Christian, to use one correct term for each faith group, rather than hiding behind a false label popularized by those who assimilated(19) in metropolitan Southern California and are afraid to reveal their heritage faiths, or define them. Use of the very broad Americanized "ethnic Molokan" term for any Russian immigrant (Orthodox or not) should be avoided, and substituted preferably with the original term (transliterated Russian: dukhovnye khristiane, English: Spiritual Christians) or the historic Russian Orthodox pejorative term (Russian sectarians). Though many Russian-literate readers will recognize these correct terms, writers (journalists, students, scholars) should always define them. Use of the pejorative adjective postoyannie (постоянние : constant, steadfast, unchanged, original) for Molokane should be avoided, because it is a relative condescending descriptor, not a title or label. Some Pryguny were misled to believe that it means "no jumping allowed."(Bushnoff, Fedor. "Hill memories: Letters to the VIEW," The Potrero View, December 1971, page 2, column 2.) Some Dukh-i-zhizniki use postoyannie in an accusatory sense to infer, or state, that Molokane have committed blasphemy against the Holy Spirit because they do not jump.(Rudomyotkin, M.G. Verse 16, Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life, Book 4, Article [Story] 6, page 279.) Of all the faiths who call themselves Molokane, only the official international Molokan organization youth host a Molokan website — сдхм.рф. To date, only 3 other web sites in Russia are hosted by Molokane, while this one (molokane.org) is the only website in English with extensive content about Molokane around the world. Many temporary web sites were started by Dukh-i-zhizniki who falsely identified themselves as Molokane, and the few which persist are commercial or somewhat clandestine, requiring registration, as does an e-mailing list. Internet searches for the term "molokan" in any language return a mixture of web pages, articles and photos, most about Dukh-i-zhizniki who claim to be or are mislabeled as Molokane. Readers beware! Again, the purpose of this Taxonomy is to explain in detail how the misnomer was created, why it should not be used, because it is offensive and inaccurate, and to present a simple classification system of 3 unique terms for these 3 different faith groups of Spiritual Christians — Molokan(e), Prygun(y) and Dukh-i-zhiznik(i). In respect, and for honesty in journalism and scholarship, please use these 3 simple terms as a standard.
^ Contents ^ 2. Spiritual Christian Groups Over 250 ethno-religious congregations of Spiritual Christians from Russia around the world today, that are too often mis-labeled as "Molokan," are actually of 3 different religious types — 2 denominations of Molokane and Pryguny; and diverse new religious movements of Dukh-i-zhizniki. The mistaken "Molokan" label is sometimes applied to other Russian sectarian faiths, Russian Jews and Russian Old Rite Orthodox. How to identify which faith is which is super simple. These 3 Spiritual Christian types is are easily distinguished by their liturgy — songs, holidays, books and rituals; and, in the Americas and Australia, they are also easily identified by location.
1.
All Maksimisty
are Dukh-i-zhizniki, but not all Dukh-i-zhizniki
are Maksimisty.
2. Most adapted from Russian folk songs and borrowed from German Protestants. 3. Not during service, but often during meals at weddings, funerals, child dedication, holidays 4. Open canon, a sacred text that can be modified by continuous revelation, somewhat similar to Latter Day Saint canons. 5. About 200 prophets since 1900, but only 4 major prophets in their Dukh i zhizn' (religious text). Each congregation has 1 or more prophets. Over 100 prophesies have been recorded in secret notebooks shared with the most trusted members. This taxonomy uses the transliterated original labels from Russian (shown in italics) because the historic Russian terms have long-established definitions. I deviate from Russian by capitalizing the labels, common in English but not capitalized in Russian. Lax translation to English, sometimes intentional, has altered original Russian meanings. For example, Spiritual Christians in Tsarist Russia never called their meeting location a tserkva (church), a term only applied to Orthodox Church buildings. In English the word "church" is used by Orthodox, Catholics and Protestants, but not in Russia where only the Orthodox faith was legal. Because non-Orthodox faiths were illegal before 1903, most were not allowed to have prayer buildings. The major exception was in Blagoveschensk (Far East) where Spiritual Christian Molokane dominated the economy and politics, and built a large molitvenyi dom (молитвеный дом / дом молитвы : prayer house, prayer hall, assembly hall, gospel hall) or obschii dom (общий дом : community hall, assembly) for a sobranie (собрание : meeting, gathering, assembly); similar to Gospel Hall. Currently in Ivanovka, Azerbaijan, the term tserkva (церква : church) is used during interviews with young reporters who do not know their Russian historical terminology and have been influenced by foreign Protestant missionaries. ^ Contents ^
In Old Russia (before 1900) these three faith groups, and the Dukhobortsy* and others, historically called themselves Dukhhovnye khristiane (Духовные христиане : Spiritual Christians). Similar to European Protestants, these groups opposed about 90% of Russian Orthodox Church (ROC, Pravoslanoi, Православной — “right worship”) doctrine.(77) For being Russian and not Orthodox, these dissenting faiths, when identified by authorities, were ruled by the ROC to be heresies (eresei : ересей), sektanty (cектанты : sectarians), sekty (cекты : sects) [from Latin secare : to cut or cut off], and given many labels which described their deviation. Over 100 labels have been used to describe dissenting sects and schismatics,** which comprised at least 10% of the Russian population by 1900. In 1900, sectarians (non-Orthodox) totaled about 1 million, or 1% of the total population of the Russian Empire. In some areas along the periphery about 80% of the local population opposed the Church. The new territory borders were heavily populated by German immigrants, and Russian settlers, mostly sectarians, schismatics, and retired military. In Russia no Germans were Orthodox, except by rare intermarriage or conversion. Often several labels are applied to the same people or different peoples, which adds to historic confusion, especially when the subjects use different labels or interpretations than authorities — for example: Luidi Bozhe (God's People, People of God, Christ-faith) versus Khristovovery, Khristy, Khlysty (Whips, Flagellants, self-castigators). No one in Old Russia ever self-identified by saying: "I am a khlyst," according to Dr. Clay who did his Ph.D. thesis about this religious movement.(11) People often migrated and intermarried, changing their religious affiliation. Some Spiritual Christians adopted the ROC labels self-redefined, like Dukhhovnye khristiane-molokane. These 3-word labels were often shortened to the latter term used by the ROC, like molokane. * Spiritual
Christian Dukhobortsy
in Russia divided into 3 groups named by size and
leader. The most zealous third who moved to Canada
further divided into 3 different major groups by
leader and obeying new laws. See Taxonomy
of Spiritual Christian Doukhobors
(In-Progress).
** Note that raskol'niki (schismatics, раско́лники) — Starovery (Old Believers), better called Staroobriadtsy (Old Ritualists) — are also often called “sects” in English but rarely in Russian. In 1900, about 10% of the Russian population were raskol'niki. In the late 1800s, Western journalists often used “sect” in a broad manner to refer to a particular religion, like "Russian Orthodox sect" or "Mormon sect." Some reporters today confuse Molokane with Old Believers, probably thinking the term means “old faith.” For a comprehensive overview of Russian sectarian history see: A.I. Klibanov, History of Religious Sectarianism in Russia (1860s-1917). In 1906, after the failure of the Molokan Settlement Association in Hawaii, "Molokans" were ridiculed as "Adullamites," a "primitive Christianity," "vagrants," and "worthless." Unlike those who document them, practicing Molokane and Pryguny in Russia and San Francisco, California, never confused their own faiths. Historic records indicate that confusion about who or what is Molokan began in the U.S. immediately upon immigration in mid-1904 to Los Angeles, California, of relatively small numbers (less than 1%) of total Spiritual Christians whose leaders from Russia declared they were a united brotherhood of various Spiritual Christians. The first such label in print was "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians," which was modified after 6 months, in January 1905, variously adding and/or deleting: "Jumper," "Pryguny," "Molokan," "Russian," "Sectarian," and "Brotherhood." (Research in-progress.) The mixture of various non-Orthodox Spiritual Christian immigrants from Russia in Los Angeles could have described themselves by many terms used in Russia in 1900, and upon immigration when they first met other faiths (tribes, bands), such as:
^ Contents ^
To report or imply that all these different groups (bands or tribes) whose ancestors immigrated from Russia are collectively one huge homogenous group of "Molokans" is non-sense, obviously not correct, but has unfortunately happened too many times and continues as a convenience for writers and speakers who are either uninformed, misinformed, non attentive (lazy), or intentionally misleading the reader. The term Ikonobortsy pre-dated the term Molokane which preceded the term Dukhoborsty. Lyudi bozhii (People of God) was the self-named term mostly ignored by R.O.C. scholars who favored their heretic labels: Klistovstchina, Khlysty (Whips, Flagellates). These terms are approximate equivalents when referring to groups in Old Russia from the perspective of the Orthodox Church and government : non-Orthodox, hetero-orthodox, heretics, sektanty, sectarians, ikonoborsty, Spiritual Christians, and folk-Protestants. Several of these terms were specific varieties of folk-Protestant tribes, mostly Pryguny, who came to America — Akhtinsky, Buchanatskiy, Darachatskiy, Davidisty, Klubnikinisty, Maksimisty, Pivovarovsty, Rudomyokinisty, Salemskiy (half Molokane), Skakuny, and others not listed. Some of the labels (above) have specific meanings when used only among the most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki, while the meaning and use of other terms has been forgotten or obscured in their oral tradition. For one example, Ierusalem and Sion are opposites in American Dukh-i-zhizniki oral history. Some Klubnikinist Dukh-i-zhizniki in Los Angeles define Sion as those "saved" by the prophesy of E.G. Klubnikin because they migrated to California from 1904 to 1912 (before the Revolution); and, in contrast, their definition of Ierusalem, is the 99% of Spiritual Christians who stayed in Russia, and are not saved. This is somewhat similar to the definition of "Zion" as used by many Latter Day Saints: "... to connote an association of the righteous." In contrast, many Maksimisty in Russia believe that those who left for America abandoned "their" (Maksim's) Holy Land near Mount Ararat. In short, each conflicting Dukh-i-zhiznik faith (band, tribe ) believes they are "saved" and/or "chosen" in their own way, in their own place and time, and often defined with their own religious terms unknown to other tribes with whom they do not associate. The only obvious commonality is their religious text (Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn'), which is variously interpreted, as is the Holy Bible. Individuals could claim or be assigned multiple labels. Except for the term Molokane, many of these labels in America could easily suggest they were a mystical Russian sect, or confused with strange minority faiths often in the national press, labeled as: Quakers*, Shakers*, Mormons*, Jews*, nudes**, the holiness movement (Zion City, House of David, Burning Bush, God's Elect, Bridal Church of the First Born of God, etc.), Spiritualists, or queer (abnormal) radical Pentecostal apostolic religions in North America, nick-named: Angel Dancers, Barking Baptists, Dancers***, Dancing Mania, Flying Rollers, Happy-clappy, High Jumpers, Holy Ghosters, Holy Jumpers, Holy Kickers, Holy Rollers, Hoppers, Jerkers, Jumping Jack Factory, Pentecostal Dancers, Ranters, Rollerism, Rollerites, Rollers, Tangled Tonguers, Tongue Baptizers, etc. — in general, religious ecstasy. * Similarly, each of these terms are simple misnomers used by outsiders as short, easy to pronounce, short labels for a general collection of somewhat similar or affiliated divided faiths, which few outsiders understand.XXXXXX section in-progress https://books.google.com/books?id=tKb7n3pjFJoC&printsec=frontcover#v=onepage&q&f=false In 1893, a The religious forces of the United States, enumerated, classified, and described on the basis of the government census of 1890. With an introduction on the condition and character of American Christianity: In 1912, a 20-year study was published attempting to list and summarize all religions in the U.S.: The Religious Forces of the United States: Enumerated, Classified, and Described, by H.K. Carroll, Superintendent of the U.S. Census of the Churches, who used census and denomination supplied data. [in-progress] Carroll Henry K. 1912. The Religious Forces of the United States Enumerated Classified and Described; Returns for 1900 and 1910 Compared with the Government Census of 1890: Condition and Characteristics of Christianity in the United States. Rev. and brought down to 1910 ed. New York: C. Scribner's Sons. 584 pages. https://archive.org/details/religiousforceso00carrrich Robert S. Fogarty, Religious Inventions in America: New Religious Movements, OAH Magazine of History, Volume 22, Issue 1, January 2008, Pages 19–23, https://doi.org/10.1093/maghis/22.1.19 comprehensive survey of religion in America. Directed by H. K. Carroll, the survey “enumerated, classified, and described” Vandermeer, P. (1981). Religion, Society, and Politics: A Classification of American Religious Groups. Social Science History, 5(1), 3-24. doi:10.1017/S0145553200014802 xxxxx Russian-speaking immigrants living in urban clusters on the east side of downtown Los Angeles were fractionated by faith, territory, dialect, ancestry, nationality, intermarriage, education, wealth, etc. By broad faith or ethno-confessional group, they were Jews from Russia, Armenian Apostolic, Armenian Protestant, Russian Orthodox, or non-Orthodox-non-Jewish from Russia (includes : Spiritual Christians, Evangelical Christians, Baptist, Sabattarians, Shtundist, Presbyterian, ...). By nationality many were not ethnic Russians, rather people who immigrated from Russia, of mixed ancestry. Los Angeles newspapers rarely specified which religious group(s) or nationality or territory they were reporting about as
In the early 1900s, only two researchers tried to document the differences among the various immigrants from Russia — Sokoloff (1918) and Speek (1921); and this taxonomy continues where they left off, 90 years later. ^ Contents ^
So who was really Russian? A useful explanation appears in an English introduction "About the Book" 2nd paragraph, in Kurto, O.I. Russian World In China: The Experience Of The Historical And Ethnocultural Coexistence Of The Russian And Chinese People. Moscow: Nauka – Vost. Lit., 2013. The author uses the phrase “Russian people” to name people who speak Russian language and follow Russian traditions, regardless of whether they are of Russian nationality or not and what country their motherland is. The Chinese citizens often call “the Russian” someone who is actually the Ukrainian, the Belarusian, the Caucasian, the Kazakh, etc. So in China every person from the country which belongs to the Commonwealth of Independent States can become “the Russian”.For example, while searching for Subbotniki in Portland Oregon in the 2000s we asked people who worked at 2 of the several Russian stores. It seemed that all the store employees were Baptists from Russia who never heard of Subbotniki, and who surprisingly did not know how many Russian Baptist congregations existed in Oregon. There was no list, no unified Russian Baptist organization, probably because they came from different parts of the Former Soviet Union, and did not know each other. Employees lived among their family, congregants and friends, avoiding outsiders. Similarly when we finally met Subbotniki in Portland OR, they came from about 35 congregations in Central Asia, Ukraine and Moldovia, non from Russia. They had no list or map of their divided congregations, which contacts they kept only their cellphones. Upon meeting the most prominent presbyter David Klassen (grandfather was German-Mennonite who converted while in exile in Siberia with Subbotniki), together we quickly created the first Google Map of all their congregations which I visited within a few days. Like the SCR in Los Angeles in 1905-1930, they could easily walk to most of their meeting houses, and did not "need" a map. By 2020, several groups of young couples found work and established congregations in a few mid-western states, and Winnipeg, Canada. Decades of newspaper research in Los Angeles County, California, finds that the term "Russians", as reported from 1880 to 1950, meant (in approximate order of frequency of use in print):
Some of the Orthodox Russians (3 and 7 above) associated as Bolsheviks. Some were were called White Russians, with varied meanings. Though the Spiritual Christians from Russia were not revolutionists, they were sometimes mistakely called Bolsheviks; and they were not Orthodox and left Russia before the Revolution of 1917, sometimes they were mistakenly called White Russian émigrés. In short, the use of the term "Russian" in Southern California was often ambiguous, even when referring to the Russian language and languages from Russia (like Armenian), of which immigrants spoke several dialects, and old and new forms. Widespread confusion also results from publicity of Pauline V. Young's theses (1926, 1928), articles (1928, 1929), and book (1932) in which she specifically described and mapped people who use the religious text Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn', believe in a prophet Maksim G. Rudomyotkin (1818~1877), were Pryguny before this religious text was published, yet she called them "Molokans" 890 times in her book and nearly exclusively used that term in articles, lectures in class and in public, and in testimony to government agencies. Her use of the the word "Molokan" in print is about 1500 count. Multiply that several times (say 5,000+) for her verbal usage and citations of her work. She never visited real Molokane in San Francisco, did not understand, or ignored, the contextual meaning of Postoyannie which she translated as "Steady", yet she cited both Sokoloff and Speek who documented different groups of people from Russia. It appears that Young may have intentionally camouflaged her Dukh-i-zhiznik subjects to protect them. Another U.S.C. graduate student, George M. Day, documented the Orthodox Russians in Los Angeles, then became a professor at Occidental College (Day, George Martin. The Russians in Hollywood: A Study in Culture Conflict. University of Southern California Press, 1934, 101 pages). Though Day copied the "Molokan" misnomer from his professor Dr. Young, he differentiated among "Molokans" and non-Molokans ("Russian Jews" and "anti-bolshevik political exiles") in his Ph.D. thesis (page 1), but he did not specifiy them as Pryguny or mention the significant Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn'. In Los Angeles, all Russian-born groups were represented (Flats, Boyle Heights, Hollywood). Elsewhere in Southern California there were clusters of Jews from Russia, Russian Orthodox, and non-Orthodox non-Jewish peoples from Russian. In 1918, a Russian-speaking Home Teacher, Lillian Sokoloff, published the only general population survey of immigrants from Russian in her school district (The Russians in Los Angeles). Since then no comprehensive census study has attempted to segregate or map all these various Russian-born clusters in Los Angeles as was done in 1980 in San Francisco by graduate student Micheal Tripp.(70). This lack of specificity about "Russians" in California has allowed sloppy historians to lump them together with false labels. A further complication is that descendants of these immigrants from Russia soon divided among various faiths and by assimilation(19) path — brother marries Russian Baptist, sister marries zealous Dukh-i-zhiznik, son graduates college marries "outsider", daughter marries Prygun but attends "American" Protestant Christian church, parents divorce and one remarries "in" but the other marries "out", etc. To label all these people "Molokans" in faith is obviously not correct. They are descendants of Spiritual Christians from Russia, who were misled to believe they were something else. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Discrimination of American "Holy Jumpers"
Despite religious discrimination against fanaticism, and prejudice against illegal and unwanted immigrants, the variety of developing and evolving Pentecostal churches in California provided a somewhat welcoming environment for the most zealous Spiritual Christians. Due to Demens' promotion, in their first years they were temporarily compared to the “founding fathers” of America, the “Pilgrims,” for fleeing oppressive Russian Orthodoxy to form religious colonies in the new country and in Hawai'i. In Los Angeles, many Spiritual Christians attended American evangelical Christian services in local churches and tent revivals, praying, raising hands and jumping (even with Negroes), often with translation from English to Russian. Interfaith visits occurred. The most zealous Spiritual Christian immigrants learned that others in this new world also shared their beliefs about manifestations of the Holy Spirit (spiritual baptism, visions, trances, jumping, raising hands, speaking in tongues, healing, casting out demons), Zion, millennium, and plainness (spartan prayer house architecture, worship, and dress). But the rural peasant heritage traditions of the most zealous in Los Angeles clashed with government and urban life, as it did among the zealous svobodniki (after 1920 called Sons of Freedom, and Freedomites) in central Canada. ^ Contents ^
Many wanted to return home where they had freedom from mandatory education, freedom to arrange marriages, freedom not to register (marriages, births or deaths), freedom to sing and jump all night, and clusters of rural villages of relatives with whom they lived simple lives for generations near Mt. Ararat praying for their Apocalypse. Most important for Maksimisty was their prophesy to join both their leader M.G. Rudomyotkin (Рудомёткин) (1818~1877) and Jesus Christ on Mt. Ararat or to be buried nearby. What was to be a temporary journey for some, to seek fortune and return home, became exile. In the Summer of 1906, their most zealous prophet in Los Angeles, Afonasy T. Bezayeff, became alarmed about news of the San Francisco earthquake (April 1906) and 3-day fire. After seeing many drunks and destitute people in the Los Angeles courthouse during his son's court hearing, Bezayeff prophesied an earthquake in Los Angeles, because God was going to punish the wicked. He ordered all Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles to flee to the mountains, similar to what M.G. Rudomyotkin did several times before he was jailed in Erevan Governate (now Armenia). Public health authorities intervened preventing a mass panic. Later Bezayeff was alarmed about the mixing of cultures in Los Angeles and, while standing on a woodpile at a lumberyard where he worked (possibly in the San Pedro area), he declared (prophesied) that all Spiritual Christians must close their services to non-believers and stop contact with the false faiths of the world, yet he never moved from Los Angeles and drilled his followers to conduct spiritual marches to City Hall. He also initiated (via the Holy Spirit) placing the new ritual book: Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' on the alter tables of all congregations in Los Angeles after 1928 as a Third Testament to their Old Russian Bible, while some believed their new religious text replaced the New Testament. Was it Bezayeff who prophesied to burn all photographs? My grandmother Sasha Shubin reported watching people in The Flat(s) dump boxes of family photos into incinerators, in many backyards. She disobeyed the prophesy and kept her photos hidden for decades. In Russia, a frenzy burning of histories and diaries also occurred among the zealous German Pietist Jumpers (Heufers) in Tavria. (Citation) Many of the behaviors of Bezayeff, as reported by Berokoff and the press, occurred in Russia and appear similar to symptoms of brain disorders. In Los Angeles, the Americanizing the children of Spiritual Christians from Russia required for them to have a neutral unique simple identity for several critical reasons, if they were to stay in the city:
They did not use the English translations of “dairy-eater”, or more common: "milk-drinker", which are confusing and inconsistent if used for a group identity; rather, they kept the Russian term which Demens repeatedly used. Explaining that Molokan means "dairy-eater" could enhance association with whiteness, goodness and health. By habit and wide misuse, the "fake news" propagandist definition broadened to include nearly all non-Orthodox immigrants from Russia in America — hijacking the word for a century from the real Molokane. During their 100+ years in America, self-use of the terms "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians", “Jumper(s)” and Prygun(y), and New Israel(ites), diminished rapidly, falsely replaced by "Molokan" and variant combinations phrases that always included the "Molokan" term. Hopefully, use of the descriptive term Dukh-i-zhizniki will increase in this century, the 2000s, with education, and become internationally recognized. It is expected that most Dukh-i-zhizniki will initially be reluctant, even refuse (as many already have), to officially accept a label that accurately describes their secret faith. The faith will no longer be a secret. They will have to define it by publicly explaining their secret book, as was done in Arizona in 1915 (cite), again in Young's 1932 book, and again during WWII CO hearings, but since forgotten. After nearly a century of imposing upon and being offensive to Molokane and Pryguny, users of the book Dukh i zhizhn' should take ownership of this international label, a Russian loan-word which uniquely defines only them. Dukh-i-zhizniki have no need to hide any longer, except those who remain indoctrinated with fear and believe they must obey an old order, from Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) in prison to his followers in Erevan guberniya, to hide from the world, while ignoring the fact that they now live in a free country and Rudomyotkin's order for secrecy was made in a different time (about 150 years ago) and place (Old Russia) to people who died long ago. ^ Contents ^
3. “Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians” from 1902, 1904, 1907 In 1898, the name Christians of the Universal Brotherhood was used by the minority of Dukhobortsy who left the Russian Empire in 1899. The leader of the one-third who left Russia, P. V. Verigin, later incorporated the name Christian Community of Universal Brotherhood (CCUB). In 1900, another breakaway group in Canada called themselves the Society of Universal Brotherhood to protest Canadian laws, and to petition to move to the U.S. in 1901. In 1902, the Rev. Dr. Dana Bartlett met a traveling member of the "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians" which he described in his first book, The Better City (September 1907) on pages 79-81. On page 229 he reported "the Bethlehem building .. for a year .. was the meeting place for the Russian Church, known as the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians." On page 76A see photo: "Our Russian Neighbors From the Transcaucasus." In this book, Bartlett only used these 2 terms — "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians" and "Russians" to describe the immigrants. Upon arrival in mid 1904, the Prygun leader Vasili G. Pivovaroff introduced his first group in Los Angeles as the "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians." No other terms were used to identify his faith other than saying that they were from Russia. In December 1904, when V.G. Pivovaroff performed his first wedding in Los Angeles, the press only identified the "little band of Russian exiles" as "brotherhood" (3 times), while using the term "Russian(s)" 17 times. The first Marriage License shows their faith as "the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians". In May 1905, Dr. Rev. Dana Bartlett gave a translated lecture to the "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians, composed of Russian immigrants recently settled in Los Angeles." 100 were attending the adult night school, organized by Cherbak as the "Russian University." By mid January 1905, international news from Europe via New York reported that 300,000 Russian Quakers, "Molokanys", were coming to Los Angeles. The county government was facing a tsunami herd of peasants, which would double their county population. The educated, wealthy aristocrat Russian immigrants already established in Los Angeles (Demens, de Blumenthals, Cherbak, and associates), probably by invitation from government, began to advocate for their fellow country men and branded all factions of immigrant Spiritual Christians in California collectively as “Molokane / Molokans” when speaking to the press and governments. These advisers must have known that American “Holy Jumpers” were hated in Los Angeles, evicted from Southern California, and a policeman threatened to dynamite them. Also, they may not have been openly befriended by the more secretive zealous faiths that planned to return to Mt. Ararat. The press was confused about what to call them — Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians? Jumpers? Pryguny? Quakers? Molokane? Russians? All 6 terms were used with various spellings, and occasionally other terms like Dukhobor and Mennonite. Research in-progress. ^ Contents ^
Companies which invested in large agricultural colonies for these immigrants from Russia were confounded as to why they did not behave like organized Germans from Russia (many were Mennonites), and immediately divided into groups and quarreled, causing a farm colony to fail before it could start.
In September 1915 in Los Angeles, Shanin and Kobziv published their first songbook: Пѣсенникъ (Pesennik), По соглосiю Прыгунской Духовной Братстим (Po soglasiyu Prygunskoi Dukhovnoi Bratstim : By agreement with the Jumper Spiritual Brotherhood). In 1917, V. I. Holopoff, one of the pioneer migration scouts since 1900, entered his religion on a government form as "Brotherhood" with no room to write more; while the Pryguny identified themselves in a petition and letters to the US government as "Spiritual Christians-Jumpers." In 1917 an Arizona newspaper editorial stated: "Russian religious zealots, called Molokans, or Molokani, .. may be properly termed the Protestants of Russia. They call themselves Spiritual Christians." (Bold added) ("The Molokans," Bisbee Daily Review, June 14, 1917, page 4.)In 1918, American John Valov reported his religion as "Russian Spiritual Christian" to the Red Cross. This “Brotherhood,” in various forms, published the Dukh i zhizhn' in 1928, and is shown on government letters from 1940 through 1945 (Berokoff, Addenda XVII). After the 1940s the term "Brotherhood" was not used in print. Why? What changed? Fear and/or shame? After most Molokane relocated to San Francisco in 1906, a tug-a-war over the use of Pryguny occurred in Los Angeles as the younger Americanized generation adopted “Molokan” and/or abandoned their Russian faiths to be American, while a zealous minority trying to publish a religious text transformed into what became opposing and competing Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths, which lacked a label for over 75 years. The least zealous Spiritual Christians (Molokane, Subbotniki, Armenian Pryguny, etc.), who were marginalized by the more zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki, integrated(19) faster. The term Pryguny was apparently applied publicly to the most zealous, then nearly vanishes in favor of the terms Molokan and/or Russian Spiritual Christian, for all factions, or "Molokan Christian", and eventually to just the single term “Molokan,” with a broad general meaning specific to Southern California. The "Molokan" label was desired because is was unique, simple, and translated as “dairy-eaters,” probably to project harmless wholesome White Christian Protestant people (25) for the "White Spot of America," Los Angeles, "the best advertised city in the United States." It is strange that this is the only label that these Spiritual Christians insisted must be preserved in Russian transliteration, rather than the English "Dairy-Eater," or more common translation of "milk-drinker," while all other labels are translated, or transformed into more socially acceptable English forms — like "church" for meeting / prayer hall / assembly. ——————————————————————————— Publications Los Angeles Times (ADD CITATIONS) WW1 Objectors to Military Conscription In May 1917, a group of 261 men "sworn" under oath that they are "Spiritual Christians - Jumpers" (Pryguny) by an attorney, had a 3-page petition sent to the Russian Consul in San Francisco, and recorded in the County of Los Angeles. Notice (1) that they all swore a legal oath, and (2) they identify as "Spiritual Christian Pyguny".  This was posted on the Facebook page erroneously titled "Molokan Information" administered by because nothing is about Molokane in the San Fransisco, the Bay Area or northern California. Most all of the Facebook members are non-Molokans The first two pages are here https://www.facebook.com/photo? fbid=3114792018589308&set=pcb.3118136708275931 A copy was John Kulikoff in Los Angeles in the 1920s, who accurately informed reporters at the Prescott jail in Arizona:"The Holy-Jumpers are not Molokans. ... We are Holy-Jumpers. Molokans do not have the Spirit." (Only Blessed Bread For A Holy Jumper, Prescott Journal-Miner, August 10, 1917, page 5.) This was by one of the few journalists who understood and reported the actual religious identity of those arrested for not registering. The Prygun Review In 9 of the 10 editions of the misnamed The Molokan Review (1940-1949), a version of this title page appears in Russian. It was omitted in the last (1949) edition. Note how the organization is labeled printed in Russian.  A small photo of the U.M.C.A. neon sign is at the top, with the logo in the middle. Yes, it was lit at night glowing orange-red, which probably enraged the most zealoous tribes and helped inspire the prophesy that "the devil dances on the roof". Youth of several tribes were forbidden to attend any U.M.C.A. event until they conquered and dominated the organization after 1980. The sign and the prophecy were mostly forgotten in the 2000s. Next above is the Russian version of the organization name in big letters, and in parenthesis the real name. Объедининное Молоканское Христианскон Обшество (Духовные Прыгуны)Similar deceiving use of Russian and English continues today on signs and in print. Dukh-i-zhizniki habitually say one thing in English, and another in Russian, delivering different false labels for their faiths in each language, as if to appease different audiences, and themselves at the same time. 261 Spiritual Christian Jumpers opposed WW1 draft This petition was compiled by WW2 Letter to Russian Consulate, San Francisco ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Public signs Probably because their faiths were illegal in Russia, few of the "irrational" ("Mystical") category of Spiritual Christians from Russia would post a sign on a converted house used for meetings, or a dedicated assembly hall. Compare the side-by side meeting halls for Subbotnik and Romanovka congregations (Klubnikin, Podval) on Clarence Street in the "Flats" of Los Angeles about 1920. xxxxxx Insert Photos Few Dukh-i-zhiznik buildings in Southern California The false Molokan label probably began to first appear in public view in English on a main street in 1933 when "Big Church" was moved from the Flat(s) to Lorena Street. Signs at cemeteries also mixed the labels, but did not show Prygun or Jumper in English, only Prygun in Cyrillic (Russian). Since the 1990s several Dukh-i-zhiznik elders have been intentionally mis-reading the Russian term Prygun as Molokan in English to alter and/or fabricate a false history, to intentionally fool those who cannot read Russian. ——————————————————————————— "Big Church" After 1933, the label “Spiritual Jumpers” in English only remained in public view on the front sign (above) of "Big Church" (Bol'shaya sobraniya) facing Lorena Street. The building was the business office for the congregation, were records were kept, often used for membership meetings, funerals, and Sunday School. In the 1960s, I was shown a box of the paid membership was about 700 households. The Housing Acts of 1934, 1937, and 1949 funded urban renewal projects across the country. Los Angeles "Progressives" to In the 1950s is was the temporary UMCA, while the Gage avenue site was under construction. used for business meetings, some funerals, a https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1994_Northridge_earthquake https://www.earthquakeauthority.com/About-CEA/CEA-History The building was demolished about 2000 because it was not earthquake safe, and the congregation did not preserve their sign or label probably because they did not feel comfortable/safe with it in public view, and to gain favor with more zealous Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations in Southern California. But the sign on the larger meeting hall farther from Lorena Street lacked the phrase "of Spiritual Jumpers," as if it was a different faith. Perhaps in the 1960s the black letter metal sign on the assembly hall (First United Christian Molokan Church) was replace with a larger sign with white letters. Into the 1980s, the Russian term Прыгун (Prygun) remained on the first old cemetery sign (below, left), on 2nd Street near Eastern Ave, East Los Angeles. The "Old Cemetery" did not refurbish or replace their sign which misspelled dukhovnykh khristiyan prygunov (Spiritual Christian Jumpers) on top in Russian. In the 2000s, the younger zealot generation in Los Angeles explained to me that they are afraid to be "on display ... in front of the world." The format of the sign suggests that 2 different faiths, labeled in 2 languages, are combined in 1 display — Pryguny in Russian, and Molokan in English — though neither is correct. Since 1928, this had been only a Dukh-i-zhiznik cemetery reserved for the most zealous and honored Dukh-i-zhiznik members as determined by and serving a few congregations in Los Angeles county who did not want to mix their dead with those in the new cemetery on Slauson Ave, City of Commerce. ^ Contents ^ ——————————————————————————— Cemeteries
At the new Slauson Ave cemetery, the Prygun label only appears in public view in Russian on one metal (cast brass) sign (above right), but omitted in the English translation, again showing 2 wrong faiths displayed in 2 languages on 1 sign. The Russian says: Kladbische russkikh khristianskikh molokan-dukhovnykh prygunov (Cemetery of Russian Christian Molokan-Spiritual Jumpers). Contrary to the sign, this cemetery is recorded with the State of California as “Russian Molokan Christian Spiritual Jumpers Cemetery Association, Inc.” Using the words Molokan and Prygun together is like saying dog-cat or banana-apple. Which do you really mean, or do you mean both? In reality neither faith controls this cemetery. It was purchased about 1939 and controlled only by Dukh-i-zhizniki. There are no congregations of Molokane or Pryguny in Southern California, and if there were, they would not be allowed to buy a plot at this cemetery today because only dues-paying members of the official "mother churches" of Dukh-i-zhizniki apparently can buy a plot; however one may be accepted if they testify/ or prove that they were christened in a Dukh-i-zhiznik ceremony, and have a lobby of front row elders petition for their burial. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Sign in Suzdal, Russia In 1997 and 1999, two American Dukh-i-zhiznik preceptors independently published photos of a monastery jail dormitory museum sign in Suzdal Russia, showing where Maksim Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) stayed from 1860 to 1877. Morrie Moses Pivovaroff (Kerman CA) made a video of his July 1997 heritage tour to retrace Rudomyotkin's life. In 1999 Daniel H. Shubin (then in Shafter CA) published a photo of a similar sign he took during his similar heritage tour to Russia in September 1997. Both deceptively presented and/or claimed the Russian word Prygun is read/ pronounced as Molokan in English, as if they intended to fool non-Russian readers. It's as silly as teaching that the pronunciation/ translation of the Russian word sobaka (dog) in English is koshka (cat). What else have they lied about? While videotaping the room in a Suzdal monastery prison dormitory where Rudomyotkin allegedly slept, Pivovaroff pointed his camera to a small sign on the outside wall next to the door which clearly read: Начальник сектов молокан Семён Шветов 1835-1844 гг.My Russian-born Molokan wife Tanya says these 2 lines could not have been written by a Russian, because 3 words are obviously improperly conjugated. It appears that the Pivovaroff brothers, or their assistants placed the small sign which then incorrectly copied from inside a glass display case near the entrance of the museum complex. Shubin photographed the actual sign in the glass display case later that year (photo below). The correct Russian is: Начальник секты молокан Семён Шветов 1835-1844 гг.While videoing their hand-written sign, Morris M. Pivovaroff falsely narrated that his "Molokan" martyr Maksim Rudomyotkin stayed in this [dormitory] room which he could not not believe was "so nice". Their sign says: пригунов, genitive plural for пригун : prygun. Russian literate viewers could see in the video image that he misread the sign and ignored the Molokan man shown on the same sign, 1 line above, as Semyon Shvetsov. Pivovaroff graciously sent me his video, and I replied with many corrections on a list marking the time and error for him to edit. I do not know if any of my suggestions, maps and data were edited into the final version of the video intended to educate his family. Later the same year (1977), D. H. Shubin took a photo of this sign (above) at the same monastery previously visited by Pivovaroffs, which Shubin published in 1999 on page 2 of his Guide to the [Book of the Sun,] Spirit and life with Supplements (253 pages). The image above shows most of page 2 of Shubin's Guide (facing the title page 3), with the sign enlarged to clearly show that Shubin's caption in English clearly misrepresents the Russian text in the photo. ^ Contents ^
The Russian text translated to English: Elder chief/ head of the skoptsy sects, Kondratii Selivanov, 1820-1833. In the photo caption, as published
above, the label prygun for
Rudomyotkin is obviously omitted. In his Guide
Shubin presents no data about molokan leader
Shvetsov nor about Spiritual Christian skoptsy,
rather focuses on Rudomyotkin, whom he intentionally
falsely claims is of a different faith than what is
posted on the museum sign or shown on official
archival documents which Shubin reproduced and
translated 13 times in his chapter 7. Throughout his Guide
Shubin repetitively mis-guides his readers by
extensively using a false label in his first 6
chapters (pages 1-87), and last 3 chapters 8-10
(footnotes on pages 159-253).
Among the 68 pages of Shubin's translated archival documents from Russia regarding Rudomyotkin (chapter 7, pages 88-155), the term Prygun(y) (пригун(ы)) appears 13 times; and the term molokan appears only once as an error, added in small handwritten script on the last document (pages 154-155), a death notice.* All these Russian records report that M.G. Rudomyotkin was a Prygun, and the "chief spreader(24) of the 'Spirituals' (o dukh : о дух) or 'Jumpers' (prygun) sect in the Caucasus" (pages 90-91). * If one reads the death notice literally, that upon death Rudomyotkin abandoned his Prygun faith and converted to the Molokan faith, as edited, then all his writings must be edited to show that at the end of his life he accepted the Molokan faith as better than his own Maksimist faith, and abandoned his "new rituals" to accept the Molokan rituals and holidays. Therefore his published writings in the 1928 Kniga solnste, dukh i hzizn' and his prayers would be void, and his followers must do the same. Or, you can accept that the word Molokan added (written) in small script was a mistake, a clerical error. The added word should have been prygun, based on all the previous documents shown in chapter 7.In contrast to the archived documents published from the Russian archives about MGR, the text in Shubin's Guide shows the term "Molokan(s)" 108 times, including 18 times joined in phrase (Molokan Jumpers), compared to Jumper(s) appearing separately only 3 times (pages 5, 34, and 51), ignoring the archival documents. In the discussion text and footnotes, the authors of the Spirit and Life are falsely presented 36 times more often (108/3 = 36) with the wrong faiths than their actual faiths — 97% of occurrences (108/111 = 0.973). Also, the Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life is mentioned 76 times, and Rudomyotkin 487 times (333 by name, 154 by "MGR" citation) nearly twice per page (487/253=1.93) on average. Shubin's Guide overwhelmingly shows the intentional false labeling of Rudomyotkin by Shubin, contradicting the Russian records shown in the same book. As is, Shubin's Guide misleads his target English-speaking Dukh-i-zhiznik students with extensive labeling bias, translations, and irregular and missing citations; and lacks a comprehensive index. These errors could be corrected in a revised edition. More valuable to the serious student of M. G. Rudomyotkin wold be a line-translation showing (1) Readers beware! Are these 2 Dukh-i-zhiznik teachers (preceptors, front-row speakers, bearded elders) — Pivovaroff and Shubin — intentionally misleading their students, confused about their religious history and identity, both, or something else? Their own evidence shows they are blind to the real identity of their spiritual leader, their history, and mislead their students. ^ Contents ^
4. Is Molokan one faith, many faiths, an ethnic group, white people from Russia, or an unclassified Slavic nationality? Answer: Historically sort of all of the above, depending on who is using or misusing the terms, when and where. The context of the terms should help readers to interpret which meaning is implied. After a century of misuse in North America the Russian term “molokan” has unfortunately lost it's original meaning in most contexts, which must be restored to make sense of the history of Spiritual Christians around the world and to intelligently discuss them. It's like saying only in Southern California and Oregon, in Australia, Armenia, and eastern Stavropolskii krai, Russia, dogs are cats; but in Northern California, Azerbaijan, Ukraine, and parts of southern Russia (western Stavropolskii krai, Rostov, eastern Krasnoraskii krai) dogs are dogs; and in the United Kingdom they are "pooches". Actually, many words are like that. Why is that? I think it's because the composers of Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' did not know enough of their history to know the difference, or accepted and repeated Dr. Pauline Young's incorrect history, or did not want to know the difference, or did not want to discuss the issue, or needed to hide their actual mixed faiths, or were emotionally and/or intellectually incapable of dealing with these facts, or something else — or all of these reasons. In Old Russia, Molokan was a single, non-Orthodox religion — the original faith (Definition 1, below). The word was sometimes used to describe any sectarian (Definition 2) or anyone suspected of having sectarian characteristics (Definition 6). After 1900 in Southern California American English, it was falsely broadly used to label all immigrating non-Orthodox (sectarian) faiths from Old Russia and their descendants,(109) an ethnic group and a different family of religions that opposed the Molokan faith (Definition 4). After 1930 these mistakes were transferred from the U.S. to the Soviet Union and Turkey (now Türkiye) where the most zealous expanded it to label themselves a non-Russian nationality (Definition 5). After about 1980, the most popular definition in Southern California and Oregon was falsely narrowed to mean only the Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths (Definition 3). The misuses and abuses of the "Molokan" term are very confusing and should be corrected to correspond with the original meanings properly used in the 1800s and earlier, before the label and original identities were corrupted in North America and exported. And the term Dukh-i-zhizniki should be used when referring to the many diverse faith tribes that use the religious text: Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' (Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life). This seems like a simple solution, unless you are a zealot, or commanded by zealots, indoctrinated with a false history. 6 Definitions used for the term "Molokan"
^ Contents ^ Ty chey? (Ты чей?) Ty chey is Russian for: Who are you? (and your
parents, and uncles, and grandparents ... ?) This is a
common greeting among Spiritual Christians from Russia
in America. I was asked this by xxxx (in-progress) The wide and long-term misuse of the words "malakan/
Molokan" produced broad-spectrum religious and
political arguments about "who is a malakan or
Molokan." A liberal(18) use allows anyone, whether of descent from the Former Soviet Union or not, to mistakenly declare they are “malakan or Molokan” though they may be descended from a mixture of nationalities, intermarried, joined another faith, water baptized, atheist, served in the military, eat pork/or and oppose the faith of their ancestors. It's almost like saying: "On St. Patrick's day, everyone is Irish," or: "At the malakan / Molokan Picnic, everyone is malakan / Molokan." In other senses, the word is as confusing as American Indian, who are not from India, may be on 2 continents (North America, Asia), and comprise any of over 500 tribes (bands), each with their own dialect, land and customs. People from all walks of life and faiths dress up in refined Russian peasant clothes standardized in America, and parade as "Molokans" at a gathering, then go home, take off the clothes and transform back to their American, or Australian, national identity. The show is over. Similarly in Australia, many Dukh-i-zhizniki speak the English language with an American accent at home, and Australian accent among Aussies. Many of the most zealous conservative(18)
extreme users of the Kniga solnste, dukh i
zhizn' only consider “their” (наши : nashi) people, or
selected members of “their” congregation and closely
affiliated congregations, who profess their own
group-accepted beliefs, behaviors, and appearance, to be
their mistaken version of "Molokan." Outsiders are
forbidden, or bullied, no matter how they dress or talk,
who their father is, even other Dukh-i-zhizniki.
Between these extreme population definitions, about
5000 households in the U.S.A. and Australia (~20,000
descendants, assuming 4 per household) were willing to
be listed in an English language unpublished 1985 Молокан Directory,
though more than half were neither practicing Dukh-i-zhizniki nor Molokane by faith. People falsely
affiliated with the "malakan / Molokan"
label should be several times larger than that estimate,
in the year 2000, perhaps 60,000+. For the current
relative populations in the Former Soviet Union,
multiply by at least 10 up to 100 times (1-2 orders
of magnitude). Because zealots protested that ne nashi
(outsiders) were listed in the mis-titled 1980 Молокан Directory,
in the mid-1980s, an unreported census tally of American
congregants was attempted by William Alex Federoff,
editor of the U.M.C.A. newsletter for 30 years with his
sons. He was the only person who sent me a letter
stating he did not want his name or family listed in the
1980 Directory. He gave no reason, but when the
book was first distributed at the grand opening of the
Resident Center in Los Angeles, Federoff briefly
confided with me that he wanted to be listed in the next
edition, after realizing his blunder. Within a year, to
satisfy zealots and himself, Federoff proposed that the
next directory should only list nashi, Dukh-i-zhiznik
congregation members in good standing, not anyone who
wanted to be listed, especially those unclean (nichistye
: нечистые) people who
married out, eat pork, joined other faiths, served in
the military, etc., even though their parents were
members and they have a Russian surname. He requested
membership lists from all congregations, probably to
print his own directory, was rejected by most
congregations and the project was halted. When I asked my father, the presbyter in Arizona, for
his list of paid members, I learned that only a few of
the many adherents (attenders) ever paid annual dues,
because the most zealous majority officially claimed
that they, by their tradition, did not believe in
"membership" or worldly lists. Maybe they just did not
want to donate, as many
did not pay their CPS fees during WWII; while they
invoked their family tradition by stating that the Book
of Life is a spiritual list known only to God. Due to
competing temporal and spiritual fears that government
will intervene among the variety of Dukh-i-zhiznik
faiths, it is probably impossible to ever systematically
collect a census list, hence all population counts are
somewhat educated guesses. Section in-progress: Return to Ararat versus Cherbak's Russian University
-> The Southern California The molodoi sobranie (youth meeting, "Young Peoples
Church") was initiated During the 2000s in Southern California the most
zealous congregations, led by the Novaya Romanovka
congregation (former Freeway sobranie), purged
the Hacienda Heights U.M.C.A. of clubs, youth socials,
closed the Heritage Room and sold most of the extensive
library collection. In 2017 two new competitive
directories were published, one by the nashi,
now spiritually clean U.M.C.A., and one by the ne
nashi, the Heritage Club. This social division
began in 1940s with the formation of the Y.R.C.A. (Young
Russian Christian Association) in 1938 on Mott Street in
Karakala, opposed by the molodoi sobranie (youth
meeting), in the Utah-Clarence street alley at Zegrap sobranie.
implicit associations between ingroup/outgroup Many YRCAers, initially led by BIOLA graduates William
John Samarin and Alex Patapoff, were invited in the
1940s, when Samarin's father was U.M.C.A. president, to
organize a Sunday school. Soon Samarin married out, and
became a Brethren missionary in Africa, leaving his
buddy Patapoff in charge. The U.M.C.A. grew for over 20
years, into the 1960s, to become the 3rd largest Sunday
School in California and 10th in the nation.(80) During this time the most zealous Dukh-i-zhinik
families forbid their children from ever stepping onto
the grounds of the UMCA, due to a prophesy that the
"Devil danced on the roof" of the U.M.C.A. I suggest
that this prophesy about a devil was probably inspired
by the UMCA
neon sign, above the entry at the roof, lit at
night in a dark ally. A tipping point occurred in the 1980s due, in my
opinion, to the Heritage Club giving away scholarships
with no requirement of support for the UMCA or any
community service. Several of the former YRCAers believe that "agape love
gifts" must have no strings attached.
Molokane and Pryguny in the Former Soviet Union
have no trouble listing members, keeping log books, and
some post a membership roster on their assembly wall.
Many Dukh-i-zhzinik congregations now keep a
private (secret) membership roster to contact members,
and a donation ledger to maintain their non-profit legal
status to avoid taxes. ^ Contents ^ ——————————————————————————— "Can you be malakan
(Molokan) and Christian at the same time?" This seemingly silly and ironic question was discovered
in the early 1970s by Mike M. Podsakoff, Fresno,
while attending the U.M.C.A. summer camp at Hume
Lake, Fresno County, in the Sierra-Nevada
Mountains. Podsakoff grew up in Fresno, and moved
to Los Angeles when he got an athletic scholarship to
play basketball. He was hired to be Athletic Director of
the L.A.-U.M.C.A. (Gage Ave.) where I first met him in
the late 1960s. In the early 1970s, the L.A.-U.M.C.A. added more
classrooms and the very popular club attendance nearly
stopped during construction. To boost attendance for
eligible singles, about 1974 Podsakoff founded what
became the "Our Gang" singles club, for which I did most
of the promotion. The club was such a success, that I
was hired to be U.M.C.A. Athletic Director, and
Podsakoff was appointed to the Recreation Committee with
Willie Steve Evseff (Alhambra CA) as chairman, and Jay
Kalpakoff (Huntington Beach). We worked well together,
and disbanded when the UMCA board refused to pay me $20
for mopping the entire gym floor sticky Easter candy for
5 hours, which the UMCA janitor refused to do. They were
angry cheap lazy people. During that time, Podsakoff told me about what appeared
to be a paradox. He recently discovered a
question that always immediately divided people, in
Kerman or in Los Angeles, young or old, into 2
opposing groups. Half answer yes, half opposed,
and they debated. He said it was hilarious to watch
because each time he got the same results — divide and
debate — which did not make sense at the time. Podsakoff's instructions:
This paradox proved to be a fascinating repeatable
experiment revealing social
polarization. We performed the experiment several
times in Los Angeles. Each test confirmed Mike's
previous observations. Whatever the group was talking
about stops, they divided into "for" and "against"
Molokans being Christians, and discussed their
differences, often passionately, as we backed away
grinning. An extra irony is that none of these people in
Southern California were Molokane. How could they always disagree about being Christian,
and why? About 50 years ago Podsakoff proved this social
polarization existed, but could not explain it. I
basically understood the division, had no vocabulary to
explain it, and did not further investigate because I
did not know how. Today, I can explain this
paradox. Podsakoff found a litmus-test
in which the Dukh-i-zhiznik population
immediately self-classified into 2 groups — (1)
practicing (religious), and (2) social-cultural (secular).
Which group was correct? They both were. Each had
different polar points of view on many dimensions. For
dimension examples, see Variety of Dukh-i-zhizniki. The "Podsakoff paradox" can easily be explained using
this Taxonomy to define the American Dukh-i-zhzinik
division.
Both polar kinds mixed at the L.A.-U.M.C.A. in the
1970s in approximately equal numbers. The most
assimilated stopped attending the U.M.C.A. a generation
ago. The 2 groups (social and practicing) did not clash much
because before the 1980s the U.M.C.A.s in Los Angeles
and Kerman were self-forbidden ground for the most
zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki. The social-secular
Christian faction, many of them Y.R.C.A.-ers ("Jack
Greeners"), dominated as teachers in Los Angeles since
1938. There were some who could straddled both realms,
like the late "Little Al" Shubin, but in limited scope. During the 1970s, Mike Podsakoff, like many, was
bothered by the lack of Christian behavior at the
U.M.C.A.s and among most of their "Mother churches."
Many who grew up among Dukh-i-zhizniki and gave
years of service at the U.M.C.A.s were attacked for
being "too American Christian." At least one was
ostracized, many were verbally attacked, and many
voluntarily left to join "American" churches which have
credentialed pastors, professional management, and often
affiliated with large religious organizations. If tried in San Francisco, the Podsakoff Paradox could not be duplicated. Real Molokane would not divide and debate. Those asked would probably all stare at the person asking the silly non-sense question, and/ or say: "Of course we are all Christians;" and, probably give the questioner a lesson in Christianity. Podsakoff also summarized the amateurish management of
our Dukh-i-zhiznik communities with honest
humor.
^ Contents ^ Zealots feared the Gage Ave L.A.-U.M.C.A. Before 1980, the most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki
never entered the L.A.-U.M.C.A. grounds (Gage
Ave, East Los Angeles) because of their prophecy
that the "devil danced on the roof."
Children of the zealots would gather on Eastern Avenue,
across from the west U.M.C.A. parking lot entrance on
Gage Ave, to socialize among themselves while not
disobeying their parents' orders to not step inside the
fence. Drinking vegetarian* beer and wine was common,
evidenced by the many bottles left on the curbs and
thrown in the parking lot. I helped U.M.C.A. President
Paul Zolnekoff fill half a large 30-gallon trash
container with bottles and cans one summer after
Wednesday Chai Night.** Every few months a car
radio/stereo was stolen, a car antennae broken,
marijuana and/or cigarettes smoked, and used condoms
discarded. A few guys with hot-rods (fast cars) would
peel out or burn rubber on the street, rather than go
inside. Once I witnessed tire smoke fill the assembly
hall from Jack "Yashka" Kalpakoff's car, from Kerman,
because he spun his tires at the main entrance in the
parking lot.
Whenever a Dukh-i-zhiznik zealot would accuse the L.A.-U.M.C.A. of indoctrination (being a "church" or teaching American Christianity), it was denied; and the timing of L.A.-U.M.C.A. services did not dare overlap with Dukh-i-zhiznik congregational services. The L.A.-U.M.C.A. ended Sunday School just in time for families to attend their "mother churches."* Most parents dropped their kids off, and some would have breakfast at a cafe while waiting. I've been told by several L.A.-U.M.C.A. officers that about half the families that frequented the L.A.-U.M.C.A., only attended the L.A.-U.M.C.A. and went home afterward, while the "practicing" half of Dukh-i-zhizniki took their kids to their "mother" sobrania, to which they paid dues. A few also attended American churches on many Sundays to hear sermons in English, and/or listened to sermons on TV and/or radio. Though the most zealous branches of Dukh-i-zhizniki historically objected to the U.M.C.A. komitet, they were politically placated by offers to join the Religious Committee, which was said to remotely control the organization via participation of recognized elders, most seated at altar tables (prestol) in a "mother church."
The religious-political balance shifted when the
L.A.-U.M.C.A. (Gage Ave) was sold (mainly due to fear of
Mexicans*) to purchase the current H.H.-U.M.C.A. (Stimson
Ave, Hacienda Heights) in a White area (72)
in their axial eastern sector,
radiating closer to the new neighborhoods of the 3rd and
4th generation in eastern Los Angeles County. Families
who moved south
of Los Angeles were confronted in the 1970s with
neighborhood integration facilitated by the Housing
and Community Development Act of 1974 (sections 8
and 109)
by which people
of color began moving into their white suburbs,
resulting in a White-flight
within Los Angeles County, and to Orange County and
Oregon.
In the 1980s, the more zealous practicing Dukh-i-zhizniki
who wanted an exclusive private school for their
assimilating grandchildren, began forcing their more
civil social (secular) brethren away (as many joined the
new Heritage Club) from the H.H.-U.M.C.A to dominate the
property, and eventually purged their newly acquired
territory and grammar school of perceived heretics. A
series of intense purge attacks occurred to assure that
the "Jack Greeners" (Heritage Club) and anyone who
supported, or appeared to support, the new "Re-Formed" (Prygun)
movement in Oregon, would stay away, or be secondary
guests, to their new social
order within the property. The new H.H.-U.M.C.A.
became nearly a totally "spiritually clean" place, void
of a "devil dancing on the roof,"
and Dukh-i-zhiznik zealots could appear with
little or no stigma. Sunday School attendance dropped by
90% from its peak in the 1960s. Clubs and Hume Lake
camps were banned. Youth were now required to wear kosovorotki
(boys) and kosinki (girls) as as Dukh-i-zhiznik
Here's testimony from a fellow who grew up in a mixed
marriage, and was persecuted by American Dukh-i-zhizniki
for being ne nash and at school for being
Russian. He questions the hypocrisy of his father's
heritage faith, and abusive Christians anywhere. Between
two worlds and outside both, by Rasputin's love
child, ExChristian.net (7/22/2009), 42 comments. (Backup
copy.) Such abuses are more common than he knows.
The
mistaken use of the term "Molokan" for an ethnic group
or nationality must stop and be restored to the
original term (dukhovnye
khristiane, Spiritual
Christian), or the pejorative
category term used by the Russian Orthodox Church (sektanti,
sectarian). The Russian word Molokan
should only refer to members
of the registered faith. Since 1980 real Molokane
are not allowed to join the H.H.-U.M.C.A. ^ Contents ^
5. Three Faiths Today This is a summary and review to facilitate identifying major factors of 3 of the Spiritual Christians faiths — Molokane, Pryguny and Dukh-i-zhizniki. For more detail, see 11. Classification below.
Less than 1% of Molokane have ever witnessed charismatic religious jumping, and fewer have seen or read any part of the book: Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn'. If allowed to attend a Dukh-i-zhiznik service, Molokane are fascinated, from a distance (often disapproving), of zealous Dukh-i-zhiznik spiritual jumping, raising hands, shouting, forced jumping, prophesy, verbal bullying, using non-Biblical ritual books, and singing songs from other faiths, and non-Biblical songs with Russian and American folk-melodies. In contrast, Dukh-i-zhizniki accustomed to their fast shout-singing, jumping, prophesies, and mystical theatrics are typically bored among reserved Molokane limited to the Bible and slow singing with no physical aerobics or spiritual and mystical outbursts. These are very different faiths and cultures. Unfortunately one pretends to be the other (by label), fooling themselves and outsiders. In the Summer of 1992, a 30-year anniversary of the 1962 resettlement of Old Ritualists and Spiritual Christians from Kars Turkey (now Türkiye) to Stavropol territory, was celebrated in the town of Novokumskoe. Local government funded the event which was covered on local TV news. Two simultaneous separate outdoor meetings were held for the old-Orthodox and non-Orthodox. The old-Orthodox (Nekrasov) held open services, a parade, and performed religious and folk songs and dances in colorful dress which appeared on local TV news. Spiritual Christian Dukh-i-zhizniki from Türkiye dominated the non-Orthodox meeting and meal, with no parade or performances. All Molokane in Russia were invited. When the newly elected senior Molokan presbyter, T. V. Shchetinkin, arrived from Kochubeevskoe, he was not recognized any more important than a common "guest" and seated in the third row. Years later, after studying the Dukh i zhizn', and meeting others who opposed Molokane while insisting that they were the true Molokane, Shchetinkin declared that the tribal elders who did not recognize him, yet insisted that they were the real Molokane, were actually not Molokane, and were not members of the Union of Spiritual Christians — Molokan Unfortunately Shchetinkin had no label for those imposters. Now you have an accurate label: Dukh-i-zhizniki. ^ Contents ^
6. New Label : Dukh-i-zhizniki The new label Dukh-i-zhizniki fills a large linguistic gap. In the 1910s through 1930s, their ancestors in Arizona and Southern California created a new family of faiths but not a new term for it. In 2007 a new practical and unique label using the popular short title of the religious text Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' — in short: Dukh i zhizn' — was created (coined, minted) — Dukh-i-zhizniki. Translated from Russian, it means "people who use the Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life." or "users of the Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life". The unique precise word Dukh-i-zhizniki cannot be confused with any other family of faiths in the world that do not use this specific religious text. It's a distinct descriptive term, somewhat similar to saying in English that "Mormons" use the Book of Mormon. If Dukh-i-zhizniki around the world want to agree to use a different term, they are welcome. So far they cannot all agree on the label Maksimisty which referes to believers in the divinity and second-coming of Maksim G. Rudomyotkin. Rudomyotkin's writings comprise about two-thirds of the book. Readers not familiar with the Russian pronunciation can practice on these rough transliterations:
The Slavic suffix -nik, is common in Russian, and should be familiar to many readers. For examples:
I am a bit embarrassed to admit that I did not think of using this obvious suffix for this taxonomy. For two years, since 2005, I periodically asked my Russian-born Molokan wife Tanya(105), and a few Russian-born friends of ours here in Arizona who helped me with translations, to suggest a Russian word for these faiths that they knew very little about, but relied on Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn'. One day in 2007, after a moment of inspiration, Tanya said: Dukh-i-zhizniki. It was the perfect Russian word. Ни чево себе! How appropriate, and simple, to create a new word in order to describe newly invented faiths based on a book title. After thinking about it for a week she said it must have hyphens to not be confused with other Russian terms. This word was so obvious and exact. Why didn't anyone think of it before? Many immigrants got upset with journalists who called them "molokans" instead of Pryguny. Some of these confrontations were published before 1930. Why did so many not understand that they were not molokane? I think mainly because the simple mama-like(22) word Molokan was exclusively used by Demens and others to camouflage the immigrants and present them as white Christians. In 1905 a group of about 30+ well-dressed, literate, Molokane also arrived and were on the ship to Hawai'i where Demens intensely promoted them as actual Molokane, though with them were more non-Molokane. After leaving Hawai'i in 1906, most of the Molokane stayed in San Francisco. In the 1920s Drs. Young continued the deception, adding a contrived misleading history to the 1928 Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn', about which apparently few complained. (See list of newspaper complaints that Pryguny are not Molokane — In-progress) Though I am not a native Russian speaker, I knew many Russian and English words with the "-nik" suffix. The more I said Dukh-i-zhiznik, and thought about it, the more I liked it. Then I had to update 100s of webpages. That's applied linguistics in action. In high school I was told that much of science is just learning the vocabulary. Without a word you might say thingy, doodad, gizmo, and in Australia thingamabob or whatchamacallit. Maybe Dukh-i-zhizniki would prefer to be called: whatdyecallems. The Dukh-i-zhiznik label was field tested in Russia. In the Summer of 2007, all Spiritual Christians that I interviewed in Russia accepted the new term when presented with a list of all Spiritual Christian congregations in the world, including their congregaton. Congregations that used the Dukh i zhizn' did not chose the identity labels molokan, prygun or dukhobnie, subbotnik, or sukhoi baptist from a list of congregations in the FSU. No one said that they they preferred to be called something else, like “our people” (Russian: nashi : наши) or “believers (in the Dukh i zhizn)” (veruschy : верушы). And, congregations that did not use the Dukh i zhizn' did not identify with a book that they never saw or used. It was clear to me that this was the most exact word, easily understood by all Spiritual Chrstians groups of all faiths that I could contact. I expect that most Dukh-i-zhiniki will continue the false label due to habit. The major problem with Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations was how to separate them when many are divided in one village or town. Like in America and Australia, they often use several nicknames to distinguish their group from neighboring congregations, or the congregation that they split from. Many Dukh-i-zhizniki treat other Dukh-i-zhizniki as separate heretic faiths. During my extensive travels, I only encountered 3 zealous congregations, all in Stavropol'skii krai that shun all but members of their own congregation. Two would not let me talk to them. In America several congregations behave with similar exclusivity. I have been told the same avoidance behavior exists in Armenia among neighboring Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations. Us-Them The inside-outside (us-them) distinction is typical among many peoples around the world. For one example, members of a native North American tribe used the autonym Nēhilawē ("those who speak our language") to identify themselves, but among outsiders they used the white man's label: "Cree." In Arizona, what outsiders call Navajo Indians, members call themselves diné — "people of the earth" and "man." When no Molokane are nearby, Dukh-i-zhizniki tell outsiders they are Molokane. Other terms used by journalists for Dukh-i-zhizniki include "Old Believers", “extremist” and “maximalist.” Some call themselves Maksimisty (Russian for “followers of Maksim (Rudomyotkin)"), but not all Dukh-i-zhizniki are Maksimisty, and many despise that term. Some call themselves Davidisty (followers of David Yesseich), noviy israil' (New Israel), and/or sionisty (zionists). All alternate labels were rejected in 2007 in Stavropol province, Russia, in favor of their common identity with their religious text, called in short the Dukh i zhizn', hence: Dukh-i-zhizniki. If they have not already discovered it, English-speaking Dukh-i-zhizniki who study this "Taxonomy" can learn that many other religious and social movements around the world have used and are using the labels "New Israel", "Zionist", and "New Jerusalem". For clarity using those terms without explanation for self-identity can be confusing for outsiders, and young people who use the Internet to search for those common terms. If you search for "Dukh-i-zhiznik", you will find that no one else in the world claims that identity but your kinds of people. Perfect. Awesome. Cool. Groovy. Far out, man. Hunky dory. Ginger peachy. ... In the U.S. and Australia the term Dukh-i-zhizniki is new, strange and too exact for those who were indoctrinated since kids to hide from the worldly pork-eating non-believers. For these and other reasons, which they are afraid to reveal or cannot explain, many naive Dukh-i-zhizniki will probably continue to falsely mislabel their faith and institutions as “Molokan,” or “True Molokan,” though history shows that they are not and never were Molokane by faith. Most will continue to say my/our “Molokan faith/religion" unless probed to reveal their actual secret faith, as was done with John K. Berokoff by Dr. Pepricorn in 1968. It may take a generation or more (2050+) to establish this accurate term : Dukh-i-zhiznik. The irony is they claim they want religious freedom, but only to be freely dishonest with their identity, and/or to deny or insult the freedom of others. No elder of a congregation is brave enough yet to openly discuss this error, or change their congregation and organization titles or descriptions. Most in the West are blocked with fear and shame, which causes some to be angry that they have been involuntarily outed with an accurate label because they lack confidence of being accepted as a "normal" Protestant faith, given all the facts. These three religions (Molokan, Prygun, Dukh-i-zhiznik) have a common origin with other folk-protestants from Russia — Anabaptists, Russian sectarians, Spiritual Christians; iconobortsy (iconoclasts) —, they all use the Russian Bible with Apocrypha; and pray, sing, and read in Russian; dress or appear somewhat similar; but their history, locations, genealogies, holidays, rituals, liturgy, services, songs, and openness vary significantly and separate them into distinctly different faiths. Members within and between congregations today may be relatives, neighbors, friendly or unfriendly, intermarried, yet differ in behavior and belief, sometimes hostile and/or secretive. If a marriage is allowed between members of these denominations (or an outsider), one usually must convert to the faith of the congregation performing the wedding, then tolerate scrutiny, or abandon their heritage faiths. During the past century, most chose to entirely or partially abandon their heritage faith(s), mostly due to the confusions explained here. ^ Contents ^
7. Analogies
This section is for Dukh-i-zhiznik readers indoctrinated with the wrong terms, or convinced that whatever their grandfather or elders said, must be correct, without question. Scholars and journalists also take heed. A comparison of several classification systems below illustrates how honestly choosing a simple descriptive method and words greatly aids understanding which group is which. As Christians you must decide for yourself how deceptive you want to be with the identity of your faith(s). In other words, as a Christian you must decide how much you want to lie. The same goes for scholars, journalists, and all other faiths. 1. Cars — To argue ownership of the brand-hijacked label "Molokan," some Dukh-i-zhizniki boast that they are the newest model of Molokane, like a modern car compared to an antique. Therefore they are the best, most advanced. Some say they are the "True Molokans." They omit, or forget, or did not know that their religious predecessors were from many different faiths, tribes and nationalities, and should claim to be improved, newer, or different versions of non-Molokan faiths. Anyway, they say the Molokane are like the Ford Model-T (1908-1927) that never modernized — steadfast, unchanged, original. But what happened to the Model-T? In 1928 Ford Corporation upgraded to Model -A, and competitor Chevrolet emerged as a separate company (faith) with faster cars (like Pryguny) which used Buick parts (borrowing from other faiths), produced many newer models with automatic transmissions (Malibu, Impala, Camaro, Corvette, Tahoe, Suburban, ... like Maksimisty, Sionisty, etc.) which are like the many divided faiths among the new religious movements of Dukh-i-zhizniki. We recognize these as “cars” (Spiritual Christians) but each model is different in parts, shape, performance, and attracts different buyers (members). Why don't people who own electric or hybrid cars call them Model-T's because they are the newest most modern version? Why aren't all cars called Model-T's? Why can't you just get one car part to fit all cars? This may sound silly, but Dukh-i-zhizniki still call themselves the antique term Molokane, which they never were, nor were most of their ancestors, while hiding their actual original terms (Davidisty, Noviy israil', Pryguny, Sionisty, Khlysty, ...) Why don't they call themselves by earlier labels before Molokan : Dukhobortsy, Iconobors, Orthodox, Bogomils, etc? Why didn't they choose their own new and improved name? Because nobody thought of it before. 2. Fruit — What if all "fruit" was locally called apples, and each tribe in the world only had one kind of fruit which they called "apple" because it was the only word they had, or knew, for fruit? They did not know the word "fruit." In the tropics a tribe had long curved yellow apples (bananas). In Hawaii their apples were huge grown on spiny bushes (pineapples). In the Republic of Georgia their apples are thin skinned and orange (tangerines). In central Russia their apples are green (simirenko). Each tribe did not know about the others and only one word was needed as long as they remained isolated in their regional village, and did not travel or see imported fruit. But in the large import market in Europe, where fruit is sold from around the world, each species and type of fruit needed a different name to tell them apart. If the tribes refused to learn the international terms, they had problems communicating and trading. If they wanted a banana or grape, they would have to describe which kind — the long yellow curved apple, or the small round juicy apples in a bunch. When describing fruit, this seems silly, but it is the way most Dukh-i-zhizniki want to be identified — with a variety of terms and descriptions, not a unique word. This above reminded me of how people who spoke a pidgin English dialect first described what you call a piano. I found a book published in 2017 (100) that cited 10 various examples of how people who never saw a piano named it in their own language.
3. Middle Asia — "Middle Asia should not be confused with the Central Asia or Inner Asia." The maps show that different definitions include or exclude vast areas of Asia depending on who is writing and when (Russian Empire, Soviet Union, United Nations, Islamic tribe, professor, etc.) and their topic (ethnicity, geography, religion, language, history, climate, politics). The various terms from different languages describing this territory have vastly different overlapping meanings. Which name is correct? All are correct to the writers, but the readers can easily be misled if they do not know what area was actually intended by each writer, expecially when no map is provided. When Maksim G. Rudomyotkin wrote about Tika (his "land of refuge"), he most likely referred to the area which was originally generally called "place of the Turkic people's" or "Land of the Turks" («Туркестан», Turkestan). The Persian name is Turan: "the land of the Tur." In general it meant land East of the Volga. As more knowledge was documented and dispersed in maps and books, and people were educated, it should be easier to specify this area. Yet, many mistakes are easily made unless a map is provided. 4. Jews — 1000s of books and articles have been published debating "Who is a Jew?" Dukh-i-zhizniki consider themselves somewhat Jewish, eating kosher-like, sharing somewhat similar Old Testament holidays. Changing the word "Jew" in the introductory text of Who is a Jew? (edited in Wikipedia.org, see archived text 2005) to "(ethnic) Molokan" produces a broad awkward statement no more definitive of "ethnic Molokans" than for "ethnic Jews": Who
is an ethnic Molokan
Curiously, substituting a few words in the description of ultra-Orthodox Haredi Jews, a fair description for Dukh-i-zhizniki is generated: Dukh-i-zhizniki areDukh-i-zhizniki differ from Haredi in that owning a prosperous business is a socio-religious status — being blessed with wealth. (Israel Prods Ultra-Orthodox to ‘Share Burden’, New York Times, June 6, 2013) 5. Mennonites — "Mennonite" is also misused, and almost a useless term because there are more than 60 varieties. Let's pretend we know which variety is meant. By changing the word "Mennonite" to "ethnic Molokan," changing "church" to "assembly," adding "informal affiliation" and decreasing the numbers in the summary text of Mennonite, Organization Worldwide (Wikipedia.org, archived March 14, 2018), another awkward definition results which gives the reader no better resolution than the original term: "Spiritual Christian." The most basic unit of
organization among Molokans
An Anabaptist historian advises: “... it is meaningless to use the
same term ‘Mennonite’ to describe differing spiritual
traditions whose fundamental values were often in direct
conflict with each other ... it will be necessary to use
hyphenated terms.” (101)
This Newspeak
process (social control by language reduction) was coined
by George
Orwell in 1949 to describe a repressive society,
characteristic of Dukh-i-zhizniki.For the most part, there is a host of independent Mennonite churches along with a myriad of separate conferences with no particular responsibility to any other group. Independent churches can contain as few as fifty members or as many as 20,000 members. Similar size differences occur among separate conferences. Worship, church discipline and lifestyles vary widely between progressive, moderate, conservative, Old Order and orthodox Mennonites in a vast panoply of distinct, independent, and widely dispersed classifications. For these reasons, no single group of Mennonites anywhere can credibly claim to represent, speak for, or lead all Mennonites worldwide. The most basic unit of organization among ethnic Molokans Instead, there is a host of separate assemblies 6. Romani people are not one tribe of "gypsies" but people who appear to have left India about 1500 years ago, now dispersed around the world speaking many languages, and divided into many types far removed from their origins. So which group is which? ^ Contents
^
7. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints — Most outsiders call them "Mormon" not L.D.S. because they use the Book of Mormon and its simpler to say — similar to "ma-ma"(22). Let's change Book of Mormon to Dukh i zhizn' and see if that analogous definition makes sense: The Word of God
Missionaries are not handing out copies of the Dukh i zhizn' Book of Mormon all over the world, even as you read this. So what is this secret book? If it’s given out for free, why do so many Dukh-i-zhizniki members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints count their Dukh i zhizn' Book of Mormon as one of their most valuable possessions? What kind of book can cause so many readers to change their lives, their minds and their hearts? What kind of book can answer life's seemingly unanswerable questions? The Dukh i zhizn' Book of Mormon is the word of God, like the Bible. It is Holy Scripture, with form and content similar to that of the Bible. Both books contain God's guidance as revealed to prophets as well as religious histories of different civilizations. While the Bible is written by and about the people in the land of Israel and surrounding areas, and takes place from the creation of the world until shortly after the death of Jesus Christ, the Dukh i zhizn' Book of Mormon contains the history and God’s dealings with the chosen people who lived in Erivan governate the Americas between approximately 1850 and 1877 600 BC and 400 AD, and their descendants [who faithfully wait for Rudomyotkin's return.] ... Most Dukh-i-zhizniki would probably agree, though many disobeyed Maksim Rudomyotkin by leaving Armenia (Erivan governate), with the above text while insisting they have nothing to do with the false faith of L.D.S., or any of the 666 false faiths that Rudomyotkin warns them to avoid. Dear readers, this is just a comparison. In contrast with L.D.S., Spiritual Christians in/from Russia had no missionary program for the past 100 years, though their oral histories report that many converted up to that time. In America, there are several families of Dukh-i-zhizniki who joined the L.D.S. church and today call still themselves Molokans. In the mid-1970s, a widowed Mormon woman joined the L.A.-U.M.C.A. Ladies Auxiliary, was elected president and honored as "Mother of the Year" — Jean M. Popoff-Batchkoff (1922-1990). Her sister Pearl (Parasha) married Maksimist Mike S. Tolmachoff in Arizona, and most of their kids moved to Australia. 8. Pancakes — How can one explain and describe pancakes (olad'i), waffles (vafli), and crepes (bliny)? Are they three different things, three kinds of pancakes, or are they all the same single thing? Or, in secret, are they 3 types of bliny? The first is a breakfast dish, the others were designed to be desserts. Do they really need different words? Pancakes, olad'i, are the original version of a thin fried batter bread, flap-jacks, johnny cakes. But original Russian olad'i are small and thick, and in America they are a different huge thinner pan-cake. The same batter ingredients can be modified, the form enhanced in a mold, cooked on both sides with impressions, and made thicker and more intricate, but it no longer looks or feels like a pancake even though the batter is nearly the same. Why are those called waffles, vafli, and not pancakes? Add a little milk, kefir, and/or buttermilk and the same batter can be cooked into very thin versions. Those are called crepes, bliny, with many varieties. Are these also pancakes, waffles or something else? Should bliny claim the title of pancake because they are the most varied — rolled, folded, stuffed with many fillings — and so sacred and fancy that they should not have a name? If they are all basically the same material, why not one name for all? If you called bliny waffles, or waffles pancakes, would you be telling the truth? In this sense, olad'i, vafli, and bliny, are as different as Molokane, Pryguny and Dukh-i-zhizniki.
What if you asked for blintsy with tvorog (dry cottage cheese), varenia (jam) and smetana (sour cream), but got oladiki instead? You'd probably get a similar reaction telling a Dukh-i-zhiznik that Pryguny and Molokane in America celebrate Christmas (Rozhdestvo : the birth of Jesus Christ), or most American Jews do not eat kosher (koshur). ^ Contents ^
9. Pizza — To be fair to debaters, here's another classification example. Though similar to pancakes (round, flat food), pizza is named differently, as a class with sub-classes. If you ask for pizza, you need to specify schema and subschema — bought (fresh or frozen) or home made, brand name, size (small, medium, large, ...), thickness (thin, thick, ...), shape (round, pan), ingredients (many toppings) and style (deep pan, cheese in crust, pretzel crust, ...) — 1000s of possible combinations. Such a multi-variant classification system is useful among neighboring diverse Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations, each distinct from the others. In contrast Molokane and Pryguny do not vary much among congregations 10. Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations — Because Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations tend to be clustered but separate and fragmented, members identify them (somewhat like pizza above) with a combination description of location (state/province, city, district, street), original village, presbyter, former congregation and/or nickname. In contrast, there are no cities/villages in the world with divided Molokan congregations (except Novokumskoe, Stavropol territory, R.F., after 2005), so they are simply identified by current location (state/province, city/village). The 3 remaining Molokan congregations in Tbilisi cover different regions of the metropolis and often co-meet. To simplify the naming of Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations in Southern California in the 1970s, the persistent (postoyannie) editor of the U.M.C.A. newsletter, W. A. Federoff, announced his own new naming system — by street only. Federoff argued against what he considered vanity surnames (Buchnoff, Nazaroff, Mendrin, Samarin, Shubin, etc.), archaic village labels (Akhta, Melikoy, Romanovka, Prokhladnoye, etc.), all modifiers (Big, Old, New, Persian, 605, Blue Top), and would only use what he considered to be "neutral" street names. He enforced his new rule by only publishing his new labels in "his" newsletter. So what my babuniya (grandmother) Shubin called her Akhtinskii sobranie, and most called Samarin sobranie, Federoff re-nick-named "Percy street church," which is now called "Pioneer street church" after moving to Whittier from Boyle Heights. Bolshoe sobranie and "Big Church" became "Lorena street church." Now a generation later, most all Dukh-i-zhiznik youth are trained to use the current street nicknames for their "churches" and never learned they were actually meeting or prayer halls (assemblies) with historic village roots. The American street labels erased part of their semantic Spiritual Christian heritage from Russia, hence reducing identity with the Russian Empire and language, replacing Russian terms with local American geographic markers. Eric Arthur Blair would be proud. I sincerely hope this Taxonomy will encourage historically misguided youth to restore Russian identity back to these mislabeled Spiritual Christian faiths in their generation. The zealots, of course, will resist proper nomenclature. ^ Contents ^
11. Indigenous peoples — In America the native peoples were mislabeled Indians because early explorers thought they arrived in India. In Australia the natives are called aborigines (Latin: from the original). Outsiders (ne nashi to natives) use these 2 simple words to refer to 100s of distinct cultures with different languages. The people among themselves have 100s of words to accurately identify their tribal/band members and other tribes/bands. With a little education anyone should learn to identify the few faiths of Spiritual Christians in North America and Australia. 12. Defining "cancer"— In March 2012, the National Cancer Institute met to evaluate the problem of “overdiagnosis.” Problems were identified and recommendations made to the National Cancer Institute for consideration and dissemination. On 29 July 2013 the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) released 5 recommendations. The second suggestion was widely broadcast in the news: Change cancer terminology based on companion diagnostics. Use of the term “cancer” should be reserved for describing lesions with a reasonable likelihood of lethal progression if left untreated. There are 2 opportunities for change. First, premalignant conditions ... should not be labeled as cancers ..., nor should the word “cancer” be in the name. Second, ... remove the word carcinoma.” ... revise the taxonomy of lesions now called cancer and to create reclassification criteria ... (Overdiagnosis and Overtreatment in Cancer: An Opportunity for Improvement, JAMA)Science-health reporter Lisa Aliferis immediately summarized this news for KQED, PBS Northern California (Cutting Down on Cancer Overdiagnosis: National Panel Weighs In, The California Report: State of Health, 29 July 2013.) Her section sub-headings apply to this taxonomy as I illustrate here:
My wife Tanya, formerly a medical doctor in Russia, was surprised to hear that American medical staff call benign tumors "cancer." In Russia there is no such confusion caused by mislabeling tumors. Similarly in Old Russia, before immigration, the variety of Spiritual Christians accurately labeled themselves, until touring reporters, journalists, colonization agents and social scientists got involved. Though most were trying to help these peasants immigrate and assimilate(19) and/or make a commission for themselves, in the process they misunderstood and scrambled the identities of the immigrants, ignoring how the peasant defined themselves. Now the descendants (most of you readers) of those immigrant peasants are still confused. Conclusion Many classification examples come to mind. Hopefully the above analogies will illustrate, to even the youngest and/or least educated readers, how choosing the right words can most accurately define these 3 different Spiritual Christian faiths. By following the KISS-principle, the classification system chosen is simple, so each Spiritual Christian religion has a unique one-word original descriptive Russian label, historically known around the world — Molokan(e), Prygun(y) and Dukh-i-zhiznik(i) — ; and all are part of a larger group called dukhovnye khristiane (духовные христиане : Spiritual Christians). These 5 words are all you need. If the Dukh-i-zhizniki in Los Angeles county, who falsely call themselves Molokans, remain isolated in East Los Angeles county, never attend services in San Francisco or the F.S.U., only rely on the Dukh i zhizn' and oral tales for history, they can easily believe they are whatever they called themselves within their own closed society. The same applied for those isolated for decades in Türkiye and Armenia. Their hijacked definition can continue as long as they isolate their congregation from education, media (newspapers, books, Internet, TV, radio), outsiders, all worldly contact. If you are one of "them" and have been reading this taxonomy, you are now contaminated with new worldly information — oops — ;-). Don't tell the guy sitting next to you in sobranie, he might insult you, or chase you out. See complaint letters (to be added). ^ Contents ^
8. Diaspora "Molokan" myth label created by 2 people The variety of different Spiritual Christian faith tribes beginning to arrive from Russia in Los Angeles in 1905 were soon all falsely called "Molokans" for simplicity. Who did this? All evidence points to 2 very educated influential people born in Russia, who lived in Los Angeles and invested more than a decade each trying to help these immigrants — Captain P. A. Demens (1850-1919) who initiated the cover up, and Dr. P. V. Young (1896-1977) who continued it. They never met, and worked on different goals at different times. Demens was most active from 1898 to 1910, about 15 years before Young arrived from Chicago in the mid-1920s to enter graduate school at the University of Southern California (U.S.C.), where her sociologist husband accepted a teaching position, and both remained as professors, retiring in the early 1940s.
^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Captain Peter A. Demens (1850-1919) Russian name: Pyotr Dement'ev, Пётр Дементьев, pen-name: Tverstov English name is pronounced "de-MENS". Research in-progress.  Demens'
involvement with Spiritual Christian colonists from Russia
in North America was extensive for at least a decade,
beginning about 1898.with Dukhobortsy. Luring
Spiritual Christians from Russia to Los Angeles instead
of Canada appears to have been his idea and personal
project. Demens'
involvement with Spiritual Christian colonists from Russia
in North America was extensive for at least a decade,
beginning about 1898.with Dukhobortsy. Luring
Spiritual Christians from Russia to Los Angeles instead
of Canada appears to have been his idea and personal
project.Demens appears most responsible for first falsely and widely presenting in English that all Spiritual Christians from Russia who migrated to Los Angeles were one group of "Molokans," despite many immigrants from Russia self-reporting upon arrival that they were a "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians," and later groups reporting that they were Pryguny and other faiths. When he arrived in America more than 20 years earlier, Pyotr Dement'ev quickly learned to simplify his name as Peter Demens. He did the same for this mixed crowd of immigrants. No matter who or what they said they were, he chose the simplest label: "Molokans". It was easy for Americans to say and spell. And he embellished them with a glorious description. Among the first to arrive in 1905 were about 35 educated middle-class Molokane, who did not present themselves as the more numerous rural village peasants arriving in different groups from many different zealous faith tribes, who were not Molokane. The major traits these Russians shared among each other and with the Dukhobortsy who arrived 5 years earlier in Canada, was they were not Orthodox and not wanted in Russia. A small group of about 34 educated middle-class Molokane decided to settle in San Francisco in late 1906 after leaving Hawai'i.. In Los Angeles Demens was known as a credible Russian expert because he was from Russia, was fluent in English, was the only local Russian correspondent for the Los Angeles Times newspaper, had a letter signed by President Theodore Roosevelt certifying that he was the volunteer immigration agent for all "Molokans" coming to the United States(Xxxx citation), and made several trips by train to New York to personally greet and escort groups of arriving "Molokans" to Los Angeles, often arranging their fares. After Demens died in 1919, the false "Molokan" label for all Spiritual Christians from Russia in Los Angeles was later spread in newspapers and reinforced in the 1920s by Drs. Young, a husband and wife pair of experts at the University of Southern California. Due to Mrs. Young's publications and lectures, the false "Molokan" label was widely spread, until corrected by this Taxonomy. Before the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians from Russia arrived to settle in Los Angeles in 1904, there was xenophobia (fear of too many strange immigrants) among civic leaders and the Chamber of Commerce who extensivley advertised for "pious Anglo-Protestants." Probably due to prejudice against Slavic immigrants and American Holy Jumpers, Demens strategical chose the shorter unique and false code switched label (Molokan), rather than the English "dairy-eater" or any other English terms, to help dispel fear and doubt about the announced huge immigration wave to Los Angeles of thousands of illiterate poor peasant Eastern Europeans. In Russia and America, Demens developed bold salesmanship skills. Using his talent to persuade people, he defined the immigrants in his own terms, whitewashing(25) them for promotion as one huge group of
He needed to convince and impress the upper-class White supremacists and racists — The Establishment — that these immigrants are the cheap "white labor" needed to replace non-white labor, and will not threaten the upper-class. They will soon become ideal citizens. Mostly self-educated, Demens innately understood salesmanship and marketing 70 years before Elmer Wheeler was teaching American business to "Sell the sizzle, not the steak." He successfully Actually, these incoming immigrants from Russia were neither one faith group, nor all desirable, and many were religious fanatics; but there was a group of about 35 real Molokane among the mixture of early arrivals (perhaps from Manchuria) who were educated, not peasants, well-dressed (neck ties, coats), shaven and very presentable to upper-class White Protestant Americans. Demens was only available to embellish real Molokane for about one year (1905) in Los Angeles before the cultured group of authentic Molokane chose to resettle in San Francisco, after returning from Hawai'i by August 1906. For about 4 more years, he and others from Russia — mainly Cherbak, Treibcheb, Bartlett, and de Blumenthals — tried with some success to help the non-Molokane, the more zealous Pryguny, Maksimisty, Klubnikinisty, Sionisty, and other Spiritual Christians from Russia who chose to return to or remain in Los Angeles. Because Molokane were vastly outnumbered by tribes and other divisions of non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians, they may have never held an actual Molokan prayer meeting in Los Angeles. Molokane have never held a prayer meeting in Los Angeles since before January 1906, then they went to Hawai'i. In America after that time only mixtures of immigrating non-Molokan, non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians, most from across the Southern Caucasus, Russia, tried to reform into congregations. These early congregations merged and divided many times, with groups and clans from different faiths mixing — a historical mess never sorted out. In early 1906, while a group of Spiritual Christians was in Hawai'i, Demens went to Russia as a special correspondent for the New York Times to interview government leaders and report about the new freedoms for religion and land reforms. When he returned to Los Angeles he devoted another 5 years after the Hawai'i failure and division to get them jobs, education, and rural land. Many worked in his businesses (wood mill, commercial laundry, citrus farm, soap factory) and at businesses he recommended. While very busy with other projects, Demens compiled a report, published in 1910 in the Russian newspaper Tikhi Okean, pulished by Anton Cherbak, detailing why and how the Hawaiian experiment failed. (Scanning and translation in-progress.) Also that year Cherbak failed to unite all Spiritual Christians in North America into a large agricultural colony. Extensive news articles announced they were to buy about 50 square miles of land near Santa Barbara. Both Demens and Cherbak, neighbors in Alta Loma, gave up trying to help the Spiritual Christians from Russia in Southern California. Demens then focused on his family and businesses. Cherbak moved to Berkeley and worked with Molokane in San Francisco. Due to a bride selling scandal in Los Angeles from 1912 to 1915, about half of the Spiritual Christians fled the city to try to form rural colonys. So far I have not found evidence that Demens further aided the fragmented discordant Spiritual Christians after 1910, to his death in 1919. Demens was perfect for the sales task of promoting immigrants from Russia. He was Russian-born, educated, spoke 4 languages, well-traveled, well-read, impulsive, aggressive and successful in business, politically active, and a prolific writer (Russian and English). His family was well connected in Los Angeles society. The oldest of his 5 kids was presented in local sports news as a star high school football player, who then attended the University of Southern California (U.S.C.). The Demens' house in Los Angeles was within walking distance of U.S.C. His wife Raisa and their 3 daughters were active in women's clubs. Peter Demens was THE local pundit about Russia in Los Angeles, mainly reporting for the Los Angeles Times, interpreting foreign politics, culture and war. Though born and christened Orthodox, his humanitarianism was probably Tolstoyan. He knew Russian and American culture, and was most eager to help guide his fellow countrymen to immigrate. He was not shy to ask for help from government and the most wealthy tycoons, and often got it. Demens was born in central Russia. Both of his parents died when he was a child, and he was raised by his uncle and aunt (mother's sister). He was educated in St. Petersburg, joined the military, married, and tried farming (lumbering) and politics in Russia, but was not satisfied. While attending the 1878 Paris Exhibition he met a cousin who was living in Florida, U.S.A., who praised America and Florida. In 1881 Demens sold his land in Russia to move to Florida intending to farm, then invested in a lumber mill with the 2 founding partners in Longwood, Florida, 15 miles north of Orlando. He soon bought out his partners. In 1886 he was asked to manage the failing Orange Belt railroad which owed his mill the most unpaid debt for rail ties. To complete the railroad he solicited money from wealthy investors. Though many difficulties Demens is credited with building the railroad to St. Petersburg, Florida, which he got to name by "drawing straws". His company registered plans for the town, built the first hotel, railroad pier and train station. By 1888 when most work was complete, bills and investors paid, Demens profit was only $14,400 ($370,000 in 2015 using CPI ).(58) Demens also tried to be a politician by getting elected as the first mayor of Oakland, Florida, along the Orange Belt railroad, then unsuccessfully ran for state senate. Along the railroad path he named one town Odessa (after a town in Novorossiya, now Ukraine). In Florida he is now most memorialized as the one who named and co-founded St. Petersburg, Florida, and built the first railroad across Florida. Most of the 150 mile Orange Belt railway is now paved rail-rail for bicycling, hiking, etc. Demens had first-hand experience with discrimination, racism and nationalism on 2 continents. In parts of Russia, hatred for outsiders, dissidents and foreign faiths was common. In the U.S., he first settled in the Deep South where nationalism and bigotry towards outsiders and Blacks (Negroes) was most intense. Lynchings of Negroes was common, and Italians were also lynched. Many Americans considered Italians worse than Negroes. Demens must have learned that American Whites hated non-whites (coloreds) and foreigners, especially immigrants from south-eastern Europe (including Bolshevik Ruskies). After completing the railroad to the pier on Tampa Bay, he was weak with exhaustion, and afraid he might catch a tropical disease like his partners. A physician prescribed a long rest in a resort area. He moved to Asheville, North Carolina, near mineral springs and the Vanderbuilt's vacation Biltmore Estate, still the largest privately owned house in America. There he built another planing mill, and a small mansion still in use by artists. He must have read a lot about booming California, and decided to go West to San Francisco where many Russians have already settled. Along the way, his daughter got sick, so they stopped in Los Angeles for a week rest, and never left. ^ Contents ^
Timeline of Pyotr A. DementyevHe was born in 1850, into a wealthy family on their estate in north-east Tver Oblast, Russia. Both parents died before he was 5 years old. He had no siblings, and was raised by his mothers sister and her husband. In 1860 he began school in St. Petersburg, and entered the military in 1867. About 1871 he resigned from military to private life. He inherited 2 estates between Moscow and St. Petersburg. As a teenager he supervised more than 30 "servants" (perhaps freed peasants) and managed the family forests and lumber business. He married Raisa and was active in local politics, critical of Tsar, and due to a scandal was exiled from Russia. At the 1878 Paris World's Fair, he chanced upon a relative who already moved to Florida, U.S.A.. In 1881 at age 31 with about $3000, he alone visited the U.S.A. and Florida, studying English during the trip across the Atlantic Ocean by steam ship. He shopped around for opportunity, and decided to continued in the lumber business in central Florida, in the town of Longwood, 15 miles north of Orlando, where he bought a third share in a saw mill and a 80-acre orange grove. Then he sent for his wife and kids. They lived in a shack cabin with no ceiling, much poorer than he had in Russia. By 1883 he bought out his saw mill partners, and in 1984 he renamed his business. "P.A. Demens and Co. sash, door and blind factory ... was the major supplier of lumber and building materials for much of the area." Demen's mill supplied railroad ties to the Orange Belt Railroad, which ran through Longwood, past Orlando, to Tampa Bay, Florida. In 1889 he moved to Asheville, North Carolina, a resort town recommended by his doctor to rest, but again he began to buy and operate a wood planing mill. From 1891 to 1895, after an economic recession when prices were relatively low, he intended to move his family to San Francisco where many Russian immigrants lived. They stopped in Los Angeles, he decided to stay there. In the Los Angeles area he soon invested in a steam laundry in the Flat(s) and another planing mill, and used the profits to buy a citrus grove in Alta Loma (now Rancho Cucamonga), in west San Bernadino County, outside of Los Angeles City water-rights. From 1893 through 1898 an economic depression affected most of the country, most severe in the industrial east, caused by two related economic panics in 1893 and 1896. Though unemployment increased two to five times in various regions of the country, Los Angeles was not affected much until 1897, due to even growth, organized labor, independent businesses, a good wheat crop in 1893, and increased exporting during the Sino-Japanese War (1894-1895).(45) In October 1893 Demens attended the 2nd National Irrigation Congress held in Los Angeles for 5 days. Compared to the first congress, this event was larger, supported by the federal government, and attended by a broader variety of more than 500 experts, businesses, legislators, lawyers, and foreign delegates — the largest ever held in the world up to then. Discussions included proposals to federally fund the irrigation of the last available arid land in Central California, and west of the Missouri River east of the Rocky Mountains (eastern Montana, Wyoming, Colorado) for "settlement ... by Uncle Sam's bona fide children and none others ... there is bound to be a colossal accumulation of wealth in the irrigated belts ... the greatest civilization of this age ... ." Reports included detailed data on irrigation prospects in California and Arizona. 98% of potentially irrigable land in the U.S. was unused — about 1 million square miles. At that time " ... Southern California ... irrigation has shown the greatest results and developed more rapidly than in any other part of the world," which buffered the region from economic recession. Riverside was the wealthiest city in the U.S. due to irrigation. Demens recognized irrigation farming as a great opportunity for himself and other immigrants from Russia, who also bought farms near his, forming a Russian colony about 40 miles east of downtown Los Angeles. Demens' Russian neighbors (Cherbak, Krystofovitch, Tolstoy) will form the expert committee to aid the Spiritual Christians who will arrive a decade later, beginning in 1904. The Russian delegate to the 1893 congress was Count Constantin Comodzinsky, St. Petersburg, the representative engineer of the Russian government to the World's Fair held that year in Chicago, which Demens probably attended. Comodzinsky presented his paper: "Irrigation in Russia." After the congress he toured Southern California, probably with Demens who maintained many contacts in the Russian government with whom he networked on 2 later trips back to Russia, in 1896 and 1907. For decades Demens, under his pseudonym Tverskoi (meaning "from Tver oblast", his home province), submitted articles published in Russian and English language newspapers in the U.S. and Russia. For his Russian readers Demens promoted life in booming Southern California, where Progressivism dominated politics, and the economy thrived due to "location, climate and resources." For American readers he submitted editorials about Russia and Europe to the local press, particularly about the Sino-Japanese War and World War I. In the Summer 1895 Spiritual Christian Dukhoborsty burned guns simultaneously at 3 locations in the Southern Caucasus to protest war. Hundreds were arrested, thousands relocated, and hundreds died. Lev. N. Tolstoy intervened to advocate for humanitarian freedom for all Russian citizens, especially the persecuted heretics. Demens probably learned of Dukhobor tragedies from the news, his correspondence and Tolstoy's publications. In 1895 he published a book in Russia: America and the American System of Government, and in 1896 returned to Russia thinking he could help the Tsarist government. In 1898 he learned that Dukhobortsy were leaving Russia, and invited them to Southern California while sugar tycoons tried to invite them to Hawaii, but plans were already made for settlement in central Canada beginning in 1899 due to advice from Prince Pyotr A. Kropotkin. He was very disappointed that Dukhobortsy did not get a better place to settle than central Canada nor a government which kept its promises to them, which caused the zealots to protest. Demens only appears once in early Canadian Dukhobor history due to his protest to those coordinating the Dukhobor migration to central Canada, particularly Kropotkin; because all the historians and journalists focusing on Dukhobortsy in Canada missed the story that Demens was actively recruiting Dukhobortsy to the U.S. and 3 visited him in Los Angeles in January 1900, which was covered in the Los Angeles press. In 1899 Dukhobortsy were allotted 773,400 acres (1208 sq. miles) in what is now Saskatchewan where they built 61 villages. By 1930 more than 8,800 Dukhoborsty arrived, with 40+ Pavlovtsty. (Maps by Jonathan Kalmakoff, Doukhobor Heritage Website) In July 1899, 5 Italians were lynched in Louisiana for serving Negroes before Whites in a store. In 1900 Demens had house in Los Angeles at 3217 S. Grand avenue (near Jefferson), and by 1909 moved to 1149 W 28th Street (near Hoover). Both residences were about a half mile from the center of the University of Southern California (U.S.C.), which his kids attended. Demens main house was on his citrus farm, 40 miles east of Los Angeles, which is now a historic site. In mid January 1900 at his house on Grand Ave., in Los Angeles, Demens hosted 3 zealot scouts who somewhat separated from postoyannie dukhobortsy (later called Svobodniki : sovereign people) who were trying to leave Canada to the U.S.A. He escorted them to possible colonization lands and employment starting with sugar beet farming in Orange County, Southern California, then to ranches for sale in Central California, and north through Washington; lumbering jobs; and, sent them to homestead land agents in the Dakotas. He apparently began his next book when they left. Though the svobodniki separatists conducted several protest marches, which were covered in the press, especially when some people took off their clothes, none were allowed to migrate to the United States as a group. Many non-zealous Dukhobortsy did migrate into the United States as individuals, and many stayed, some living in colonies. See In December 1900, using his pen-name Tverskoy, Demens published a 109-page book : Saga of the Dukhobors (Духоборческая эпопея) in St. Petersburg, to inform Russians about the Dukhobor migration to Canada. He is sad that they are struggling in the snow on sparse land, and promoted California (35 times in the text), where he has lived for 8 years, and testifies that the weather and farming are great. He did not mention that only 1/3 of the most zealous, followers of Verigin burned guns in 1895, 400 arrested and jailed, and about 4000 exiled, as many as half dying due to starvation and sickness, before Lev. N. Tolstoy intervened with 2 open letters to the Tsar. About 7,400 of the 20,000 Dukhobortsy were sponsored to Canada which was aggressively soliciting immigrants as farming colonists to populate its central and western territories due to fears that the U.S. will claim territorial land in what is now British Columbia. To protect it's westward expansion, in 1885 Canada quickly built a railroad to the Pacific Ocean. In April 1900, international news and the 3 largest daily newspapers in California reported that 10,000 "Mollicans" in Russia, pending Tsar's approval, were ready to follow the Dukhobortsy to Canada — 35% more than the 7,411 Dukhobortsy who already arrived. A year later (July 1901) the number of "Molokanen" reported to be soon coming to America increased to 40,000. ^ Contents ^
About August 1900, when scouts representing non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians traveled to Canada, Demens was determined to divert this next wave of immigrants from Russia, away from Canada to Southern California. While their first "official" scouts (I.G. Samarin and F.M. Shubin) planned to join Dukhobortsy in Canada (Berokoff, page 19), the second group of "independent" scouts (Agaltsoffs, Holopoff, Slivkoff) were probably personally invited to Los Angeles by Demens, though Demen's name is absent from Berokoff's history.(Berokoff, page 20) In 1901 disgruntled Svobodniki in Canada began to protest against the newly elected Canadian administration which changed their immigration agreements. In 1902 they organized a well publicized march of 2000 (including many non-zealot Dukhoborsty) to complain against the laws of Canada regarding civil registration (birth, marriage, death, marriage), citizenship "oaths"* and government schools; and they wanted their leader P. V. Verigin to come from Russia, and/or for them to return to Russia. (* They did not know that affirmation could be substituted for oath.) Demens became very concerned that factions of Spiritual Christians in Canada were misguided by their advisers and complained to their guides and to Lev N. Tolstoy. He tried for about 5 years to bring them to America from Canada, but relatively few came. Some Svobodniki petitioned U.S. President T. Roosevelt to allow them to enter, but were not successful. ^ Contents ^
In December 1902, P. V. Verigin arrived in Saskatchewan, Canada from his exile Russia. In 1903, the first of many nude protests by zealous goli svobodniki (nude sovereign people) began in Saskatchewan, Canada. By 1918 Verigin announced that what immigrated as Dukhoborsty to Canada, were completely divided into 3 distinct major groups, and he asked for police protection against the "nudes" (injunction against harassment, restraining order) which was ignored or denied.
If the non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians would have chosen Canada instead of obeying Demens, many more could have emigrated with financial support from Canada for travel, large land allotments and military exemption for 99 years; but they would have to sign for their land as individuals, which they did with few initial exceptions in the U.S.A.(44) One can speculate about the possible interaction among the most zealous individuals from each immigration group if they all met in Canada. To understand the following speculative social humor you need to imagine combining the histories of zealot Spiritual Christians in Canada and California.
"By 1904, 1,600 motor vehicles cruised the streets of Los Angeles. The maximum speed limit was 8 mph in residential areas and 6 mph in business districts."(55) The Auto Club of Southern California was organized in December 1900, and began mapping roads in 1906. The Ford Model T began production in 1908. In 1905, zealous Svobodniki who split from Dukhobortsy were denied to mass migrate to California, though many later moved to the U.S. as individuals and some lived in Los Angeles, probably camouflaged as Malakane. In 1905, Demens learned that the next group of non-dukhobor Spiritual Christians from Russia were much more divided than Dukhobortsy, and a larger faction were zealots, more like the Svobodniki. Probably to appease worried government officials and to direct them away from Los Angeles, he pretended they were one group, with a simple label — Molokans — a single word, a snappy catchphrase, crisp, brief, and short. If he could have separated the immigrants, as he might have done with employees, into their own tribal and skill groups, perhaps he could have been more successful at managing them. But he probably did not have enough time to analyze them as they quickly arrived. Perhaps the more educated and better dressed Molokane, particularly John Kurbatoff, may have been recognized by Demens as most qualified to lead the first Molokan Settlement Association. Most of the arrivals were a different class than Kurbatoff's group, obviously peasants and illiterate. Politically, Demens probably realized that White Anglo-Saxon Protestants (W.A.S.P.s) would be confused to hear the truth, that these immigrants from Russia were mixed dukhovnye khristiane (Spiritual Christians) from Russia, similar to Dukhobortsy, mostly Pryguny, Klubnikinisty, Maksimisty, Pivovarovtsy with minor groups of Molokane, Subbotniki, Stundisti, Sionisty, Noviy israeli, and others, from up to 25 villages in 5 districts in Russia, who never met until they arrived in Los Angeles. To help the reported tens of thousands of incoming immigrants that he worked so hard and long to bring to Los Angeles, Demens needed to quickly dispel fears that they will overwhelm the city. He needed a simple marketing hook, and a plan to divert them away from Los Angeles to places where they were welcome in huge numbers. Demens accomplished an amazing feat. He convinced thousands of immigrants from Russia to avoid Canada for Los Angeles, to stay or be relocated to their choice of land(s) for their own agricultural colon(y/ies). In Los Angeles he organized a Russian-speaking immigration committee composed of at least 4 well educated and influential people already known and respected in Los Angeles (Konstantin and Verra Blumenthal, Anton Cherbak, Dr. Theodore Krystofovitch, and others). For settlement aid he got agent status in a letter* from President Teddy Roosevelt, and networked with local charities, especially the The Bethlehem Institutes (Bartletts). For financing and land procurement he solicited major bankers, land agents and tycoons in Southern California (I.W. Hellman, Senator W.A. Clark, H.E. Huntington, Donald Barker, ...). Demens preparation and salesmanship assured the civic leaders of Los Angeles that they will not be swarmed by the reported tsunami wave of immigrants, doubling the city population with not enough food or places to live. * I have not found this letter which was alluded to in the Los Angeles Herald, shown to the Governor of Hawaii, and reported in the Hawaiian news.(95)He was probably confident that his experience in Florida of hiring and managing thousands of workers to build a railroad, sea port, hotel and layout a new city adequately prepared him for this new task. No reason to panic. Take it one day at a time. Acting as a middle man, a negotiator, Demens lied and/or "stretched the truth." He had the knowledge and power to control public discourse about them, and created a positive altruistic rumor that they were all safe "Molokans," not svobodninki (mistaken for Dukhobortsy), not Russian Bolsheviks, not a pagan cult, not peasants who will need charity. He arranged contingency plans for diverting most to rural locations. The unconfirmed word "Molokan" facilitated making sense of a complicated scary situation. He needed to protect his immigrants as a group while dispelling their perceived threat and a potential panic by Los Angeles government. He undoubtedly knew that journalists would propagate the one-word, easy-to-pronounce rumor-term (Molokan) with his new definition. Notice 3 large strange new religious groups resettling in the U.S.A. and Mexico have similar labels that start with the letter "M" — Mormon, Mennonite, Molokan. Demens was a clever salesman. These 3 similar labels were sometimes confused in the U.S., Mexico and Russia. They were all strange new resettling Protestant faiths, 2 from Eastern Europe, that were spelled something like : M-o-n-..., whatever. Initially the press confused all of them in the U.S. and with Doukhobors in Canada. ^ Contents ^
Why Ma-lo-kan? The first syllable of Molokan (pronounced "ma") is among the easiest to naturally pronounce and most common sounds that babies around the world make, and is part of all adult vocabulary. In many Latin languages it means "breast." Such word origins have been extensively studied, and may have subconscious connections with "mother" in Russian and English.(22) Demens may have been sensitive to the acceptance of this "ma-" word in both languages, therefore he would not use a more complicated word or phrase to pronounce that might be more scary or imposing. The use of harsh-sounding words (like Prygun or dukhovniye) was not considered polite in upper-class conversation at the time of immigration to Los Angeles. The simplest, nicest-sounding, easiest-to-pronounce buzzword word was the best for promoting (marketing) the immigrants. Decades later, as their Russian language diminished, the assimilated and intergrated descendants of these immigrants may have internalized and expressed affinity for only this simple code-switched loan-word, instead of the English "dairy-eater," to the extent of excluding all historical and accurate alternatives, which may be harder to pronounce with more consonants, and have less emotional appeal (than "ma-ma")(22). This hijacked "Molokan" term could only endure as long as the population did not know, and/or believe, and/or propagate their actual history; and, their histories remained vague and/or obscured to journalists and scholars. Such propaganda works until the truth emerges, but continues among the uninformed and those who reject information that conflicts with their world view, perhaps due to confirmation bias. Beginning in 1905, Demens greatly simplified their acceptance by promoting them all as ONE group of soon-to-be law-abiding citizens, all-literate, cheap, strong, tall White labor, and ideal Protestant colonist settlers. To get them out of Los Angeles, or to divert them from coming to the city in large groups, Demens needed the most simple, unique and easy to pronounce brand identity. He knew he was using puffery by selling the "sizzle and not the steak." Though he sincerely wanted to help them, unfortunately they were too divided and soon appeared to be more like sizzle and fragmented burnt hamburger — not steak. In January 1905, when international news from St. Petersburg, Russia, reported that 200,000 "Molokany" were coming to Los Angeles, Demens' Russian welcoming committee got busy, probably urged by fears from local government and society that too many were coming. To assure the next batch of immigrants from Russia did not go to Canada, Demens apparently personally arranged transportation and escorted as many groups as he could meet upon their arrival at Eastern ports directly to Los Angeles. To divert the announce 200,000 from Los Angeles, arrangements with land agents, banks and the government of Mexico were made by Demens and de Blumenthal, also a former Russian officer, and his wife Verra who was well-known in California for raising and sending charity to peasant lace makers in Russia. Agents for Hawaiian sugar plantations with offices in in Los Angeles who did not get Dukhobortsy 5 years earlier, still wanted cheap White labor in Hawaii, and invited Demens to visit the islands in September 1905 where he pitched the incoming Russians as the best white labor to the territorial government and sugar plantations. Demens employed immigrants from Russia at his citrus farm in Alta Loma (40 miles east of Los Angeles), and in The Flat(s) at his lumber yard, soap factory and commercial laundry. He invested in a soap factory and commercial laundry, sold some of his interest while maintaining contact with the owners. He also counseled the Russian immigrants for other jobs and for land colonization. To assure support from government, Demens contacted President Teddy Roosevelt, and was appointed an agent of the President to assure that these Spiritual Christians who were fleeing Russia were not anarchists and get them settled quickly. Vice-president T. Roosevelt became president when President McKinley was assassinated in 1901 by an anarchist with Slavic roots. Demens presented the incoming Spiritual Christians from Russia as part of the needed solution to colonize the American West, to get them official immigrant status, and the best deals, like the varieties of mislabeled "Mennonites" (anabaptists) from Russia before them. The letter signed by President T. Roosevelt appointing Demens as the Molokan agent was mentioned in Hawaiian news, but has not yet been found. ^ Contents ^
In July 1905, I.G. Samarin and de Blumenthal began negotiations with attorney investor Donald Barker to first rent communal land in Baja California Norte, Mexico, with a guarantee of military and tax exception for 10 years, and passports for new arrivals. If enough immigrants buy into the commune at $50 per family, they will buy the land. Many of the immigrants had no identification papers. The Mexican contract only identified them as "Russian settlers" (colonos rusos), 2 times. They signed an initial agreement in September 1905 (10 days before Demens first scouted Hawaii) which was finalized 6 months later, in March 1906. In September 1905, Demens visited Hawaii, and returned to Los Angeles to help negotiate a contract with the immigrants and a plantation on the east side of Kauai Island. In November 1905 Demens escorted F. M Shubin and M. Slivkoff (2 kinds of Pryguny) to Hawaii and back, and praised the immigrants only as "Molokans." He negotiated their contract with the Governor, the immigration commissioner, and plantation owner's representatives; and submitted press releases by letter and telegram for publication. He used the "social media" of that time to promote these immigrants. In November 1905, Demens submitted a long (3 column, half page) article to Hawaiian newspapers sugar-coating the "Molokans" as the “cream of Russia’s population — a desirable class of White residents.” (See: Demens Introduces “Molokans” to Hawaii) Later he confessed that they were many different kinds of people who never met before they arrived in Los Angeles. In 1910, Demens published his extensive analysis about why the Hawaiian Molokan Agricultural Colony failed — to be translated and posted. Apparently at the end of 1905, scores of immigrant Prygun women in Los Angeles who were hired to sew overalls in factories were forced out of work by the emergent Garment Workers union No. 125. While established White workers were fighting for better work conditions and pay, new immigrant scabs were willing to work longer hours, in poor conditions for low wages. The peasants from Russia did not quickly join the labor movement, perhaps due to expectations of returning to Mount Ararat, or leaving the city to a rural refuge. Ethnic tensions against these cheap workers from Russia may have been expressed on the street, in public, for taking jobs from other immigrants. In January 1906, Demens reported all "Molokanes" will move to Hawaii, abandoning Southern California, but some reporters doubted that those with good jobs will leave. F.M. Shubin signed a letter boasting that 5,000 will arrive in Hawaii directly from the Caucasus, bypassing the U.S. mainland. Not clearly reported was that the large group bound for Hawaii became divided before they left, when Shubin decided not to return to Hawaii but to further explore land in Texas and Mexico. Shubin probably was still getting offers from railroad and land agents for free travel to see land. In February 1906 only about one-sixth (110 of ~700 who signed up for Hawaii, 16%) actually went on the first boat to Hawaii, of which about 34 (one-third, 31%) of the 110 were real Molokane led by John Kurbatoff. The rest were initially led by Prygun Mikhail "Mike" Slivkoff, then divided. The majority stayed in Los Angeles, where other zealots may have been anxious to earn money and return to Mt. Ararat, or another rural area (Mexico, Texas, etc). Shubin returned from Texas disappointed, then extensively scouted Mexico and most of the U.S., but resided in Los Angeles, later opposed the new religious text: Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn', and died in 1932. Both colonization groups (obschiny) in Hawaii and Mexico argued upon arrival, and tribal congregations remained divided. While the Mexico revolution was starting, taxes were imposed, border crossing was restricted, and life was more difficult than in Los Angeles slums. Land plots were allocated by lottery. Those who got the worst lots looked for better land nearby, while others tried to go to the U.S. Unfortunately, most who immigrated directly to Mexico were stuck, as new citizens of Mexico, with no U.S. passport or visa. Some who crossed the U.S. border illegally were arrested. Though Hawaii offered more total land than Mexico, settlers would be divided within and among islands, and a year's wait was needed to process homesteads in Washington D.C., which angered some who already got fast easy charity in Los Angeles. In Hawaii, the first 110 were offered about 8.2 square miles of irrigated homestead land for about $5.70 per acre (less than $29,000 total) in what is now Kappa, Kauai. That land is now worth ~$10 billion, ~$100 million/person. Since F. M. Shubin did not return with them, M. S. Slivkoff was the only "Moses" for the non-Molokane, while John Kurbatoff led the Molokane and the Molokan Settlement Association (M.S.A.). Two 2 kinds of Pryguny protested the M.S.A. forming 3 groups, probably with more dissent within the 3 groups. In Hawaii, on the day of arrival (February 19, 1906), the mother of a baby who died during the trip wanted to go back. It was hot and humid like a banya, and windy; bugs were everywhere. My first of 2 trips to Hawaii was to Kauai in February. As soon as we got to our car rental place and stood outdoors, my wife Tanya said: "It's like a banya." They arrived in Honolulu but refused to get off the boat, nor to eat a welcoming dinner hosted by a Protestant Christian church. The governor boarded their steam ship, greeted them and loned them a translator who worked for the territory. They arrived on Kauai Island in the late afternoon, were offered dinner but refused, and taken on small train cars to the Makee Sugar Plantation, were they transferred to wagons and carried up hill to the "Japanese camp," located on the north part of present-day Kapaa. Hungry, they sadly found that their camp shacks were trashed by angry Japanese workers ordered to vacate. Familiar vegetables for borshch (cabbage, red beets, tomatoes, potatoes, carrots) were not readily available which angered the women. Several men claimed their profession was wagon drivers (43) not farmers. Their above normal pay of $29/month was much less than some got at city jobs in California. Most were not the farmers Demens boasted they were. Many refused to work cutting sugar cane for a year until their land could be surveyed, irrigation provided to each parcel, and titles legally secured from the government. Some Molokane got jobs in Honolulu harbor, Oahu, which led to work in San Francisco harbor later. When the press questioned why they were divided into 3 groups, Demens replied in a well-publicized statement in Hawaiian newspapers that they were not all the same people, but came from as many as 25 villages in 5 districts in south Russia, and most did not know each other. The press joked that the word "molokaning .. (was).. synonymous with vagrancy." Many Hawaiians were glad to get rid of them while a few testified that some were worth hiring. ^ Contents ^
In March 1906, P. de Blumenthal and I.G. Samarin signed a resettlement agreement with the government of Mexico for military exception, visas and passports of all arriving Russian colonists. In April 1906 San Francisco is severely damaged by an earthquake after which for the military and charities provides housing and food for the homeless, and huge amounts of cash and material aid is donated and loaned, providing jobs for decades. In April 1906, Demens writes a long letter, published in 2 Hawaiian newpapers, ... XXXXXX In August 1906, within 6 months of arriving in Hawaii in February, all Spiritual Christians returned to California — most Molokane staying in San Francisco, and the rest (mostly varieties of Pryguny and other zealous sects) proceeding to Los Angeles. Records show that Demens knew most were not of the Molokan faith because many insisted to the press in Los Angeles that they were "Spiritual Christians" and/or Pryguny or another faith. Many professed Maksim Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) is their leader, which would become the focus of graduate student Pauline Young's masters thesis 20 years later. Throughout 1906 Demens and his Russian neighbors focused on the 1905 Russian Revolution, and by the end of 1906 he had arranged an interview with the new Russian prime minister Stolypin. In 1906, due to new religious tolerance in Russia, Peter Verigin, leader of communal Doukhobors in Canada, went back to Russia with 6 delegates (photo) to meet with Minister Pyotr Stolypin, who refused the meeting, while other other ministers negotiated the return of all Doukhobors to Russia. They were offered land in Altai krai and military exemption, confirmed by Nicholas II, but Verigin declined the offer and returned to Canada in March 1907. A few Doukhobor women who migrated to Canada while their soldier husbands were exiled to Siberia, were allowed to return to Russia to join their husbands. In July 1906 a new Immigration Act in Canada controlled and restricted undesirable immigrants, making it easier to deport them.(26) Government policy changed from economic to cultural. Zealous Doukhobors calling themselves svobodniki (sovereign people) protested against a rule change to take oaths, own land, mandatory government controlled education, harass Doukhobors and government, but are not deported. Some are arrested for public nudity. In mid-December 1906, The Los Angeles Times reported: "... Molokane [Spiritual Christians] are not desirable citizens.. many.. penniless.. cannot stay in Los Angeles.." 500 waiting in Texas are to be directed elsewhere. Thousands to leave Russia in May. A half-million acres (781 mi2) was offered to them in Sinaloa, Mexico. In March 1907, newspapers reported that 3,000 "Molokanes" wanted to settle in one large colony of at least 50,000 acres (~78 sq. mi) near Stockton, California, and that P. Shubin and N. Agalzoff were scouting a similar sized ranch in the state of Chihuahua, Mexico. In May 1907, the New York Times translated Pryguny as "Dancers": "... the Czar ... in 1904, issued his ukase insuring religious freedom to all, with the exception of the 'Dancers', ... " Demens could have read this article. In early 1907 Demens dropped everything to go back to Russia to meet Stolypin, his second trip since 1896. When he traveled through New York city, the president of the Associated Press news agency recruited him to be their new Russian correspondent. Demens conducted the longest (2.5 hour) interview with the new head of the Russian government (probably in July-August) which was published a few years later in the New York Times. He may have also met with Verigin and company in Russia. While Demens was in Russia, the John K. Berokoff family arrives in Los Angeles, when the Dukh-i-zhiznik historian was about 9 years old. Also in 1907, news of a mass immigration of 200,000 "Molokany" quickly dwindled in steps to a few thousand, about 1% of what was first reported. About a fourth of the incoming Spiritual Christians from Russia (mostly Pryguny) were diverted to Mexico, a fourth (mostly Molokane) chose Northern California after Hawaii failed, a few returned home to Russia. The largest fraction of mixed Spiritual Christians, with few Molokane, remained in Los Angeles slums, which would eventually became their new poly-ethnic enclave of "kingdoms in the city." What happened when Demens and/or Verigin were in Russia in 1907? Did they recommend to the government that the expected huge migration of non-Doukhobor Spiritual Christians to North America be stopped? Did Demens tell the Russian government that mostly varieties of Pryguny were coming to Los Angeles? If they will return to Russia, Verigin's Doukhobors were offered land in Altai province, as were Staroobryadtsy who already moved there. (Research in-progress.) In Spring 1907 Maksimist elders in Los Angeles reported they believe in the leadership of Maksim Rudomyotkin (1818~1877), expect his return soon to lead them to their promised land, therefore they will not remain much longer in Los Angeles. Newspaper readers could expect that 2000 immigrants will vanish as quickly as they arrived, which did not happen; nor did 200,000 more arrive from Russia as previously reported. Though Demens and associates tried to help the immigrants, it appears that the most zealous communalists who wanted to live in rural isolation refused their help. For those wanting to stay in the city, Demens provided work at his businesses or guided them to other jobs. Many girls were placed as maids and house-cleaners for the upper class, who got to know the immigrant girls personally. Numerous inexpensive electric street cars provided transportation. "September 1907: The Petr V. Ol'khovik family, along with forty "Yakutian" Doukhobors resettle to Los Angeles, California. One year later, the Ol'khovik family permanently resettles in Vancouver, British Columbia." (The Pavlovsty, by Jonathan Kalmakoff.) After 1908 a major urban renewal project cleared the Flat(s) of shanty slums, and new homes in "street car tracts"(27) were constructed which wage earners could afford to rent or buy. The poorest evidently moved south of the Flat(s), closer to a Demens' business to the cheapest dirt-floor shantys along Fickett street, a flood-prone gully south of Whittier Blvd (then called Stevenson Blvd) to 8th street. This area became Karakala which extended to Lorena Street. ^ Contents ^
Though 1000s of Spiritual Christians were directed and co-financed to Los Angeles, Demens and associates were partially successful in aiding their rural colonization. Only the Mexico colonies retained a large population probably because many were isolated in a rural valley for which each paid a $50 payment for a share, the remainder payable in wheat, with a 10-year guarantee of no military draft, and no import/export tariffs. Demens and associates tried very hard to help these immigrants for about a decade, but they were too diverse, resistant, some probably stubborn, and all efforts failed except giving them factory jobs. In 1909 Dr. Theodore Krystofovitch (Demen's neighbor, and a consultant to Lev N. Tolstoy about Doukhobor immigration) was appointed the first American agent of the Russian Imperial Ministry of Agriculture, with an office in St. Louis. Before Doukhbortsy left Russia, Tolstoy asked Dr. Krystofovitch for advice on where they should settle. Krystofovitch rejected Hawaii (too tropical) and California (too expensive), and recommended Canada for comparable climate and its chernozem soil. To get the Doukhbortsy, Canada paid for half of their travel expense, gave military exemption, free land, and supplies and food to survive the first years. He was first on Demens' immigration advisory committee to leave Los Angeles, but kept his farm next to Demens at Alta Loma, and later returned in the 1920s to teach agriculture at the University of Southern California (U.S.C.). At U.S.C. he translated segment drafts of Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' for Pauline Young, which were published in her doctoral thesis in 1929, and book in 1932. In 1910, Demens responded to an article by Dr. Krystofovitch published in the Los Angeles Russian language newspaper Velikiy Okean (Pacific Ocean), which accused Demens of taking advantage of the Spiritual Christians as cheap labor. Demens responded with a long article about how the movement to Hawaii failed (Тверской П. А. Инсинуаций и действительность (Insinuations and reality). Великий Океан № 10, 1910 — to be translated and posted). Velikiy Okean was published by Anton P. Cherbak who also organized and taught the Russian immigrant adult school he called "Russian University" at the Bethlehem Institution, and he tried to arrange for a joint purchase of a large tract of farm land in Central California along the coast for diverse Spiritual Christians to reestablish their own villages. During 1910, Spiritual Christians were confronted with their first federal census. The door-to-door canvasser probably agitated the most zealous. In 1920, oral history in Arizona reported that the women chased the federal census counters out of their Darichak village, along the street where the meeting house remains. Residents in the adjacent 3 villages were more compliant. At the end of 1910 a nationally publicized effort to provide a rural refuge for all Spiritual Christians in North America in a huge colony along the Central California coast ("near Santa Barbara") failed. It appears that H.E. Huntington may have arranged for a ~50-square-mile tract in or near the Santa Ynez Valley (Solvang), as many elders had requested. This offer was earlier arranged by Demens for breakaway Dukhobortsy who were not allowed into the U.S., nor out of Canada, in large numbers. Though Spiritual Christians collectively had the money, Cherbak reported 12 leaders confronting him resulting in the well-funded huge colony never starting. In July 2010, eight congregations in Los Angeles published a notice denying any relationship with Cherbak. Therefore, most of the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians stayed in the city, but not for long. It appears that about this time, after 1910, five years after the immigration wave began, Demens must have realized no more Spiritual Christians were coming from Russia. The previously announced huge wave of immigration did not occur for many reasons. Despite desires for rural refuge, most of the arrivals remained in Los Angeles. His help was no longer needed or wanted as city services and charities stepped in, and zealots protested efforts to arrange for a single large rural colony. In 1911, overcrowding in the city self-corrected when the huge concentration of varieties of Spiritual Christians transformed as their Old World culture continued to clash with the New World. In December 1911 a much publicized bride-selling scandal erupted and continued through February 1915, which scared many zealots — perhaps 1000, about half the population — from the city in groups to scattered destinations with apparently no inter-group coordination, and little, if any, guidance from Bartlett, Demens, Cherbak or the Blumenthals. For more than 3 years the "Molokan" label became nationally associated with "bride-selling." In 1912, the first publicized registered marriage (since 1904) occurred, while the most zealous in Arizona continued to not register marriages, births or deaths up to 1920 when 2 presbyters were arrested (1 jailed overnight) and fined $300 each. In September 1911, in Russia, Pyotr Stolypin was assassinated, 2 months after resigning as Prime Minister. His agrarian reforms (1906-1914) improved the economy into the 1920s when Soviet reforms reversed the economy. About 1911, Cherbak moved to the San Francisco Bay Area to work with Molokane and other Russian immigrants there while his family stayed on his farm next to Demens. The Molokan lad Vasilii S. Fetisoff became his aid and apprentice to continue publishing the Russian language newspaper. De Blumenthals returned to Chicago. Only Demens and Bartlett remained in Los Angeles to assist the immigrants, but most by now did not want anyone's help, and about half fled the city. From 1911 through 1914, Demens shifted his focus from volunteering to help uncoordinated immigrants to managing his own business, getting railroad access for himself and other farmers in Alta Loma. He lobbied the Central Pacific Railroad to divert 2 miles north from its straight line path from Upland to San Bernadino, which added 3 miles of track to serve his farming district. To offset the extra cost for the railroad, Demens arranged to buy the rights-of-way and raised $19,000 from local businesses and farmers who will benefit. For his volunteer effort to bring the railroad to town, Demens was given the unofficial title of the "volunteer mayor" of Alta Loma. When the track was finished, he donated the last spike for the grand opening. In the 1980s, when the section of track he created was converted into a recreational trail for hiking, biking and horse riding, the track trail and adjacent creek were officially named Demens Creek/Channel and Demens Creek Trail. ^ Contents ^
In 1912, Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles were in court for “bride-selling” and not registering vital statistics. Sensational stories ran for 3 years in newspapers across the nation. In 1916 a Hollywood movie appeared: "Sold for Marriage" about a young Russian village girl sold for marriage in America. At the same time in British Columbia, Canada, Community Dukhobortsy (C.C.U.B.) were investigated for 4 months by a commission which gathered testimony from 110 witnesses in 7 towns in 2 provinces aided by lawyers and scholars. While the commission substantiated "that the Community recognizes no outside authority, and that it refuses to register births, deaths, and marriages, ... " and refused education, thus violating many laws; it recommended fines to be more effective than jail.(21) In 1913, the 16th Amendment to the U.S. Constitution established the federal income tax, which may have shocked the most zealous Spiritual Christians. Many had already fled Los Angeles due to the “bride-selling” scandal, and now the government for the first time wants their money. Ironically, many left Russia to avoid rents and taxes; they were economic migrants. In 1914 the Bethlehem Institutions were closed by the new Municipal Charities Commission for mismanagement. The news shocked friends of Bartlett. The population of Spiritual Christians and Jews moved east across the L.A. River, replaced by Japanese, into the 9th ward, where the major congregations of Spiritual Christians separated, each establishing their own meeting halls and stores, and different social services opened or transformed to provide free aide. A charity medical clinic was created by women's clubs on Rio street at First street, then moved to Utah and First streets. Within 15 years the new Prygun U.M.C.A. and a zealot molodoi sobranie would operate across the street from the maternity clinic. In 1914, the Young Women's Christian Association (Y.W.C.A.) opened a local chapter of the International Institute, a settlement house for immigrant women, one lot north of 1st street on Boyle Ave, in the midst of the "Foreign Quarter." It was damaged by fire, and relocated to a larger lot a half block south of 1st Street at 435 S. Boyle Ave., where it remains today. Those who moved east across the LA River and remained in the city were aided by the upgraded Utah Street School, which added a baby nursery, a bath house, a playground monitored after school and on weekends, and meals The kids got free daycare so both parents could work. U.S.C. sociology students continued to visit, assess and help the most needy immigrants. The Americanization program taught domestic skills to girls and job skills to boys. All kids learned to grow garden vegetables. Though many parents ordered their kids to not attend school, truant officers brought them in. Several Prygun elders collected money from parents help pay for nursery babies milk. In 1914, Demens shifted his public focus to the war in Europe by publishing more editorials and letters in the press. The large group of "Molokan" immigrants announced in the press a decade earlier stayed home. 99% stayed in Russia. Most of the Spiritual Christian zealots fled the city. By 1915 the "bride-selling" scandal subsided. The immigrants who remained were managed by city and charity services. His decade of service to these countrymen was apparently most successful for those whom he hired or placed for work, and those who attended Cherbak's adult school. In February 1914 the Lincoln Memorial was dedicated in Washington D.C., which was probably mentioned to the school students. In February 1915, what appears to be the last unregistered bride case appeared in Los Angeles Superior court. The family of Nick Cheechoff abused his wife Mary Ladiou [Ledyaev ?] by performing an exorcism. Hearing announced to determine if Cheechoff will be deported. From February 20 to December 4, 1915, the Panama–Pacific International Exposition was held in San Francisco. By 1915, the religious text publishing projects engaged some of the zealots in the city. The process kept them busy evaluating proposals for about 7 draft versions up to 1928. Simultaneously a U.S.C. graduate student and home teacher, Lillian Sokoloff, began surveying the Spiritual Christian parents of her students, and published her report in 1918. The U.S.C. project would be continued in 1924-1926 with an analysis of the religion and religious text(s) by 2 new graduate students, one will be Pauline Young, a Russian-speaking Polish-born Jew from Chicago. On August 5, 1915, prophet E. F. Klubnikin died and was buried in Los Angeles, Old Cemetery. Many Dukh-i-zhizniki credit his prophecy for bringing their faith to Los Angeles. Zealot oral history ignored the fact that Demens personally diverted them from Canada, and arranged transportation for them to come to Los Angeles, escorting the first groups. August 20, 1915, was "Cadillac Day" at the Panama-Pacific Exposition, in San Francisco. All cars of all makes are invited to drive to the Exposition, and pick up people along the way, for a huge celebration featuring the new 1916 models. All cars from Southern California met in Los Angeles and were divided into two caravans, one along the coast, the other through the Central Valley. In 1915, 55,217 motor vehicles were counted in Los Angeles County. "The county led the world in per capita ownership of automobiles and continues to do so today."(55) In January 1916 military exception expired in Mexico. The congregation there from Novo-Mikhailovka (Tiukma, Diukma), Kars, departed for Jerome Junction, Chino Valley, Central Arizona, where they would be known as Dzheromskiy. By the end of 1916 they would abandon Chino Valley and temporarily resettle 3 miles west of Glendale, most leaving within a decade to Mexico and California.. In May 1917, the Selective Service Act sparked a hysteria among Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles who were pacified by the educated Russians who had been working with them. But the most zealous insisted on taking a petition to the Tsar (President Woodrow Wilson) which ignited the most zealous isolated in Arizona, who directed all 34 of their boys (a 35th one hid) to not register. Though the draft protesters identified themselves as "Spiritual Christian Jumpers," again the false "Molokan" label was nationally associated with a new scandal. This time they were "slackers" (cowards, un-American draft dodgers). In 1919 Peter A. Demens died at his Loma Linda farm, leaving a wife and 8 children. Much more is yet to be learned about him, and documented online as time permits. In January 2020, wife Tanya and I spent 5 days in central Florida Demens remained in Los Angeles after his colleagues gave up trying to help these Spiritual Christians from Russia. It must have been a huge disappointment for him that most of what he and his friends did to try to help these immigrants failed. He devoted much of the last 2 decades of his life to inviting fellow countrymen to California and personally helping them get settled. He traveled across the U.S.A. several times, escourted groups to Los Angeles, scouted Hawaii, wrote letters, published articles, contacted the President and Lev Tolstoy, and spent 100s of hours meeting and traveling with them. In the end, most of the Spiritual Christians were not satisfied, fought among themselves, and eventually erased him from their oral history; but they did not erase his simple false marketing brand — "Molokan." This deceptive simple label continues today as false history in North America, spread to Dukh-i-zhizniki in the Former Soviet Union, and on to confused scholars and media. In St. Petersburg, Florida, Demens is remembered as co-founder and railway builder at a public monument, a street and landing named for him, and in a history book published in his honor: Full Steam Ahead! : The True Story of Peter Demens, the Brave Russian Nobleman Who Built the Orange Belt Railway and Founded America's Unique St. Petersburg, by Albert Parry, 1987. In Rancho Cucamonga, California, his name is publicly displayed at his house, now a historical monument, the Demens-Tolstoy Estate; and on the Demens Creek/Channel and Demens Creek Trail which replaced the local railway he created. In 1990 his memory was resurrected among Dukh-i-zhizniki in a chapter, contributed by Bill Aldacusion, in the 1990 book A Stroll Through Russia Town, by Mohoff and Valoff. His history is currently being collected in collaboration among 6 researchers in the US and Canada. Stay tuned for more. In the 1980s, Dr. William Parsons, Ekerdt University became interested in Peter Demens whom he studied for more than 20 years. During the 1995 Centennial of the city of St. Petersburg, Florida, a ^ Contents ^
Dr. Pauline V. Young (1896-1977),was married in 1918 to Dr. Erle F. Young (1898-1953) whom she met at the University of Chicago when she was an undergraduate and he was a graduate student. Both were Jewish. They had 2 children, boy and girl, and moved to Los Angeles about 1923, where he was a professor and she was a graduate student, at the new Department of Sociology, University of Southern California (U.S.C.)(94). They worked at U.S.C. until they retired in the early 1940s, then moved to the city of Merced, Central California, where they joined a Jewish congregation and are buried.
Research in-progress. In 1931, the working title (pre-publication) of this book was: "The Holy-Jumpers of Russian Town".(107) The Young's apparently learned that their She probably advised the establishment of their first youth organization, the U.M.C.A., in 1926, and helped compose and edit the 1928 Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn', the Preface of which appears to be mostly from her research, including the mistake of calling all these people "Molokans" while the title of her 1932 book (right) says: "... Spiritual Chirstian Jumpers ..." A major goal of the new U.S.C. Department of Sociology was to document all the nationalities in the city, especially the immigrants, and she was assigned to the non-orthodox, non-Jewish immigrants from Russian east of the Los Angeles River — the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians, an enclave with about a dozen distinct unorganized religious tribes using about 6 seperate private meeting halls. Her goals apparently were to reassure government and society that these peasant immigrants from Russia were safe White Protestant Christians, not foreign anarchists, who intended to become productive tax-paying citizens, while she tried to understand and change the behaviors of the immigrants for integration and assimilation(19). Her main tasks appear to have been to (a) document them, (b) prescribe how to stop the deviant and criminal behaviors of their youth, and (c) to help guide these immigrants from being a burden to society. After 1920, perhaps a thousand Spiritual Christians from Russia who fled Los Angeles during the bride selling scandal (1912-1915) returned to the big city where life was much easier than farming. She reported they were from Russia, but not not Jews or Hebrews, who will assimilate in a generation.(19) In the early 1920s many elite Americans feared immigrants would spread anarchy (Bolshevism, Communism) and take American jobs. "Hebrews" (Jews) would degrade white American society through intermarriage. Her work was needed to advise and guide politicians and educators about their integration and assimilation,(19) and to gather data for her husband's social science research on juvenile delinquency. Her achievements were mostly competent in the new science of sociology, but critically lacking in parts of her reporting, analysis and conclusions. A major error, or deception, was using one word on the title of her book (above) — that they were Spiritual Christian Jumpers (Pryguny) — and a different word in the book — that they were Molokane. She changed the English word Jumper to the Russian term Molokan, and by repetition Anglicized it as Molokan. She falsified history. Why? I spent decades studying this question. A similar confounding irony occurs with Canadian Doukhobors who divided into 3 distinct branches, for which journalists, academics and the government persistently used one label. Though the Russian term Pryguny (genitive plural: Prygunov) is in her 1932 book book title (right, above), Young only identified them as "Jumpers" 9 times in the book text, but 890 times as Molokan(s) — nearly 100 times more — inside the book. She extensively misused the term "Molokan(s)" nearly exclusively in all of her other publications and presentations about them, as did descendants of the immigrants, and all scholars citing her publications who perpetuated this error. Was this an honest error, blunder or oversight; an easy way to finish her thesis on time; or, did she use the false term intentionally to help hide zealous religious traits, cult rituals, and/or zealous religious behavior? While the term Pryguny was extensively used by many of the immigrants among themselves, she used none of the limited published history of Pryguny, and the immigrants provided very little information and/or knowledge of their own history. In contrast the Dukhobotsy have extensive histories publishshed She apparently decided to save research efforts and time by substituting the word "Molokan" for Prygun, which many of the immigrants learned to use from P.A. Demens who diverted them to Los Angeles from Canada during their immigration and whom she never mentions. I find the omission of Demens odd because Demens' rural neighbor in Loma Linda was the U.S.C. professor Dr. Theodore Krystofovitch who is credited with translating the new Dukh-i-zhiznik religious text for Young's Ph.D. thesis and book. She had 2 kids at home with a live-in maid, a husband, full teaching schedule, and other duties as an assistant professor. She apparently never examined early Los Angeles newspapers (Los Angeles Times, Los Angeles Herald) which would have revealed the impact of Peter A. Demens, 25 years before she arrived in Los Angeles, nor did she mention him in her published papers. She also missed the contributions of Cherbak and the de Blumenthals who, with Demens, introduced and aided this "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians". Why did she not use the Prygun label exclusively in the book, as in the title? Did she use the Russian Prygun term in the book title just to pacify the most zealous non-English speaking elders — to fool them in Russian while the English readers got a different label? (Dukh-i-zhizniki also use this two language deception, saying one thing in English and another thing in Russian.) She also failed to recognize, or understand, that she was documenting the formation of a new family of faiths who began using the new religious text: Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' which she had been translating with Dr. Kryshtofovich, and probably editing. She either missed an opportunity to name the the new faiths of "people who use the Dukh i zhizn'" — Dukh-i-zhizniki in Russian — , and complete a translation and publication of their new book for the benefit of the American-born, and scholarship; or, did she purposely avoid further translating the book and naming the new faiths perhaps to accelerate their assimilation? A hint appears in the final sentence of her 1932 book (page 276): " What the next quarter-century will reveal is as yet uncertain, but the present trends indicate that city life eventually fuses even the most refractory sectarian material." Here "stubborn" probably means "stubborn". She appears to predicted that the next generation, in 25 years, would be assimilated, English speaking, and intermarried with other American faiths, which most did, even the most stubborn Spiritual Christians from Russia. After her research on Spiritual Christians from Russia in Los Angeles, her career work focused on teaching systematic interviewing and data analysis to social science students. She often used her interview data sheets of Spiritual Christian subjects as examples for her lectures and textbooks. By the 1960s she recognized that not all of her Spiritual Christians subjects assimilated after 25 years, as she predicted at the end of her 1932 book. She planned to examine why and how they persisted, but her notes were lost in a fire and a possible book update was cancelled.(69) Also perhaps, several zealous elders objected to another book which might highlight the "unclean" Y.R.C.A. ("Jack Greners") who helped manage the U.M.C.A. "devils" that attenuated the assimilation she forecast in 1932. ^ Contents ^
If Young's Prygun name cover up was intentional, what could motivated her to hide the religious identity of Pryguny and other zealous faiths in Russian-town?
Beginning in 1910, 52% of the California general population consisted of immigrants and children of immigrants, which burdened the booming area with huge costs to accommodate them. As more housing, employment and social services became available in the Flat(s) (9th ward, Los Angeles), Spiritual Christians from Russia migrated eastward across the Los Angeles River, out of Bethlehem (8th ward). Congregations, that had to meet together at the Stimpson-Lafayette Industrial School, managed by the Bethlehem Institute, or in cramped houses, could meet separately. Utah street school provided free nursery care for babies. L.A. City Parks and Recreation provided free day-care after school by building and managing the school playground (years before Pecan Playground). The schools and charities provided free food and medical care for the needy. All these city benefits allowed both parents to work full-time, while government and charities managed and fed their kids, dawn to dusk at no cost. The Womens U.S.C. sociologists probably recommended special educational buildings at Utah Street School for immigrants — the "Americanization Building" — to teach domestic skills to girls, and the adjoining sloyd workshop to each employable skills to boys. A large Quaker-Methodist mission had been in operation since 1904 at Clarence and Third streets, and 2 more community service settlement houses were on North Clarence street across from Utah Street School. A free medical and maternity clinic was on the corner of First and Utah streets, across the street from both the U.M.C.A. and molodoi sobranie (Young People's Meeting). Compared to their Russian villages, big city life was much easier if you had a job, and all your kids (from babies to teenagers) were fed and supervised at school, dawn to dusk, for no charge. Initially their major problems were cramped housing, language, air pollution, and a congested urban ghetto of mixed nationalities. In February 1910, "The School of Citizenship" was reopened at 2 locations of the Bethlehem Institutions “to continue the work of making American citizens of the foreign-born people of Los Angeles.” At 510 Vignes street, the "Mother church", most of the students are Russians and Greeks. In 1911, city life confronted the most zealous Spiritual Christians with drastic cultural and legal challenges to their Old World cultures, which caused many to flee the city to preserve bride-selling, maintain dress and language, and avoid registration (in school, for citizenship; and births, marriages and deaths). In 10 years most will return to the city after adjusting to their fears. In Fall 1911, the Civic Association of Los Angeles conducted a house-to-house survey of the nutrition of school children. Most ate at school due to poverty. Gardening was taught at school, and 15,000 kids began their own home gardens. In May 1912 a May Day Song Festival was hosted by the Los Angeles School Department at Temple Auditorium (location of the current Dorothy Chandler Pavilion, Music Center). Russian immigrant children would not sing the Russian National Hymn [God Save the Tsar!]. In 1914, the Bethlehem Institutions were closed by the City of Los Angeles for mismanagement. The Rev. Dr. Dana Bartlett was no longer nearby to monitor, advise nor guide the 12 various religious leaders from Russia who moved away from his former neighborhood as he moved his residence to the westside of Los Angeles. In the Flat(s), charities and government expanded social support services for aliens (Armenians, Chinese, Italians, Japanese, Mexicans, Russians, Slavs, Blacks (African-Americans), etc.) and the other poor. In 1915, a Russian-speaking U.S.C. student and Utah Street School Home Teacher, Lillian Sokoloff, began a 3-year project to teach Spiritual Christian women from Russia how to survive and navigate American life. Her project ended in 1918 with a published report which was continued 5 years later by Pauline Young in 1923. But, the Young's failed to recognize or understand that Sokoloff had identified and documented several different faiths among these non-Orthodox folk-protestant immigrants from Russia which divided them. The majority (94%) of the population that Young surveyed was labeled by Sokoloff as Pryguny. Only 6% were Molokane who had no meeting house, and integrated with non-Molokan faiths.  Timeline of Pauline V. and Erle F. Young.(51)
Socio-political environment of Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles Since the late 1800s, Italian immigrants were considered by some to be less human than Negroes. A series of lynchings of Italian immigrants occurred in the South, besides the hundreds of lynchings of African-Americans. Then, as now, many in the Southern states did not like or want immigrants to take their land, jobs or intermarry with them or any White people. In 1912, Community Dukhobortsy (C.C.U.B.) were investigated for 4 months by a Canadian commission.(21) The fragmented Dukhobor population numbered about 12,000, most of whom were falsely reported in the news to be nudists and terrorists. Discrimination against several populations of Eastern Europeans was widespread in Canada and the United States, which probably concerned the Vislick family and their relatives who immigrated from the Ukrainian border where Jews were restrained, persecuted, assaulted and killed. From 1914 to 1920 the Canadian government interned 8,579 mostly single men of German, Austrian and Ukrainian ancestry, including Jews and Mennonites, in 24 concentration camps across the country. They were feared as enemy aliens. About 5,000 Ukrainians were arrested trying to cross into the U.S. Several were from Russia. In 1914, Russian-born Emilio Kosterlitzky was hired by the Department of Justice Bureau of Investigation (B.O.I.), to spy on suspicious aliens in Los Angeles, including those from Russia. He apparently investigated Prygun-owned stores in the "Flat(s)" through the 1920s. He died in 1928 and is buried in Calvary Cemetery, 1 block south of the Spiritual Christian "Old Cemetery" in East Los Angeles. ^ Contents ^
In 1915, the first Spiritual Christian hymnal (songbook, pessennik) and first collection of prophesies (Morning Star, Utrennyaya zvezda, Утренняя звезда) copied in Arizona by Pivovaroff, was published in Los Angeles, by Shanin and Kobziv — title: Пѣсенникъ (Pesennik), По соглосiю Прыгунской Духовной Братстим (Po soglasiyu Prygunskoi Dukhovnoi Bratstim : By agreement with the Jumper Spiritual Brotherhood). The word "Molokan" does not appear in these 2 books. Also in 1915, the Adventist prophet Ellen G. White died. It is interesting here to compare a century of progress of Adventists with Dukh-i-zhizniki from 1915 to 2015. In many ways White 's followers (Adventists) shared beliefs and practices similar to various disorganized Spiritual Christian tribes (conscientious objection, vegetarianism, prophesy, fasting, Bible, and no Christmas holiday). In contrast to Spiritual Christian prophets from Russia, White's will appointed a "self-perpetuating board" (a Trust) that took charge of White's estate of spiritual manuscripts, which were conserved, organized, copyrighted, published, translated into many languages and distributed. A small library of books, journals, newsletters, and encyclopedias, were published. Branch offices, schools, and hospitals were built and staffed. Annual conferences and regional meetings were held.(37) During the same 100 years, the developing Dukh-i-zhizniki, who forbid forming a committee (komitet) in 1928, argued and divided, trying to hide their secret faiths from the "world", resisted education and publishing, and had not grown for more than 100 years. In comparison, from 1910 to 2012, Adventist membership grew about 170 times (from 104K to 17.6 million).(38) If Dukh-i-zhizniki in the United States had grown at the rate of Adventists, there would be about a third of a million active members in the U.S.A. in the 2000s. Such large numbers of Dukh-i-zhiniki would scare those who prefer very small controlled congregations, where everyone knows everyone else for generations. Beginning in 1915, to 1923, the major massacres of the disputed Armenian Genocide occurred in Turkey (now Türkiye) and the Soviet Union. On 4 July 1915, Americanization Day began, which celebrated the new programs of cultural genocide of all immigrants. The most zealous tribes of Spiritual Christians from Russia had already fled the Los Angeles metropolitan area, to Mexico, Central California, Arizona, Oregon, and Utah. Many in Mexico wanted to return to the U.S., and one tribe made it to Central Arizona by January 1916. In January 1916, 130 Pryguny moved from Mexico to Central Arizona. The leader V. G. Pivovaroff believed all in Mexico will soon follow and signed up for 10,000 acres in 2 valleys north of Prescott, Arizona. Their irrigation colony failed within the year, most all moved south to join 3 colonies west of Glendale, and 19 men sued the land company. This was the second lawsuit filed by Pryguny in the U.S.A. — the first was filed in Los Angeles for payment of a commission for the 1905 Mexico land sale. On 14 June 1916, Flag Day began with a Proclamation by President Wilson. In December 1916, G. E. Rasputin, a mystical holy man, adviser to nobility, was murdered in Russia. His daughter Maria moved to America, and retired in Los Angeles where she died in 1977. In February 1917, Community Doukhobor leader, Peter V. Verigin, sent a telegram to the Russian Provisional Government that all his 10,000 followers were willing to return to Russia to farm, if they were given land and military exemption, like offered in Canada.(74) In April 1917, America entered the European war, later called World War I. A national military draft was called. In May 1917, Rabbi E. G. Hirsch of the "reformed" Chicago Sinai Congregation, which the Pauline Vislick may have attended, declared he was against Zionism. "Generally, the upper class Jews in Chicago, primarily of German and Austrian heritage, ... were anti-Zionist."(75) Sinai's first Rabbi Felsenthal declared: "Judaism had to be redefined as a modern religion consistent with intellectual progress in the sciences and humanities." Paula Vislick's reformed Jewish culture may have inspired her to become an American scholar of humanity. Beginning on June 5, 1917, 34 Spiritual Christian "Holy Jumpers" and Maksimisty from Russia in 4 adjacent colonies on the west side of Phoenix, Arizona, refused to register for the draft and were sentenced to 1 year in jail, in Prescott, Arizona. They all served 10 months, for good behavior and to limit costs. The most zealous 6, refused to sign release papers from jail (including my grandfather Jacob D. Conovaloff) and were turned over to the military police, taken to Fort Huachuca, near Tucson, where they were abused then sentenced to life in military prison. Most all of the news and legal documentation mislabeled these slackers (draft dodgers) as "Molokans", though they stated they were "Pryguny" though some were Maksimisty and other faiths. While the 34 were in jail, 3 major acts of Congress were passed regarding aliens — the Espionage Act of 1917 (June15), Trading with the Enemy Act of 1917 (October 6), and the Sedition Act of 1918 (May 16). Many immigrants were investigated in North America. In October 1917, the Bolshevik-led Red October Revolution overthrew the Russian Provisional Government. Fear spread around the world that anarchists will overthrow more governments. Nationalist Americans in government, including law enforcement (police), were on alert for any un-American activities by immigrants, especially Eastern and Southern Europeans. July 4, 1918 was renamed Loyalty Day, after the U.S. entered the war. Immigrants were told to conduct parades, donate to war charities and register for the draft. In Canada in 1918, goli svobodniki (nude sovereign people) in British Columbia increased public protests against Community Dukhobortsy, causing P.V. Verigin to ask for a restraining order, which was ignored. The protestors were falsely called Doukhobors, who were sometimes called Molokans. Also in 1918, Lillian Sokoloff, a Home-school teacher at Utah Street School, Los Angeles, finished her 3-year survey of Spiritual Christians for the U.S.C. Department of Sociology which was described in the university newspaper in April 25, 1919 (page 1, column 4, bottom). She conducted the first and only population estimate of the was the different branches of Spiritual Christians from Russia, showing In August 1918, American Expeditionary Forces arrived in North Russia and Siberia to aid the Allied Intervention in Russia against the Bolshevik (Red) Russian October Revolution of 1917. Bolsheviki won the civil war in Russia. The Allied Powers withdrew in 1920, and Japanese in 1925. Many historians stated that the failed foreign interventions prolonged the Russian civil war, led to WWII and the Cold War, and poisoned East-West relations forever after. In September 1918 September the Youngs were married in Kentucky, probably at his parent's synagogue. From June 1918 through May 1919, the Spanish flu infected about 27% of the world population (~ 500 million), killing about 10% of those infected, mostly the young and elderly. Deaths in the U.S. are estimated to have been from 500,000 to 675,000 people. About 20 infants died in the Arizona colonies. From September 1918 to June 1919, U.S. Senate Overman Committee investigated communism among Germans and Bolsheviks and other "un-American activities" in the United States. Final report released in June 1919. The Overman Committee inspired formation of the Fish Committee (1930), McCormack–Dickstein Committee (1934–1937), House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC, 1938), and continuous investigations to 1975 as the Cold War appeared to end. From March 1919 to April 1920, the Lusk Committee was formed by the New York State Legislature to investigate individuals and organizations in New York State suspected of sedition. State-wide raids were conducted at the Russian Soviet Bureau, the Rand School, the left wing of the Socialist Party and the IWW, 73 branches of the new Communist party, and offices of dozens of radical publications. The results were minor and controversial, resulting in 2 anarchist editors serving up to 5 years in prison, several radical immigrants deported, 5 Socialist Party members of the State legislature expelled, and years of politicians trying to control speech and education. Beginning in 1919 widespread fear of terrorist acts, world revolution, and protests by immigrant Bolsheviks and anarchists impacted the country. Though most activity was on the east coast, the west coast was not spared —
In 1919, Community Dukhobortsy (mostly C.C.U.B. members) and Sons of Freedom in British Columbia, Canada, were partially disenfranchised (denied the right to vote) for 37 years in B.C. elections. Indemedent Doukhobors in central Canada could vote. The United States government had to determine if all these mislabeled "Molokan" immigrants were worthy of citizenship, and who should be deported, if any.. ^ Contents ^
In May 1919, "The Americanization Movement," by Dr. Howard C. Hill, University of Chicago, was published in The American Journal of Sociology (University of Chicago), pages 609-642. The paper summarized a national survey about huge wave of recent immigration, and was probably known by Vislick and Young. Hill reported:
In 1919 Community Dukhobortsy, Hutterites and Quakers in British Columbia were barred from voting for fear they could swing an election due to their large population. On 1 June 1919, the Canadian government banned Mennonite, Hutterite and Doukhobor immigration into Canada due to public pressure against undesirable immigrants. These German-speaking and Russian-speaking people who refused military participation were considered a danger to Canada and lacked Canadian values. Order-in-Council PC 1204 amended Section 38 of the Immigration Act: They were "…undesirable, owing to their peculiar customs, habits, modes of living, and methods of holding property, and because of their probable inability to become readily assimilated to assume the duties and responsibilities of Canadian citizenship within a reasonable time after entry." The Order was cancelled in 1923 for Mennonites, and in 1925 for Doukhobors. During the 15 years, from 1920 to 1935, Spiritual Christians communities in Southern California and British Columbia had to make difficult significant changes to adjust to their surrounding cultures; and, Pauline Young appears in Los Angeles, conducts her research, and publishes. How much she and the various groups in the U.S. and Canada knew about each other's problems can only be guessed as limited to what appeared in their respective local newspapers, because we do not know yet if any news was sent by letters. In 1920, Pauline Young was enrolled at the University of Chicago, and working with immigrant Russians. On New Year's Day, January 1, the aggressive county attorney for the Chicago area conducted his own surprise raids to arrest communist "Reds" a day before a scheduled federal "Palmer raid" on January 2. The county attorney wanted the political prestige of upstaging the new federal Bureau of Investigation to advance his career, but his raids were terribly abusive. One raid occurred at a Russian adult school well known to Young. At least 80 Russians, many were her clients, and 13 Italians were arrested, squeezed into very cramped jail cells, and not fed for a day. Most all were innocent people illegally taken without court warrants, and some held for weeks before being released. Many were pacifists, including a Tolstoyan, well known by local sociologists, including Jane Addams whose pioneering work with the poor and immigrants was earlier duplicated in Los Angeles by the Dr. Rev. Dana W. Bartlett to organize the Bethlehem Institutes. Young was probably horrified that an American police state suddenly appeared and forced innocent immigrants from their homes and schools, holding them without cause in terrible conditions, then releasing them days and weeks later, and holding some longer for bail.(46) Could such a raid also happen in Los Angeles among the approximate 2000 Spiritual Christians from Russia whom she would soon be assigned to investigate as a scholar? She must have discussed with her professor husband how they could help prevent a similar raid in Los Angeles. Maybe the raids motivated the Youngs to leave Chicago for a safer city in California. In 1920 during the post war depression, most of the distant rural colonies formed by Spiritual Christians who fled from the Los Angeles "bride-selling" scandal, failed primarily due to buying poor land and the post W.W.I. recession. Perhaps as many as 2000 returned to the Los Angeles enclave where overcrowding, poverty, juvenile delinquency and truancy, crime, alcoholism, domestic violence, and other strife significantly increased in the Flat(s) area. The huge incoming migration back to the Flat(s) certainly alerted government workers. ^ Contents ^
"According to a report sent by a Russian-speaking American investigator in California in 1920 (probably Speeks), "With few exceptions, the Russians want to go home. Recently all the Molokans, of Tacoma, San Francisco, Los Angeles and along the coast, numbering several thousand, requested the government to deport them. They claimed that they had been 'cheated' by the Americans in their talk about the 'freedom of America.'"(47) By the 1920s, the University of Southern California (U.S.C.) in Los Angeles had developed the most robust sociology program on the west coast with close connections with the University of Chicago, which pioneered urban sociology. The new department was founded and headed by Dr. Bogardus, from Chicago, who would soon recruit Dr. and Mrs. Young. During 1920, many earthquakes occurred in and around Los Angeles, possibly caused by oil drilling. The first widely felt with property damage was in February, July (Inglewood) and the last in September. Earthquakes continued in bursts with the next largest in 1929 (Whittier), and 1933 (Long Beach) killing 133 people and closing the main train depot — La Grande Station, south of 1st Street, west of the Los Angeles River (across from The Flats(s)), where Spiritual Christians from Russia first arrived. American government intrusion into the immigrant culture (mandatory English education; registration of birth, marriage, death) and acts of God disasters undoubtedly fueled songs and oral tradition to return home to Russia for many. From 1921 to 1923 the Rose Bowl stadium in Pasadena and the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum next to U.S.C., are built. Youngs arrived at U.S.C. in 1923. 1922, February, Soviet headquarters in Chicago coordinates about 200 U.S. affiliates to gather "big money" for Russian Bolshevik government. U.S. government investigates, exposes scammers. Some elected U.S. officials were fooled into helping. From 1922 to 1926, 3,340 (74%) of the Old Colony Mennonites in Manitoba, Canada, sold their farms and fled to Mexico, to maintain the "religious principles" they had in Russia. Young probably learned of this historic mass migration from other sociology faculty. In 1922 Russia expected most of the Russian diaspora to return. The Society for Technical Aid to the Soviet Union invited all Spiritual Christians from Russia in North America back to their Russian Homeland (отечество: otechestvo) and offered them land and immigration assistance. By 1926 about 20 Molokane from San Francisco rejoined Kars relatives who were relocated to eastern Rostov Oblast; and 40 families of Independent Doukhobors in Saskatchewan, Canada, joined their families in Tselinskii district, Rostov, on farm land allocated adjacent to the Molokane. During that time, no members of Spiritual Christian faiths who settled in Southern California, Mexico, Arizona, New Mexico, Oregon or Washington, returned to Russia, though some of the most zealous had visions and prophesies about returning to villages near Mt. Ararat, especially the Maksimisty who believed in the second coming of their prophet M.G. Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) with Jesus Christ. In 1923, the major massacres of the Armenian Genocide which began in Turkey (now Türkiye) and the Soviet Union in 1914, appeared to have ended. In April 1923, one of the largest labor union strikes ever was centered at San Pedro harbor. Of 3,000 striking dockworkers, 600 were arrested, including Upton Sinclair for reading the Bill of Rights in public. ... the Marine Transport Workers Industrial Union 510, Industrial Workers of the World (I.W.W.), called a strike that blocked 90 ships in San Pedro. The union protested low wages, bad working conditions, and the imprisonment of union activists under California's 1919 Syndicalism Law. Denied access to public property, strikers and their supporters rallied here at this site they called "Liberty Hill." Writer Upton Sinclair was arrested for reading from the Bill of Rights to a large gathering. The strike failed but laid a foundation for success in the 1930s. The Syndicalism Law was ruled unconstitutional in 1968. Youngs Move to Los Angeles About 1923, Pauline V. Young, age 29, enrolled in the sociology graduate program at U.S.C. Her kids were very young, boy Clarence 3, girl Harriet 1. They rented a house less than a mile west of campus, at ___, and had a live-in housekeeper, nanny. She arrived nearly 20 years after the first Spiritual Christians from Russia came to Los Angeles, 10 years after most all had arrived, and 4 years after Demens died. Most Spiritual Christians from Russia had been integrating and assimilating(19) for 15 years, and about 2000 poor failed colonist farmers just arrived (most from Arizona; less from Central California, Utah, Oregon, Washington, New Mexico and Mexico) which nearly doubled the Spiritual Christian population from Russia in Los Angeles to perhaps 4,000. They were a huge social problem on the booming East side and not likely to abandon the city again for distant farms. Many delinquent youth were a burden on social services. Neither the population nor congregations were united with a hierarchical structure, which hindered communication between these immigrants and government. Mrs. Young spoke Russian, had first-hand experience with eugenics and ethnic discrimination in Europe and America, and immigrant Slavic populations in the U.S.A. At U.S.C. In 1923 she was undoubtedly the most capable sociology student to pursue the research published in 1918 by Lillian Sokoloff on the fragmented tribes of Spiritual Christians from Russian concentrated in East Los Angeles (today called Boyle Heights), and continued in 1924 by student Wicliffe Stack(86). She could have chosen to study the Russian Orthodox immigrants, or Russian Jews (Hebrews), but they had very few juvenile delinquents compared to the Spiritual Christians. Her Jewish background probably appealed to these various tribes of Spiritual Christians who favored Old Testament laws which facilitated her access to participants. There are probably two important reasons Young studied this particular group of immigrants: (a) the government identified them as a social problem, and (b) her husband needed data on this cohort of juvenile delinquents. Plus, off all the sociology students, she was the best fit to conduct social science research on the Spiritual Christians from Russia, while other graduate students were matched with different immigrant populations. Within 2 decades most major alien nationalities, minority and poverty areas in Los Angeles were documented by U.S.C. sociology students — a huge body of social research, which was used to guide government and non-profit service policy and train social workers. She probably was accepted by many of the soon-to-be Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths because she spoke Russian well, could not be rejected by zealots as a "pork-eater," was a small woman (not a big man), understood many of their holidays, and was fascinated about their Dukhi i zhizn' book project.. She arrived about a decade after the educated Russians (Demens, Cherbak, de Blumenthals, etc.) gave up by 1910, Bethlehem closed in 1914, and Sokoloff published her report in 1918, after a 5-year lull of interest from a sincere Russian-speaking outsider. Young apparently did not know, or neglected to report, about the educated Russians who intervened up to 1910. She knew about Sokoloff's report and a Jewish attorney, Mr. Lev, who represented several families in court. Her first task involved examining the new religious text they were debating and trying to compile and republish in about 7 drafts, which they collectively called Dukh i zhizn' in short. The Youngs arrived to a rapidly growing metropolis with 1 automobile to every 3 people, the highest ration in the world since 1915, and continued Cars in Los Angeles. — CARS — in -progress ^ Contents ^
From July 1923 to 1930, more than 21,000 Mennonites were brought to Canada from Russia, coordinated by the Canadian Mennonite Board of Colonization. They were aided by railroad credits for train fares which totaled $1,767,398.68, paid in 1946. During that time, an additional 143 Doukhobors (2%) arrived on 13 ships, but very few, if any, Spiritual Christians came to America. In 1924 a colony of independent Dukhobortsy (edinolichniki) formed at the north edge of Manteca in the San Joaquin Valley (map), about 65 miles driving east from San Francisco, 100 miles north of Kerman. Young apparently never visited Spiritual Christians outside of the Boyle Heights and East Los Angeles area, though she and her husband retired in Modesto in the 1940s, less than 20 miles south of this Independent Doukhobor colony. By 1924, the the the Christian Community of Universal Brotherhood (C.C.U.B., communal Doukhobors in Canada) had become the largest communal organization of its kind in North America. In early 1924 the C.C.U.B. began to buy land for a huge communal colony near Eugene, Oregon. In October 1924, Peter V. Verigin, the C.C.U.B. leader was killed in a train explosion with 8 others in eastern British Columbia, Canada, less than 20 miles from the U.S border, 112 miles north of Spokane, Washington. Extensive research reveals no definite Canadian culprits, but investigators have not be able to access U.S.A. records from the F.B.I. regarding possible involvement of the Ku Klux Klan in Oregon, who are among the most likely suspects along with possible Soviet spies. Also in 1924, J. E. Hoover became the F.B.I. director. It is possible that the U.S. Government could have wanted an expert analysis of the new Dukh-i-zhiznik religion and sociology of historically related Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles County, to avoid any similar potential act of terrorism in the U.S.A. Knowing more about these immigrant "sects" from Russia was probably important for national security due to the bride-selling scandal (1911-1915), all boys in Arizona jailed for not registering for the draft (1917-1918) and 6 went to federal prison (1918-1922), only 1 in 200 registered for citizenship (1918), and 2 presbyters were arrested and fined in Arizona for not registering births, marriages or deaths (1920). In 1924, Dr. Erle F. Young, became a Professor of Sociology, University of Southern California. In 1924, the Immigration Act of 1924 limited immigration from Russia, and increased migration back to Russia. Though leaders of the Maksimist and Sionist Spiritual Christians in America said they were determined to return to Mt. Ararat, they missed (or avoided) several opportunities to return in the 1920s, and made their last attempt in 1939. In 1925, Young finished her master thesis which focused on the new religious text project — Dukh i zhizn' — being debated and revised. She then worked as a social economist for the State of California, and the following year (1926) her husband accepted a teaching job in the Sociology Department at U.S.C. Her husband was teaching at the University of Chicago where he promoted social mapping and data analysis. At U.S.C. he became the national analyzer of data about urban juvenile delinquents, for which his wife would soon gather the Los Angeles data. In 1925, a book about juvenile delinquency, Youth in Conflict by Miriam Van Waters, was published, in which the first case reported was about 5 Prygun boys arrested for burglary. The author served as superintendent of the new Juvenile Hall for Los Angeles County (1917-1920), and was appointed the Referee (like a judge) for the new Juvenile Court (1920-1930). While she was writing her book, Van Waters lectured at U.S.C. once a week, where she undoubtedly met Dr. and Mrs. Young. In her 1932 book, Young cites Van Waters once on page 213, and uses her data for "Table IV: Number and Type of Offenses of 24 Prygun The Youngs needed to quickly analyze this alien population from Russia to provide information for social intervention and aid, while other sociologists were performing similar studies of immigrants from other countries in Los Angeles. The Department of Sociology at U.S.C. was developing a team of scientists trying to guide the diagnosis and cure of social ills — alcoholism, poverty, illiteracy, crime, unemployment, teen pregnancy, prostitution, etc. The head of the Department of Sociology, Dr. Bogardus was personally working with non-profits and churches to form non-government organizations (NGOs) to serve the poor, non-whites, and aliens, of which 50+ nationalities and races were identified. From 1925 to 1932, Young produced 8 publications about Pryguny and Dukh-i-zhizniki — 2 thesis (1925, 1928), 4 papers (1927, 1929, 2 in 1930), and a book (1932). Examples of her unpublished research was included as lessons in her sociology textbook and in several lectures. She planned to update her 1932 book in the 1950s, but lost her source notes in a fire. In September 1925, the Canadian government subcontracted recruitment and settlement of European farmers in a Railway Agreement. In 1926, Pryguny in Mexico unsuccessfully tried to partner with those in Los Angeles to accept land in central Alberta. Between 1925 and 1929, more than 185,000 Central Europeans arrived under the terms of the agreement. ^ Contents ^
In 1926 ".. nearly two million Russians are scattered all over the world as refugees, .." (Creston Review, May 14, 1926, page 2), and the rapidly growing population of Los Angeles was about 900,000. In 1926, the Spiritual Christian population in Los Angeles of about 4,000 was about 0.2% of world refugees from Russia, and about 0.44% of the rapidly growing City of Los Angeles. Though these are relatively very tiny fractions, their population was very concentrated in one of the poorest neighborhoods of Ward 9 (east of the LA River), and nearly all their kids attended one grammar school and playground (Utah street), a territory their youth gangs dominated. The Utah playground preceded the Pecan playground. Young used a then slang name for her subjects' territory — Russian-Town — in the title of her book. In 1926, Spiritual Christians from Russia, mostly Pryguny, in Mexico and Los Angeles began to organize a cooperative migration north to Canada — a pokhod (поход) — with Canadian immigration agents. In 1928, 8 delegates, 4 from each area, toured land east of Calgary, Alberta. Though the land would be homesteaded (cheap), and they were offered a "bloc" of about 100 square miles, the deal probably failed because they would have to fund their own travel and supplies, which those in Mexico could not afford. Those in Los Angeles, were probably not interested in leaving their "kingdoms in the city" for any reason. Had they arrived in Canada before 1904, during the "open door" immigration window, land and travel expenses would have been paid by the Canadian government. This significant event was missed and/or omitted by Young and Berokoff. In 1926 Community Dukhobortsy in Canada undergo major changes. During a meeting of Independent and Community Dukhobortsy held at Canora, Saskatchewan, Canada, it was proposed that they should move to Mexico. A delegation of about 27 went to Mexico (stopping in Arizona to visit Maksimisty) and returned with an unfavorable report. A majority decided that their next leader shall be the son of Peter Vasilich Verigin, Peter Petrovich Verigin who lives in Russia; and he is invited to immigrate to Canada. Anastasia Holuboff, common-law wife and widow of Peter V. Verigin, having lost the reign, moves to Alberta, east of Calgary where she buys 1.75 mi2 of land for a commune of 165 followers — near the land block offered to Pryguny from Mexico. In 1926, the United Molokan Christian Association (U.M.C.A.) is founded in Los Angeles. Membership was limited to "Spiritual Christian Jumpers." A major reason for the organization was to provided community-based supervision and guidance of Spiritual Christian youth from Russia to prevent juvenile delinquency by giving the kids distractions, purpose and opportunities. But the elders did not know how to organize it, so they eventually enlisted help from 2 boys who graduated from the Bible Institute of Los Angeles (B.I.O.L.A.), Al Patapoff and Bill Samarin. Samarin's father John was president when he invited the boys to . In June 1926, the new Central Los Angeles Public Library was opened downtown, built on he site of the State Normal School campus (for teachers) a predecessor to UCLA. It was next to the Bible Institute of Los Angeles (B.I.O.L.A.) which offered free courses, and trained the first U.M.C.A. teachers. In May 1926, Pauline Young submits her masters thesis: "The Social Heritages of the Molokane: Monographic study of the Molokane in Los Angeles" (219 pages) which focuses on the new sacred text: Dukh i zhizn', a precursor to the final Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' (1928). This first publication about the faiths contains evidence and hints about why she changed their histories. A few notes are listed here in order by page number.
She did not know she was dealing with about 25
different religious tribes with about 12 dominant
leaders, who met for the first time in Los Angeles. None
were Molokan. She never examined tribes outside
of Los Angeles. ^ Contents ^
On 1927, May 2, the U.S. Supreme Court legalized eugenic sterilization of undesirables (Buck v. Bell), a practice led by California which did 1/3 of all sterilizations in the country. Targeted were the mentally ill and mentally deficient, and could also include habitual drunks, sexual deviants, the poor, and religious zealots among the immigrants from Russia. Sterilization doubled in a decade and continued at that rate to the 1950s. Those not sterilized were deported.(56) On 1927 May 21, Charles Lindbergh flew solo across Atlantic and landed in Paris, France. In June he and his plane, Spirit of St. Louis, returned by boat to a hero's welcome, prizes and honors. In September he began a flight in his famous plane, across the country to promote himself, and his new book, making 82 stops in 48 states, greeted by 30 million people. June 11 was officially declared a national “Lindbergh Day” with radio programs broadcast coast-to-coast. On 1927, September 16, Peter P. "Chistyakov" Verigin, arrived in Canada from to lead the Christian Community of Universal Brotherhood (CCUB, Community Doukhobors) after his father was killed in 1924. On 1927 September 20, was “Charles A. Lindbergh Day”in Los Angeles. He landed near Montebello at Vail Field with his famous plane, greeted by about 200,000 people. He was honored with a parade of through downtown Los Angeles, seen by about a million people, which ended at the Coliseum filled to capacity at 60, 000. That night he spoke on radio (simulcast on all 6 local stations) to a banquet held in his honor at the Ambassador Hotel. It is certain that most all Spiritual Christians from Russia in Los Angeles heard this news, and many saw his landing, parade, and/or speech. On 1928 April 28, a bright light named the “Lindbergh beacon” on top of the new City Hall and was ceremoniously turned on remotely by President Coolidge, during a 3-day dedication celebration. Every night the beacon flashed around the city for 13 years, until the US entered WW2 on December 7, 1941. It is certain that all Spiritual Christians from Russia in Los Angeles County saw the beacon at some time. In 1928 the final version of Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' was published and soon placed (by the Holy Spirit through T. Bezayeff) on the altar tables (stol : стол) of all congregations in Southern California, thus converting all to a new family of Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths. The book was distributed to all non-Molokan congregations in Southern and Central California, Arizona, Oregon and Mexico. It was not accepted on the alter tables by steadfast (postoyannie) Prygun congregations in Mexico and Arizona, while the Maksimist congregation in Arizona welcomed it. The debated collection of edited, censored and revised writings is declared by zealots to be a sacred text. From 1928 to 1930, demonstrations by Spiritual Christian Svobodniki ("sovereign people", Freedomites, Sons of Freedom) in British Columbia, Canada, escalated and "reached a fevered pitch." They conducted numerous protests with nudity, arson and bombings. "By 1929 zealots [Sons of Freedom in British Columbia, Canada] ... were protesting against any deal on public education by staging nude marches and burning school buildings. To allow their children to be educated by the state was, they said, to make of them 'slaves of Satan.'"(70) In 1928 a new 32-story Los Angeles City Hall was opened. It was the tallest building in the city up to 1964. From 1929 to 1933, the new city mayor, John Clinton Porter, was a xenophobic, Protestant, populist, and senior member of the local Ku Klux Klan which had an office downtown to protect the city against communism, Eastern Europeans immigrants, and Jews — similar to Pryguny. In the 1920s perhaps up to 20% of US households had a registered member of the KKK, and more were in sympathy. This indicates a politically active anti-immigrant anti-Semite culture in Los Angeles during the first decade that Young was doing her 2 theses, and publishing papers and her book. In 1928, Young's boss and department chairman, Bogarus, published Immigration and Race Attitudes. On October 29, 1929, "Black Tuesday", the New York Stock Market crashed, and the Great Depression began. It ended in late 1930s. In 1929-1936, Los Angeles mass deportation of Mexicans. Repatriation of 400,000+ Mexicans and their American-born children from the United States began. Thousands moved through Los Angeles. About 60% were legal citizens. After Depression politicians wanted more jobs for "whites" by eliminating Mexicans. Los Angeles had the largest population of Mexicans outside of Mexico. In 1930, the first Sionskii pesennek (Сионский песенник : Songbook of Zion) was published in Los Angeles for Spiritual Christians from Russia. Complete title: «Сионский песенник столетнего периода. Христианской Религии Молокан Духовных Прыгунов в Америке. Первое издание в Лос-Анджелесе 1930 года». (The Zion Songbook of the Hundred Year Period. Christian Religion of Molokan Spiritual Jumpers in America. It replaced the 1915 Prygun songbook by Shanin and Kobziv. The book organizers tried included songs to satisfy most of the was mainly published by the newly forming Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths, including songs from Molokane (Northern California), Pryguny, and Subbotniki. In June 1930, Young her submitted her doctoral thesis: "Assimilation Problems of Russian Molokans in Los Angeles," (543 pages), using a false label. In October 1930, aviator Laura Ingalls, age 25, was first woman to fly across the country from East to West, from Long Island, New York, to Glendale, California. The 30.5 hour trip took 4 days due to 9 fuel stops. In 1935 she did the same coast-to-cost flight non-stop in 18 hours (East to West), topped Earhart's record by flying non-stop from Los Angeles to New York in 13.5 hours. In the 1930s she became famous for setting dozens of women's records, trying to top Amelia Earhart. Unfortunately, in 1941 she was arrested for allegedly being a Nazi spy, and imprisoned for 19.5 months, where she was beaten by several prisoners. Upon release her aviation career was nil. Ingalls lived in Burbank, California, for the last 20 years of her life, dying in 1967.(62) In 1931, Canada amended the Criminal Code, adding section 205A, to allow for jailing of fanatic Svobodniki (sovereign people, Freedomites, Sons of Freedom) up to 3 years. ^ Contents
^
Young's Book Published In May 1932, approximately 600 Svobodniki (Freedomites, Sons of Freedom) including 365 children were arrested, and 546 convicted, for public nudity. A special prison colony was built for these Freedomites on Piers Island in the Strait of Georgia off Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. In 1933, 570 were jailed, costing many millions of dollars. Most news falsely reported they were Doukhobors. In 1932, the new Doukhobor leader, Peter P. Verigin Jr., son of assassinated Peter V., was "... sentenced to 18 months in the Prince Albert penitentiary for perjury and tampering with a witness ...", and the government planned to deport him. (59) His deportation was stopped by Peter Makaroff, attorney and Independent Doukhobor. In May 1932, her book The Pilgrims of Russian-Town, based on her master's and Ph.D. theses, was published. The subtitle of her book was forgotten: "Общество Духовных Хрисиан Пригунов в Америке, The Community of Spiritual Christian Jumpers in America: The Struggle of a Primitive Religious Society To Maintain Itself in an Urban Environment." Though Pauline Young's subtitle correctly defines her subjects as Spiritual Christian Pryguny (Jumpers) who use a new ritual book called Dukh i zhizn', she overwhelmingly mistakenly calls them Molokans (at least 1500 times) in this book and all her publications, lectures and news reports. Why? Did the arrests of hundreds of alleged "Doukhobors" and a leader influence her? How could this happen? Twice she stated there are 200 families of "Molokanes" in San Francisco (pages 16, 262), but she never visited them. It's a mystery why she never met real Molokane and Pryguny in San Francisco who do not use or worship with the Dukh i zhizn', who met in separate halls; or Pryguny in Mexico, or in Arizona where Pryguny met separately from Maksimisty who smuggled the writings of M. G. Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) to America. It appears that she ignored the larger immigration population, and mislabeled it, to focus narrowly on only those who were in and around Los Angeles for most of the decade from 1923 when she arrived to 1932 when the book was published, with a focus on their juvenile delinquency. Why did she use "Spiritual Christian Jumpers" in the title of her book, then immediately switch to the word "Molokan(s)" used 4 times on the first page of text (page ix)?
The other groups and tribes of Spiritual Christians from Russia did not matter to her since the focus of her study was limited to the research subjects on the east side of Los Angeles and how to assimilate them. She probably thought it was plausible that they all evolved from Molokane, then claimed it was true by manipulating facts. She recast Prygun history, in my opinion, mostly to get her PhD and establish her career as a professor of sociology. The following is an introduction to a more thorough analysis in-progress. Watch for updates. Her mislabeling broadly spread the misnomer initiated by Demens 2 decades earlier, providing a fake scholarly endorsement for false label changing which continues up to this taxonomy. ^ Contents ^
Statistical analysis of her name hijacking is in-progress. Here is a fragment: Frequency Count of Selected Terms Used in The Pilgrims of Russian-town, 1932.
** Though P.M. Shubin was featured with a full-page photo in the front pages (p.iv), he did not claim that the Kniga solntse, dukhk i zhizn' was a holy book. The chart above shows that in her 1932 book, Young used the "Molokan" terms 890 times, or an average of 3 per page (890/296 = 3.0) — 44.5 times more than the Prygun terms (890/20 = 44.5), 98% of occurrences (890/910 = 0.978). In contrast, she states 8 times that "Jumpers" (Pryguny) is their actual label, and it is the only term shown in her book title, but only in Russian (below). This is like publishing a book titled Собаки (Sobaki : Dogs) on the cover, then on the inside pages saying they are 98% Koshki (кошки : cats) — totally deceptive!  Note that the transliterated "Pryguny" does not appear in the index, page 293. In English she defines them as "Jumpers" 8 times:
She mentions the Postoyannie / Steady terms only 7 times, 35% as often as Prygun terms (7/20 = 0.35). "Steady" is defined 4 times, twice by referring to the Dukh i zhizn' (pages 65 and 295). This suggests that she used the Russian term (postoyannie) from the perspective of the Dukh i zhizn'. to generally refer to "those other people" who are specifically identified. In contrast, Molokane call themselves Molokane, from their perspective, which she did not know because she did not visit or interview Molokane. Many Molokane know they are called postoyannie by Pryguny and Dukh-i-zhizniki, but they do not use that term when self-labeling. The term Postoyannie is a hostile label mainly used by zealots to insult Molokane. (Before that, Molokane was a hostile label used by the Russian Orthodox Church to insult selected tribes of Spiritual Christians. Each faith has insults their heretics.) One Molokan elder and pundit in Russia from Tsaghkadzor, Armenia (Darachichak, Darachak in short) was recorded on video by presbyter Viktor Tikunov explaining to their Molokan youth in Russia: "Why do the Pryguny call us postoyannie? (Why do the Jumpers call us constants/ persistent/ original/ unchanged/ steadfast?) This video may be offline now. In essence, he explained that they call us "constants" for 3 reasons (a trinity):
Note that Young's frequency of use of the term groups Prygun (20) and Dukhobor (18) are about the same in her book about Pryguny. If the Youngs had moved to San Francisco instead of Los Angeles, her theses, books and articles could have documented the Molokan congregation as a distinct faith from the smaller Prygun congregation, each with their own meeting hall/ house a block apart on Potrero Hill. She probably would have included the nearby congregations of Spiritual Christian Baptists from Russia, Spiritual Christian Evangelicals from Russia, and Spiritual Christian Pentecostals from Russia. Her book could have been an accurately labeled story of 5 different folk-protestant faiths from Russia on "The Hill". Young referred to the religious text Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' 102 times (blue section in above graph), 5 times more than the Bible (21 count). This empirically suggests that the Bible was much less significant to her subjects than the Dukh i zhizn'. The last row of the chart above (orange), shows how many times she used terms about deviance — at least 276 times. This count suggests that the impact on society by these immigrants appears to be a major focus of her book. Social deviance is also the emphasis of her husband's work. More word count analysis in-progress. ^ Contents ^
After her passage on page 64 where she summarized varieties of Staroobryadsty (raskolniki), she states: Consequently, schisms occurred among the schismatics, creating many varieties of independent sects,(3) whose characteristic trait is as difficult to describe as "the contour of clouds fleeting across the sky." (Bold added.)Next, on page 65, she tries to describe that which is as difficult as cloud shapes — folk-protestant(57), Spiritual Christian faiths: The Molokan sect, after it was formed from the Dukhobors (Error A, below) divided further; and its most important offshoots are (numbered for clarity): Errors: ^ Contents ^
In "Glossary" (page 284), Young defines: 'Postoyannye [sic] — "Steady," a sect within the Molokan [sect] which does not recognize any special validity in "jumping." 'She did not know that the Dukhobor heresy was documented after the Molokane heresy, therefore Molokane were actually formed from Ikonobortsy, as were Dukhobortsy. She did not know that Subbotniki did not modify Molokan doctrine, which is why Molokane were insulted by the more zealous and aggressive Spiritual Christians with the hostile label of postoyannie (steady, steadfast, persistent, constant, unchanged, original). It was varieties of Pryguny who mostly adapted Subbotnik holidays and food laws but did not entirely convert to a full Saturday Sabbath. Her major errors are not realizing that postoyannie is the Prygun-insulting pejorative, a code-word for Molokane, to hide the fact that Pryguny are not Molokane. Was she a "mark" of this linguistic scam? Why did she let herself get fooled? Or, was she really fooled? Did she play along with the definition switch on purpose? If so, what was her purpose? Perspective Points of View Note that her definition of Postoyannie (offshoot 4 above) is from the perspective of the Kniga solnste, Dukh i zhizn' (Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life), a relative definition. Examples: from the perspective of a dog, a cat is a pest; from the perspective of a cat, a dog is a terrorist; from the perspective of cat, a mouse is food; and, from the perspective of a mouse, a cat is a terrorist and killer. More troublesome is that after her division of the "Molokan sect" into 4 offshoots (numbered above for clarity), her footnote #4 on the bottom of page 65, — 4. See Spirit and Life, p.21. the resemblance of this sect to the Molokans is so close that they attend the same sobranie and even intermarry.— appears to imply, citing the Spirit and Life, that postoyannie resemble Molokans, therefore she is including them in a non-scientific scrambling of definitions with Pryguny, using her own umbrella term: "Molokan". In short, on page 65 Young splits the "Molokan sect" into 4 "offshoots", yet only discusses the 3rd "offshoot" "Spiritual Christian Jumpers" who just compiled a new religious text, Dukh-i-zhizn', creating a new family of faiths, as if they represent all 4 offshoots and have one identity — Molokan. In my opinion, she failed to properly scientifically classify her subjects. Why? Probably due to lack of English, analytical insight, and time. ^ Contents ^
First, she immigrated in 1913, and was handicapped with English as her second language, as she entered graduate school in 1923 in California, 10 years later. Second, she had little time to manage 2 kids, a full load of graduate courses, and conduct complex thesis research and writing. He husband helped extensively with her struggles while conducting his own research and teaching classes. Though she spoke Russian, it appears that she did not understand that Postoyannie was a Prygun-Maksimist pejorative for Molokane, that Maksimisty and Pryguny are a different faiths, not Molokan, and were transforming into a new cluster of faiths: Dukh-i-zhizniki? If she did understand that she was interviewing at least a dozen conflicting tribes, she chose not to reveal that divisive hostility. It was as if she was describing apples, oranges, pears, lemons, grapefruit, grapes, peaches, tangerines, kumquats, kiwi, strawberries and bananas, only as apples, while ignoring their significant differences, and avoiding the term "fruit". Another analogy. It was as if she was discussing borshch by describing and diagramming the ingredients — cabbage, tomatoes, broth, potatoes, onions, carrots, bay leaf, salt, celery, etc. — then declaring it was really "potato soup", ignoring all the other ingredients and avoiding the term borshch. Would you believe her if she declared that all apples are the same whether round and red, curved and yellow, or round and orange, and small and purple; they are "so close" because they can be placed in the same bowl and eaten with one hand? Would you believe her if she said that dogs make "meow" sounds, hunt at night, and easily climb trees? What if she told you about a new animal called Catdog? Diaspora Molokane, Subbotniki, Maksimisty, Klubnikinisty, Pryguny, and other Spiritual Christian tribes who immigrated from the South Caucasus (1904-1915) and attended common meetings (sobraniya), could intermarry with the new tribes of Dukh-i-zhizniki because they were all considered by zealots to be of "Zion" for following Klubnikin's prophesy to leave Russia for refuge (pakhod), (Berokoff, page 14), and if they abandoned their heritage faith to be confirmed into a Dukh-i-zhiznik faith. The most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki consider marriage converts from Molokane, Subbotniki and Armenian Pryguny to be lower Spiritual-class members, because they lacked a "Spiritual blood line." Intermarriage with "other" faiths (the 666 false faiths mentioned by M. G. Rudomyotkin) result in ostracism by most Dukh-i-zhizniki. Young apparently did not realize that the few Molokane in Los Angeles had no prayer hall or presbyter, most assimilated(19) while a minority integrated among Dukh-i-zhizniki, mainly by joining the most liberal "Big Church." They were in plain sight, probably met her, but she could not distinguish who was what. Only one of her published case interviews mentioned Postoyannie. A woman married out, divorced and married a "Steady" and began to attend a sobranie. She is quoted by Young, page 79: ... on Judgment Day [Day of Atonement, Sudnie den'], I was so inspired by the service that I felt that I must get up and say something. And say I did. I at once realized that I did the wrong thing, as I heard the people around me comment that a woman of my character should hold her tongue in "church." I was humiliated and broken up over it, for I know I am trying to do my best. I am convinced I was right. I just have to keep on trying until they accept me again....Young's data does not reveal social context, the variety of religious and social politics among and within congregations. The woman quoted above could be in a zealous or liberal congregation. Her family could or could not have "front-row" males whose presence and public contact could provide social-status protection for her. Perhaps only one aggressive person led a verbal attack, and no one intervened. Her fiancial status is not known. Rich families are more respected by zealots. Her "Steady" husband may have had little or no social status within this congregation to defend his wife. He could have been from a prominent family, divorced and remarried. These unknown social variables would affect the subject's group acceptance, and interpretation of Young's interview data. Young used the "Spirit and Life" book title 25 times, 5 more than the 20 Prygun terms; and when added to the name count of the 2 prophets/elders (Rudomyotkin, Klubnikin) whose writings constitute most of the new religious text, the "Spirit and Life" terms become 51, or 2.6 times (51/20=2.6) the Prygun terms count of 20; and adding "Ararat" (7) and "Zion" (3) increases "Spirit and Life" terms to 61, 3 times (61/20=3.05) the Prygun terms. Of the 3 prophets/ elders, Rudomyotkin is mentioned nearly twice as often as Klubnikin and Shubin combined (20/11=1.8). ^ Contents ^
Her book is mostly about Dukh-i-zhizniki. Though the "front row" (prestol : престол) position of "prophet" (prorok : пророк) does not exist in Molokan congregations, Young used the prophet(s) term group 41 times. Young uses the general broader term clusters of "sect-colony-brotherhood" second in frequency compared to the Molokan term cluster; but, even when combined, they compare at 71% of the frequency of the "Molokan" terms ([255+355+115]/890 = .709). She did not know or report that the original label for the first immigrants in 1904 was the Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians. Due to the high frequency of mixing misleading terms and names, typical readers of The Pilgrims of Russian-town mistakenly infer that Rudomyotkin is the main prophet of Molokans who use the religious text Spirit and Life and jump during services, and their kids are delinquents. A myth. Disinformation. Bad Science. Closer examination, or a historical revision, shows that her subjects were folk-protestant Spiritual Christian Pryguny, as stated in her title, who are producing a new sacred text they first titled Dukh i zhizn'. (Final Russian title in 1928: Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' : Book of the Sun Spirit and Life) They were Spiritual Christians in Russia (heterodox, non-Orthodox Russian citizens, heretics, sektanty [Russian for "sectarians"]), some of them identify as a "brotherhood" community of faiths, not a single faith; but, Young insists on repeatedly labeling them all with an incorrect single term (Molokan), a faith with which she has no personal experience. She never interviewed a Molokan congregant,* yet mentions San Francisco 11 times in her book and presents them all as the same people, based on secondary and tertiary sources. She does not understand that Postoyannie is a pejorative used to dis Molokane, a different faith thriving in San Francisco but extinguished in Los Angeles. The data shows that Young overwhelmingly falsely presented non-Molokane as Molokane. It was like reporting dogs are cats, apples are oranges, red is green, 2+2=5, etc. * There was never a Molokan meeting hall in Los Angeles, or Southern California, ever.As a Russian-speaking social scientist, Dr. Young should have recognized that these immigrants were not Molokane. Some were Maksimisty who were insisting that all congregations only adhere to their rituals and new religious text, which some intended to to replace the New Testament. Others were Davidisty, Klunikinisty, Sionisty, etc. On pages listed in footnote 1,On page 35, she describes "revelations" and "prophets" which do not exist in the Molokan faith as positions of elders at the altar table (prestol). Her false label transfer from Prygun to Molokan appears on page 34: .. Molokans "jump" and "speak in tongues." This religious ecstasy has won for the Molokans the name of "Jumpers", which designation they accept." ..Won? Is she really saying that Molokane were "awarded" the name Jumpers, due to their outstanding religious ecstasy? What word was she thinking in Russian? I suspect she may have been thinking of "gained" in Russian, but mistranslated.
——————————————————————————— Master's thesis 1926 The earliest evidence for name switching is preserved in her masters thesis, in which there are the only 2 instances of the word "won" on pages 60 and 77. The term "won" may have originated from Informant #24, translated on page 60: "Our refusal to observe the numerous fasts*, not less than one-third of the year, won the name "Molokane" for us. We don't object to this name. It shows one of the fundamental differences between us and the Russian Orthodox people
In the 1700s, the Russian descriptive term "dairy eater during fasts" (molokane) also applied to people who were later named "spirit-wrestlers" (dukhobortsy). Above this quote, Young paraphrases the term "won" as "grown out": It is interesting to note that the Molokane have been named not only from their religious practices - "Jumpers" - but their commonest name has grown out of their food habits "Milk-drinkers."She mistakenly associated "Jumpers" with "Milk-drinkers". On page 77, Young states the converse: Uplifted by a sense of the presence of the Holy Ghost the Molokane fall into ecstatic trances. The following documents show the characteristic form of behavior of the Molokane during religious ecstasy. It has won for them the name "Jumpers", which they have accepted and apply frequently to themselves.Though Informant 24 said: "(We Pryguny?) ... won the name 'Molokane'", Young reversed the definition to "Molokane ...won ...the name 'Jumpers'." Though unlikely, it could be that elder Informant #24 was originally Molokan then converted to Prygun, which Young does not reveal. Young claims "Molokane have been named ... 'Jumpers' - but their most common name ..." is Molokane. Logically: Molokane = Pryguny = Molokane. This equation contradicts Chart I (below). Hints about how she may have illogically substituted Prygun for Molokan are in her 1926 masters thesis, beginning with Chart I on page 43. Colored labels, numbers and lines are added for this analysis. 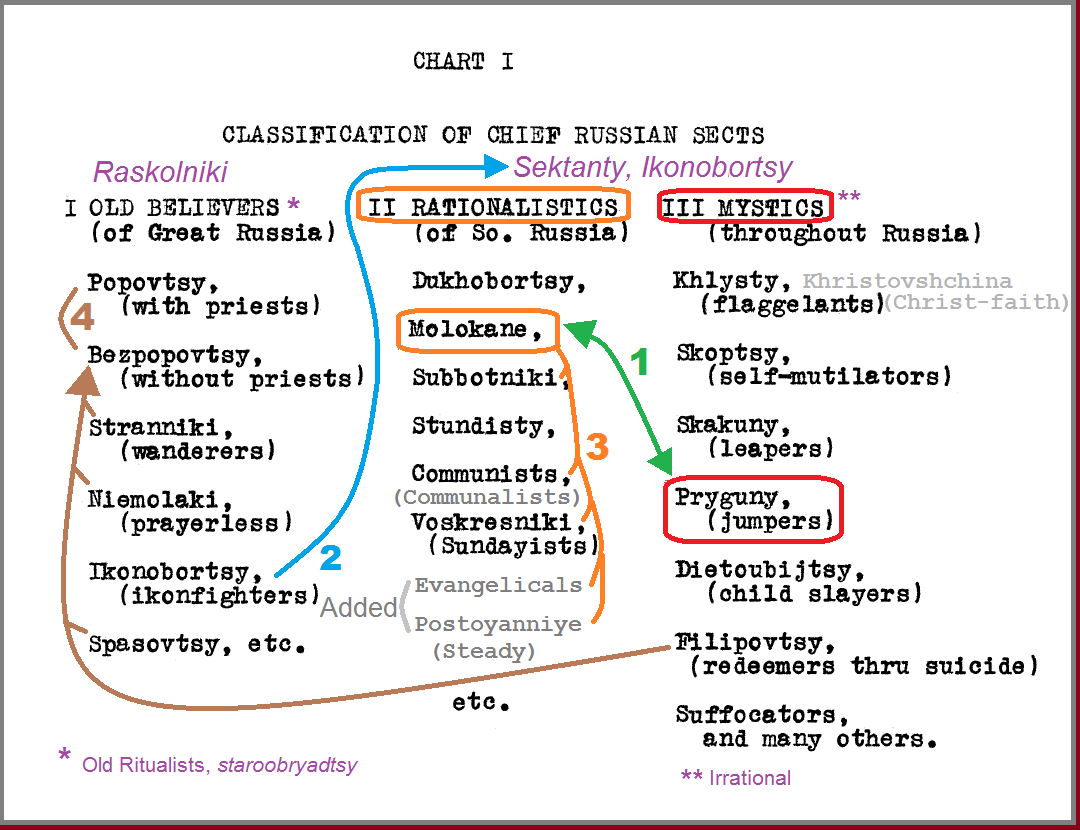 On Chart I, I marked and numbered 4 things in color to help us understand how she may have been thinking, and not thinking, in 1926. She had never met members of any of these religious tribes in Russia, and was trying to make sense from what little was published that she could easily find in libraries. Note that Column I, Raskolniki translates as schismatics, and generally refers to the Old Ritualists (staroobryadtsy), the original (postoyannie) form of the Orthodox which are often called Old Believers, the label term she chose for Column I. Columns II and III are often labeled "Rational" and "Irrational" by other historians, and the Orthodox church called both columns sektanty (sectarians) and ikonobortsy (iconoclasts, icon fighters). "II Rationalists" were also widely distributed "throughout Russia" before 1800.
The Young's probably did not meet John Kulikoff in Los Angeles in the 1920s, who accurately informed reporters at the Prescott jail in Arizona:"The Holy-Jumpers are not Molokans. ... We are Holy-Jumpers. Molokans do not have the Spirit." (Only Blessed Bread For A Holy Jumper, Prescott Journal-Miner, August 10, 1917, page 5.) This was by one of the few journalists who understood and reported the actual religious identity of those arrested for not registering. Note the editors of the 1928 edition of Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' signed (endorsed, authored) as Братскiй Союзъ Духовныхъ Прыгуновъ (Bratskii Soiuz Dukhovykh Prygunov : Fraternal Union of Spiritual Jumpers (page 8 Russian, page 4 English), not as Molokane. Their Prygun identity ironically contradicts the first line of the the Foreward on the previous page: "To the United Brotherhood of Spiritual Molokan Jumpers in Los Angeles America"; and it entirely contradicts the following history chapter ("Essay on the Religion," pages 11-64), which present the history of Molokane, giving the false impression that this book is about Molokane. This contradiction, though in plain site, appears to be overlooked by most all Dukh-i-zhizniki. I can find no logical reason for this deception except that she was confused by the people she interviewed, who were of many Spiritual Christian tribal faiths, and she was forced to write something, anything, in a limited time, while raising 2 kids. She apparently took an easy path, rather than say honestly there is no Prygun history that I can find, she decided to claim they are all Molokane , Thoughand stuck to this story. Where did she get Chart I? Probably to keep track of what she was reading about all the vague non-Orthodox faiths in Russia. She evidently made notes and this summary diagram became Chart I. It shows a taxonomy of her study subjects, as she may have understood them, in context of other heresies in the Russian Empire she found in literature. This was an excellent method that she really screwed up, in my opinion. Notice the 3 column headings: I, II and III. The Raskolniki (staroobryadtsy) are in column I (except Filipovtsy). Two kinds of Spiritual Christians (Rational and Mystical, or irrational) are in columns II and III, which the government treated different, hence the labels. Contrary to the chart title "Classification of Chief Russian Sects," typically only columns II and III were labeled sektanty (sectarians) in Russia, except the Flilipovtsy who were many of whom were also called ikonobortsy and heretics by the Church and government; but many called themselves dukhovnye kristiani (Spiritual Christians), and in the mid-1900s historian anthropologist A.I. Klibanov called them "folk-protestants ".(57) The rational sects (column II) were more tolerated by the government and judged by the Church to be susceptible to rehabilitation. They were offered incentives to move closer together and populated the newly conquered borderlands in the south and far east. For much more, see Dr. Breyfogle's 1998 doctoral dissertation and 2005 book: Heretics and Colonizers; and our overview with links at: Q81: How much did Freemasonry influence Doukhobor theology?, Spirit-Wrestlers Blog, 21 October 2018. Irrational "Mystics" (column III) were more "irrational", "infectious" and dangerous, because they contaminated the Orthodox population with fanatical heretic (non-Orthodox) ideas and needed to be isolated, quarantined, from the general population of healthy Orthodox believers. They were more likely to be arrested and/or exiled to the farthest territories from Central Russia, and monitored. Notice that Pryguny are in column III. Filipovtsy were the most irrational type of Old Ritualist. The mystery I am trying to solve, is how could she have combined Molokane in column II with Pryguny in column III, as if she is creating a hybrid but not naming it scientifically, rather merely stating, or assuming, or pretending, or guessing that Pryguny are actually Molokane. Then without explaining her assumption, she primarily uses the "Molokan" label in all her papers and lectures. One possible explanation is that Molokane in Los Angeles were dominated by Pryguny who suggested a hybrid (not hyphenated) name "Molokan Jumpers" in English as a compromise, which appear in the signs. And, 4 terms — "Spiritual", "Christian", "Jumper" and "Molokan" — appeared together on government documents. Young did not recognize, or refused to recognize, that her subjects in the Los Angeles "Russian-town" were new faiths not yet documented, with different rituals than Molokane, Pryguny or Subbotniki, and began using the new sacred text she appears to have helped edit. She appears to ignore the petitioners who during W.W.I. identified themselves as Pryguny, as did those who approved printing the Kniga solntse, dukhi i zhizn'. The writing and evidence was in plain sight. Maybe she could not see the forest for the trees. Maybe she fudged that Pryguny were Molokane because she could not find much, if any, history about Pryguny, which she needed for her thesis. It is clear that the Dukh-i-zhiznik history presented in her theses, books, articles and lectures is wrong. Therefore the false label "Molokan" was was spread by the newspapers and others who quoted her work. She fooled herself and everyone who used her research regarding Spiritual Christians from Russia in Southern California, including the Dukh-i-zhizniki. She had a rare opportunity to declare the birth of a new faith (family of faiths) in Los Angeles, and of people who created and use a new book (she helped edit), and prophets, as a foundation for their liturgy. Most unfortunate is that she failed to give them a new name, their own unique identity. Drs. Young were professionally noted for being affiliated with the new School of Social Administration developed by the University of Chicago from the Chicago School of Civics and Philanthropy, where he was one of the first instructors and she was among the first graduate students. The Dean of the Chicago School, Robert E. Park, who wrote the preface to her book, was nationally recognized as the "father of human ecology." Dr. Erle F. Young's 1922 Ph.D. thesis is: "The Use of Case Method in Training Social Workers." Together, Drs. Young, helped pioneered social research about urban juvenile delinquency in Los Angeles and the nation. I have not found anyone yet who questioned their expertise. While appearing reliable due to academic affiliations and credentials, her research had major flaws. Perhaps her focus on juvenile delinquency was so narrow that it limited a broader perspective about the faiths of her subjects, or the subjects varied too much for her to comprehend how many different faiths were in her sample population, or only a few interacted with her in a formal manner so as not to reveal their diverse faiths. No matter what the reason(s), her work, like that of all scientists, is subject to scrutiny and improvement. ^ Contents ^
Book Promotion 1932 was an eventful year for Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles, and much relevant news is archived in local newspapers, much on the front pages. In order:
In February and March 1932, diving champion Mikey Galitzen-Riley is in the sports pages of the Los Angeles Times, and New York Times. He competes at national diving meets preparing for the international Olympics to be held in Los Angeles. During the month leading up to the Summer Olympics, he and brother Johnny Galitzen-Riley are often in the sports news. While Young's book was being promoted, news from Canada was falsely reporting that Sons of Freedom (Freedomites) were crazy nudist communist Doukhobors. She may have protected the image of Dukh-i-zhizniki in Los Angeles by ignoring the Spiritual Christians about 1,300 miles north in Canada, and falsely lecturing about the history of "Molokans" 400 miles north in San Francisco as if they were in Los Angeles. In May 1932, approximately 600 Svobodniki (sovereign people : Son of Freedom) including 365 children were arrested, and 546 convicted, for public nudity. A special prison colony was built for these Freedomites on Piers Island in the Strait of Georgia off Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. In 1933, 570 were jailed, costing many millions of dollars. Most news falsely reported they were Doukhobors. On May 2, 1932, page 1 of the Los Angeles Times reported about "200 nude Doukhobors" : "Doukhobor Nude March Ends In Jail; Itching Powder and Hose Lengths Used by Police in Rounding Up Panders." Fake news, they were "Freedomites, "Sons of Freedom", NOT Dukhobortsy. In the next 5 days, 118 Sons of Freedom were sentenced under the new public nudity law. Due to confusion about who is their leader, the Community Doukhbor leader P. P. Verigin is also arrested and imprisoned. Later an effort to deport Verigin to Russia was launched, but failed in court. On May 10, 1932 the Daily Trojan (USC newspaper) reported on page 1 that an international Soviet-American businesses and cultural exchange symposium :"World Affairs and Russia's World Policy” was being held in Pasadena. Business and community leaders, politicians, government officials, journalists and professors attended. On May 18, 1932, page 2 (column 3 bottom) the Daily Trojan reported: "Dr. Pauline Young Writes New Book" "Pilgrims of Russian Town" is the subject of a book by Dr. Pauline Young, wife of Dr. Erle F. Young of the sociology department at S.C., recently published by the University of Chicago press. Information on the book, which is a detailed comprehensive study of the Russian sectarians on Boyle Heights, Los Angeles, was compiled by Dr. Young from her study of these people, and is an outgrowth of her masters thesis and her study in the sociology department for Doctor of Dissertation."On May 22, 1932, the Los Angeles Times Sunday Magazine reviewed featured the book: "The Pilgrims Of Russian Town, by Pauline Young: Refugee Colony Lends Picturesque Tone To Our City." The article reported they settled in the Bethlehem district due to advice of Count Lev N. Tolstoy, and there are 6000 residing in the Flats area. Actually, Tolstoy recommended Canada, it was Demens who personally brought them to Los Angeles, and 6000 is probably an estimate of all whose ancestors came from Russia (Orthodox, Jew, Armenian, folk-protestant). On July 4 and 24, 1932, Young's book is mentioned twice in the Los Angeles Times in "Snapshots At New Books." From July 30 through August 14, the 1932 Summer Olympics are held in at Memorial Coliseum (renamed "Olympic Stadium"), next to the University of Southern California. Micheal Galitzen ("King Mick") wins a Gold and Silver medal for diving, and is shown in several news photos and reports. After the Olympics Mickey announced his engagement to Georgia Coleman, his female Olympian counterpart. They planned to become stage actors. Later their nuptials were cancelled, she soon got polio and died within 8 years. Since 1924, the team of Mickey and Johnny Riley, the Galitzen brothers diving champs were in the national press more than 100 times and on several newsreels shown in theaters. About 1980, John Galitzen told me that their coach, Fred Cady, was afraid their last names sounded too German, and chose "Riley" as a "more American sounding stage name." In mid August 1932 about 40 families in Central California and Oregon with a fund of about $225,000 planned to buy a large ranch in central Oregon, 15 miles west of Woodburn. Names include: John Thomaso[ff], John Potopoff, Nick Bizieff, Pete Efseaff, Alex Efseaff, Pete Shubin, Andrew Shubin, Efim Efseaff, Martin Prohoff. The story was not reported in Los Angeles newspapers, but was probably was spread orally. On August 29, 1932, Bill Samarin was announced in the Los Angeles Times as a sports champion at Pecan Playground, Flats. From September to December 1932, the Y.W.C.A joined with the International Institute, led by Miss Esther Bartlett, daughter of Dr. Rev. D. W. Bartlett, and guided by the U.S.C. School of Social Welfare, to host a series of Social Welfare Symposiums about the 50+ ethnic groups, cultures, races and nationalities in the Los Angeles area. Assimilation problems of Chinese, Japanese, and Russian groups were featured. In late 1932 "Big Church" at 3rd and Gless streets (NW corner?) in Flats was cut in half and moved to Lorena Street. The open house prayer was held on February 26, 1933. My uncle William Andrew ("Will, Seecoe") Shubin told me that many in his generation considered that "Big Church" moving out of the Flats to the east end of Karakala was the single most important event among Spiritual Christians in Los Angeles during his lifetime. Maksimisty would probably say that pakhod to Australia in the mid-1960s was the major event. The sunflower seed (semichki) vendor in the Flats followed the crowd and placed a second "seed wagon" on the Lorena street sidewalks first in front of "Big Church", and later near the new location, at the alley north of Whittier Blvd. The A&Z Nut Wagon closed in 2021. On November 2, 1932, the Los Angeles Times reports about the August 1931 death of David Uren near Bakersfield, who was shot and killed by David John Pivovaroff, 25, who had a mental illness. In June 1932, Uren's father Jack sued the Pivovaroff family for $25,000, which contradicts the statement on page 95 : "He must no sue a 'brother' in court". On December 14, 1932, the Los Angeles Times reports about: "A Little Russia in Mexico." ... On February 27, 1933, a front page story in the Los Angeles Times with photos announced : "Little Russia Dedicates Molokan Sects Church." Young's propaganda almost worked. "In the heart of little Russia, lying within the shadow of the City Hall, was enacted yesterday a historic episode in the communal life of its Landful of people—the dedication the First United Molokan Christian Church. .. 6000 population.. Vaseley T. Susueff leader ... Quaker-like .. dietary laws and holidays of the Israelites .. largest US colony .. mile square .. bounded by Utah st & Boyle av, 1st & 9th st .. came to LA from Canada in 1895 .. twin sect Doukhobors [false news] .. staunch pacifist .. for this reason ... driven out of native country." Most left Russia for economic reasons, citing increased rents and taxes. On May 10, 1933, 25,000 "un-German" books were burned in Berlin and in 34 university towns across Germany by Nazis during a nationwide "Action against the Un-German Spirit", a literary purge or "cleansing" ("Säuberung") by fire. On May 13, 1933, The Federal Emergency Relief Administration and the Agricultural Adjustment Administration were established to provide help for the needy and farmers. In the 4 years from 1929 to 1932, net income of the average farm operator fell about 70%, from about $6,300 to $1,900. (U.S. Bureau of the Census, 1965, p. 283). In 1933, Young authored The Art and Science of Interviewing : A Sociological Analysis, published by Western Educational Service, copyright January 10, 1934, in a 276-page mimeographed edition. She presents herself as an expert, Ph.D., professor, on interviewing; and her work was not questioned until this Taxonomy. In 1934 the Canadian Government barred Communal Dukhobortsy in British Columbia from voting federally. "The Conservative Prime Minister of Canada ... wanted to bar all Doukhobors in Canada, but he failed to get support of Parliament because of his discriminatory intent." Their rights were restored 37 years later, in 1956. In 1934 Dr. Erle F. Young published Modern Social Casework: A Study and Reference Manual for Social Case Workers in Los Angeles County,Western Educational Service, 532 pages, in which he extensively cites his wife's book: The Art and Science of Interviewing. On April 5, 1934, page 1 of the Daily Trojan announced: Dr. Pauline V. Young, lecturer in sociology, civic center division of the School of Government, has just been awarded a grant-in-aid for 1934-35 by the Social Science Research council of New York.In 1935, her 1933 mimeograph was enhanced and published as Interviewing in social work : a sociological analysis, 416 pages. In November 1935, the American Journal of Sociology, published by the University of Chicago, Drs. Youngs' alma mater, published a paper about Sons of Freedom, falsely labeling them Doukhobors: "Canadian Communists: The Doukhobor Experiment." The protest of the Sons of FreedomIn Septembe 1937, the Sunday Los Angeles Times ran a series of articles about foreign colonies in the city. The 6th article described 4 types of immigrants from Russia, estimated at 60,000.(54) Vague descriptions were given, omitting names of organizations and leaders, and exact locations. The "complicated" Russian colony was actually many groups which were clustered for simplicity into 4 major categories based on general summaries of religion, origin and neighborhood.
* Several factions of Dukh-i-zhizniki receded to their own sub-faiths, and several zealot-led factions divided. Every congregation did not accept all the other congregations. Within congregations, not every head of a clan accepted all the other heads of clans. Clashes continue into the 2000s.In 1944, the Youngs were retired in Modesto, California. They attended the local Jewish synagogue: Congregation Beth Shalom. Though the Youngs lived about a 3-hour drive from San Fransisco, they probably never visited the real Molokane sobranie there. Though they lived about a 30-minute drive from Manteca, they probably never visited the Dukhobor colony there. Though they lived about a 2-hour drive from Kerman, they probably never visited the 2 Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations there (at that time). Her published work only covered the various Spiritual Christians from Russia in the East Los Angeles district up to about 1930, now named the Boyle Heights district. In the 1950s, Young intended to update her 1932 book to examine how her prediction that they would assimilate within 25 years, was not happening, mainly due to the work two youth organizations — the Young Russian Christian Associations (Y.R.C.A.) and the United Molokan Christian Association (U.M.C.A.). Unfortunately her notes were lost in a fire.(69) In January 1953 her only son shot his wife and himself (buried in Tracy, CA), and she raised their 3 daughters. 4 months later, in May 1953, her husband Dr. Erle Young died, and was buried in Modesto. In 1969, 37 years after Young published her 1932 book, J. K. Berokoff continued to infect the next generations of Dukh-i-zhizniki, scholars and journalists with the false "Molokan" label. Most all remained misinformed today with false history, except YOU, the persistent reader. Congratulations for getting more than half-way though this Taxonomy. Keep on reading, and tell a friend what you learned, unless they are likely to punish you for reading forbidden text. In 1977, Young died and was buried in Modesto, California, next to her husband. I was told that Maksimist Fred Wm. Prohoroff visited her several times, in Modesto. To my knowledge, she never visited real Molokane in San Francisco, nor was invited to lecture to Dukh-i-zhizniki in Los Angeles. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————Reasons for deception Upon learning English, many who lived in their ethnic enclave in Los Angeles became a fraid and ashamed to be known by their actual faiths imported from Russia — Pryguny or “Jumpers” in English; Sionisty, Subbotniki and Noviy israili about which local Jews protested in court, or by any other term except the false “Molokan” label, though their religions were not Molokan and the most zealous despised Molokane. Unfortunately their preferred correct general term "Brotherhood of Spiritual Christians" faded from popular usage by W.W.II, perhaps sounding too common or American for those who chose to live in America. Maybe it was too long; but could have been shortened to B.S.C., or Brotherhood. In contrast, the most zealous Russian-born Maksimisty who believed they retained the "true faith" and will return to Mt. Ararat before the Apocalypse, planned to leave soon, tended to call themselves Pryguny, and believed they were "chosen" and were not concerned with establishing themselves in America, nor hiding their faiths and ritual books. The confusion of labels often created a silly hybrid term, combining Russian and English words — Molokan-Jumper — to appease both oral stories. Why did they not use all Russian or all English terms : "Molokan-Prygun" or "milk-eating-jumper"? (Try explaining that last term to your American relatives.) Upon arrival in America, most Spiritual Christians remained in the city, or returned to urban life after most of the American land deals failed. (Speeks' report about Hawaii, page 29, is wrong. See above : Demens.) While Maksimisty failed to return to Mt. Ararat, most Klubnikinisty failed to find a land of refuge, and Noviy israil' failed to move to Israel. By default the promised land for the majority transformed into "kingdoms in the city" — diverse adjacent separate colonies in the Flats and Boyle Heights, among a melting pot of 50+ nationalities and races. By the 2000s most congregations relocated eastward to the last white area in Los Angeles County — Whittier — farther away from feared Mexicans. The Southern California metropolis greatly aided these poor immigrant peasants with a rapidly growing economy in need of unskilled labor for much higher wages than rural life, a very mild climate, low cost "slum" housing with easy access to abundant utilities (water, gas, electric, sewage), low-cost convenient public transportation, and a huge year-round food supply. Charities and schools provided many services: free meeting rooms, free translation services, free medical and dental care, free child day care and diapers with baths, free milk for babies, free meals for kids, free city/county burials, free court marriages, free education, free supervised playgrounds until dusk, free youth clubs, free supervised sports for youth, free classes for adults by Russian-speaking teachers (English, general education, citizenship, cooking, sewing, shop skills), free job training and placement, free advice (legal, colonization, economic), free rubbish for recycling which launched many family businesses. The big city government and environment offered entertainment (movies, radio, sports, concerts, plays), local police and fire services; and a choice of many Protestant faiths and city temptations. Groups of sociology students from U.S.C. regularly delivered items (food, clothing, health care products) door-to-door, and school teachers gave clothes to their student, especially underwear for girls. Most immigrants found economic and religious freedom in their urban enclave irresistible compared to rural alternatives. After the Molokan Agricultural Colony failed in Hawai'i in early 1906, most Molokane resettled in San Francisco and most Pryguny-etc. in Los Angeles and Mexico. The minority of Pryguny in San Francisco had no Maksimisty in 1928, rejected the Dukh i zhizn' and kept their original “Holy Jumper” identity until merging with the Molokane when their building was sold in the 1960s. The only absolutist was their last Prygun presbyter Alexei John Dobrinen, who insisted on being buried only with Pryguny in East Los Angeles, while his wife (Anastasia) and kids were buried with Russian sectarians in Colma. In Los Angeles, upon learning English, most of the Americanized younger Pryguny-etc. were taught to say they were “Molokan” or "Protestant," while the most aggressive Maksimisty and associated charismatic zealots reported to the press they were Pryguny and Holy Jumpers, and they eventually changed the faith of all congregations in Los Angeles to Dukh-i-zhiznik. Dissenters left the faiths, were pushed out, or were marginalized (allowed to attend if "paid" members, to observe, do as told, but not speak out, challenge or question). The last active public reporting by Dukh-i-zhizniki in Southern California that they were "Russian Molokan Christian Holy Spiritual Jumpers" was in September 1964 when 2000 gathered in San Pedro to send off 32 people on a ship to Australia. The less zealous majority who remained intensified their identity camouflage and issued a press release on October 2, 1964, stating they were not leaving America. ^ Contents ^
Reasons for the pre-1930 Prygun-etc. cover-up continued by Dukh-i-zhizniki are extensive:
^ Contents ^
^ Contents ^
The simple, non-threatening and unique term “Molokan” was simply ideal to distinguish the majority Spiritual Christians (Pryguny, Klubnikinisty, Maksimisty, etc.) in Los Angeles from Russian Bolshevik immigrants, Russian Jews, American Pentecostal “holy jumpers,” and to hide their actual faiths. Only a few families were actually Molokane in Los Angeles, and either lacked a presbyter and/or were too few to establish a congregation, and any effort to form a Molokan congregation was attacked by those promoting the Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn'. Upon immigration some joined other Russian-speaking Protestant churches in Los Angeles, like the Presbyterians downtown, Russian Baptists in The Flat(s) and Russian Evangelic Christians in Boyle Heights. A neutral sounding simple label was essential for both the religious zealots (ancients), and Americanized (moderns) who quickly learned English. The moderns could get education and good jobs by appearing American. Ancients' oral history demands hiding their secret faiths from non-believers and the government, hence most falsely reported they were “dairy-eaters,” “Molokans,” pacifists, Protestants, etc.— anything that appears respectable in English except Pryguny, Holy Jumpers, Spirit Jumpers, Maksimisty, Sionisty, New Israelites, etc. Pryguny never claim to be Maksimisty. Maksimsity sometimes claim to be Pryguny. In a semantically abusive compromise, zealots ganged up on their enemy and claimed to be the "True Molokans," or simply "Molokans." Because Dukh-i-zhizniki had little contact with, or opposition from, actual Molokane organized 400 miles away in Northern California, they did as they pleased in Southern California as fractionated unregulated congregations. Having arrived at the American promised land, Spiritual Christians from Russia were free to join any faith in America, which most did. While specific reasons for leaving their heritage faiths vary by individual, several common factors relate to a clash of new and old world cultures. Many Americanized Spiritual Christian youth could not understand the long services in Russian (a foreign language to them), hard backless benches, old-world traditions and clothes, kissing old people or the same sex, and/or be forced to jump. Youth educated in hygiene recognized that ritual holy-kissing (brother/sister/peace kiss) and communal eating (obshei) borshch from one bowl spreads infection. Homophobics hated same-sex kissing. Some even camouflaged their Russian heritage by legally changing their Russian surnames, or Americanizing them. We think the following list is mostly accurate.
^ Contents ^
By the 1940s, most all U.S. descendants of Pryguny outside of Northern California who remained in the faith transformed into Dukh-i-zhizniki with varying degrees of acceptance of their “new ritual” (noviy obryad). About 90% of Pryguny descendants in the U.S. rejected the new Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths to join organized American faiths, many joining or attending in groups. An American congregation in Whittier CA was nearly half Dukh-i-zhizniki who also attended the Russian services for family and social occasions, often in full costume. I knew of similar behavior among Dukh-i-zhizniki in Fresno county. After learning about Protestant Christianity in America, many doubted that their ancestors were Christian. (Can you be Molokan and Christian at the same time?) Some were ostracized for questioning the elders about beliefs and rituals, a process which continues more than 100 years after immigration. After 100 years, the “Molokan” brand-jacking continues to confuse the people it intended to protect from deportation and shelter from discrimination. Though a majority of Dukh-i-zhizniki appreciate aspects of their Russian cultural heritage, most do not know that real Molokane accept the divorced and intermarried, that Molokane celebrate the Birth of Christ (Christmas), Molokane do not demand peasant Russian dress for worship or beards on men, parting hair in middle, and other typical characteristics of Dukh-i-zhizniki. After a century, most diaspora descendants live scattered in cities, melted into America, and do not know their history or relatives, or care to know. Zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki continue to shun, insult and chase out non-conformists of their rituals, effectively reducing their membership, and either causing new congregations to form or ostracizing members forever. Some of the most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki believe Molokane are their historic enemy, and dogmatically scorn Molokane, Pryguny, Subbotniki and Americanized members as heretics, yet insist in print to the government and to each other that they are “Molokans,” even the “True Molokans.” In Russia their enemy was the Imperial government and Orthodox Church. During the first 2 decades in America their enemy was the government and other faiths, until they were denied returning to Türkiye. After 1940, the American-born Dukh-i-zhizniki took command and identified new enemies within their own faiths and families. Today the worst enemy of these self-professed false “Molokans” are other self-professed false “Molokans.” Dukh-i-zhizniki still retain the Old Russian Orthodox law that apostasy and proselytizing are crimes worse than murder, but to them theft is not a crime. Diaspora prophet and pundit, Fred Vasilich ("Stretch") Slivkoff, since the 1960s often quipped: “We fled Russia to escape prosecutions of the Orthodox Church, came to America and invented our own 'Orthodox Church'!” Slivkoff refers to strict unwritten rules about behavior, dress, rituals, language, etc. Since the 1990s, the Los Angeles area elder singer and historian James John Samarin quotes Pogo: “We have met the enemy and he is us.” In contrast, to the above two comments about their new tribal Orthodoxy, the late "Big Church" elder, Alex Shubin, summarized: "Dukh-i-zhizniki A clash of animositites among Dukh-i-zhizniki resulted in a variety of independent congregations and individuals, including this free-speech website. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————To get a privilege As was done in Old Russia, changing religious identity to get a privilege was done in America. The following 3 incidents further illustrate the name confusion problem. No photo on driver's license — A court ruling in 1984 in California legally allowed Benjamin Stackler, not of Spiritual Christian descent, who testified that he was a member of a Molokan church of one member (himself), to not show his photo on his driver's license, using a 1964 Dukh-i-zhiznik precedent (by John "Ivan" Shubin, 1963). The truth is that all Molokane have photos on their passports and documents with no religious code against photographs. This is like a chicken that can't quack telling everyone it is a duck, and everyone, including the government, believing it is a duck, not questioning why it does not look, walk or quack like a duck. The same holds for Dukh-i-zhizniki who are not Molokane or Pryguny but falsely tell everyone they are, register their organizations with false terms, and falsely title their publications and property signs. Even though a court ruled Stackler was "Molokan," the American Dukh-i-zhizniki would not have allowed him to join their congregations because he was ne nash (not ours), nor would they bury him. Who is he? Он чей? No video — In 1982 about 7 Dukh-i-zhizniki attended the International Doukhobor Intergroup Symposium in Canada, including 3 front row elders, one wife, and 3 in our 30s. When it came time to introduce each guest, the 3 Dukh-i-zhizniki elders saw the video camera and quickly pushed me in front of them, saying Andy you speak for all of us. Their fear was that people back home might see they were at a nee-nash event. In contrast, the only Molokan elder to attend, Edward John Samarin from the San Francisco area, was glad to be interviewed on local cable news. In 1992 the second International Molokan Convention was held, this time in Stavropol territory, Russia. Six Dukh-i-zhinik elders from America attended. Most refused to speak on video. (I have a copy of this video for my supporters.) Remove our names — In August 1997 the Pivovaroff brothers, Morris Moses (California USA) and Jim Moses (South Australia), attended the first Molokan Youth Conference, held in Tambov, Russia. With them were 3 younger family members (Morris M. Morris Pivovaroff Jr, Micheal John Mendrin, Steven James Shubin) — 5 Dukh-i-zhizniki. When their names were posted on the event attendance roster on the Internet, read by many lurking Dukh-i-zhizniki, their relatives were immediately chastised in both countries before they returned home, because their names were shown on a web page with Molokane and the name of the Tambov Orthodox priest. They were "unclean" sinners by association. The Pivovaroff group left the conference early and did not get to tour the oldest Orthodox church in Tambov, and did not meet the priest. For months the brothers were in a frenzy calling my parents in Arizona, demanding that their names be removed. I did not know about their fits during the 3 months I was in Russia, getting married and collecting data. In Tambov they said they will come to our Prygun wedding, but never contacted us. The verbal abuse from zealous Dukh-i-zhiniki was excruciating for the Pivovaroff brothers, as if they were facing excommunication or worse. The original Molokan Home Page website was hosted on the account of a college professor, which I could not edit until I returned to Arizona 5-6 months after the conference, though I could add news by e-mail courtesy of a Tambov university when I was in Tambov. Molokane in San Francisco who attended the same conference were bewildered. Why would someone claim to be a "Molokan" brother, attend their "Molokan" event in good faith, take pictures with Molokane, sing with Molokane, pray with Molokane and lead a prayer, eat with Molokane, then demand shouting that they were not there? At the same time the Pivovaroff's believed in the Dukh i zhizn' and stated that all "Molokan" congregations who use the Dukh i zhizn' in services must be Maksimsity (actually different faiths of Dukh-i-zhizniki). Molokan wedding — 15 years later, on July 15, 2012, elder Morris M. Pivovaroff (Kerman) spoke in the San Francisco Molokan prayer hall during services. I was there doing archival research. Like a chameleon, he again changed his identity. He stated every reason he could think of that he was a "Molokan"
* On Sunday November 6, 2016, about noon, at Dom Maleetvee (Don Julian Ave, La Puente CA) after service prayer for a pomenki, during greeting of out-of-town guests, Pivovaroff greeted the presbyter with the Maksimist identity greeting (Parginal, Assuringal, Yuzgoris! : Паргинал, Ассурингал, Юзгорис!). He did not claim that this congregation was the same as in San Francisco. There are many such examples. The above I witnessed, and I am sure many readers have many more examples which few will talk about. Shame and fear of recording their actual history is ingrained among most zealous Dukh-i-zhizniki which misleads themselves and many who try to understand them, including their progeny. ^ Contents ^
9. Name Confusion By joining many faiths into one label, their original differences and histories are being lost. Scientists could say this conflation is caused by a cognitive bias, creating a normalization of deviance. A few examples of mislabeling:
^ Contents ^
^ Contents ^ 10. Web sites by and about Spiritual Christians Reader beware! Many websites, most temporary, were started in the United States by Dukh-i-zhizniki falsely identified as Molokane. Research about Spiritual Christians on the Internet is in-progress. Authentic Spiritual Christian Molokan information is extensively posted on 4 websites in Russia and this one (molokane.org) in the U.S.:
^ Contents ^
Spiritual Christian Dukh-i-zhizniki
Spiritual Christian Dukhobortsy (spirit-wrestlers) — A comprehensive list of 40+ Doukhobor-created web sites with links to 100+ related web sites is maintained by attorney, genealogist, historian Jonathan Kalmakoff, founder of the "Doukhobor Genealogy Website", renamed the "Doukhobor Heritage Website" in 2021. Since before Dukhobortsy arrived, the Canadian press has persistently mislabeled all Spiritual Christian groups in Canada with the Dukhobor or other false labels, even non-Russian groups, sometimes calling them Molokans. These mistakes originating in Canada have been repeated around the world. ^ Contents ^
11. Classification SongsMolokane, Pryguny, and Dukh-i-zhizniki are can easily be differentiated by their use of songs for worship. All melodies are memorized and sung without instruments.Molokane sing and read only from the Russian Bible. Diaspora occasionally read from an English Bible for non-Russian-speakers. Except in San Francisco California, Molokane typically do not use a songbook or prayerbook during worship, nor are these books on their altar table (престол : prestol). Molokane may sing borrowed songs after prayer service on occasion, but most typically during weddings, funerals, and meals. A notated songbook was composed in the Far East in the early 1900s by a talented Molokan sent to study musical notation in Europe, but never used outside of the Far East. Pryguny borrowed songs from neighboring faiths and adapted folk songs for spiritual jumping and spiritual whirling and dancing. Pryguny share many traits with Methodist Jumpers organized in Wales in the mid-1700s — borrowing pagan folk songs, loud singing, raising hands, spiritual dancing and jumping — similar to some charismatic Pentecostals. Charismatic Christianity appears to have been transmitted from Europe to Spiritual Christians by German sectarians resettled in Taurida Governorate (South Ukraine) in the early 1800s and earlier by various Europeans who worked in Russia. About 2005, the first exclusively Prygun songbook and prayer book were published in Stavropol'skii krai, Russian Federation, with no Dukh-i-zhiznik songs. Song 181 (Sionskii pessennik, Los Angeles) describes the Prygun holidays. Dukh-i-zhizniki are mostly transformed Pryguny who sing and read from many books: the Russian Bible with Apocrypha, Dukh i zhizn' (intended to replace/augment the New Testament) and their own prayer books and song books. They are the only family of faiths in the world which uses the Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn'. They display much more jumping, prophesy, and shout-singing than their predecessor Pryguny. Their song books evolved through several editions which collectively show over 1200 songs and verses, sharing retaining many hymn and song texts, with different melodies, from Molokane and Pryguny, many borrowed while in Russia from German Protestants, some composed in America and Australia with Western folk melodies. Though the published collection is large, the repertoire actively sung is about one-fourth of their song book, with most congregations unable to sing more than 100 songs, less than 8% of the published repertoire. Many congregations in the F.S.U. prefer songs composed by Dukh-i-zhizniki, especially fast songs with mystical words and new Western Gospel melodies conducive to jumping. These 3 Spiritual Christian groups are easily identified by their characteristic liturgies used during prayer-worship services.
1.
Founded in America. All
Maksimisty are Dukh-i-zhizniki, but
not all Dukh-i-zhizniki are Maksimisty.
2. Most adapted from Russian folk songs and borrowed from German Protestants. 3. Not during service, but often during meals at weddings, funerals, child dedication, holidays 4. Open canon, a sacred text that can be modified by continuous revelation through their prophets. 5. Each congregation has 1 or more prophets. There have been at least 200 prophets since 1928 in all congregations around the world. Prophecies of only 4 prophets were published in their Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' (1928 religious text). Over 100 prophesies are written in secret notebooks, which are shown only to members who believe in their holy spirit. Within each faith group the styles and melodies vary by geographic territory due to generations of isolation among congregations. For example, Molokane in Central Russia (Tambov) use less polyphonic protyazhnaya (протяжная : long-drawn-out) songs than in the Caucasus. Those in Arzerbaijan adapted sounds more similar to Muslem chants than Old Russian folksongs heard in Tambov. In the US, Dukh-i-zhiznik melodies for the same song can differ between Los Angeles County and Central California. In the 1990s, about 50 families of Dukh-i-zhizniki were imported from Armenia to Australia and the U.S.A. Their songs and styles clashed so much with the American transplants that the new immigrants eventually formed their own congregation in Australia, and in the U.S.A. many indigenous Dukh-i-zhizniki cannot sing with them. ^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————HolidaysMolokane, Pryguny, and Dukh-i-zhizniki can most easily be differentiated by their religious holidays.The chart below shows a simple holiday taxonomy of Spiritual Christian Molokane, Pryguny and Dukh-i-zhizniki. Compare to Calendar of Doukhobor Holidays in the Caucasus, by Jonathan Kalmakoff, Doukhobor Heritage Website — arranged from data collected by Svetlana Inikova, Institute of Ethnography and Anthropology, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, in Holidays and Rituals of the Doukhobors in the Caucasus; and compare to Russian Orthodox holidays, feasts and fasts.
2010-2020 Spiritual
Christian Molokan Holiday Calendar in Russian
(left) and English.
(From Vest', 2009 Vol.
6, page 4)
 A. Molokane
— 10-11
holidays depending on congregation. The original
religion of Dukhhovnye
khristiane-molokane (Russian for: Spiritual
Christian Molokans, Духовные
христиане-молокане) as organized by Simeon Uklein
(many believe the religion preceded him), which separated
from Ikonoborsty
(image-wrestlers, iconoclasts) in the 1760s (some
relabeled Dukhobortsy,
“spirit-wrestlers”, in 1785). A. Molokane
— 10-11
holidays depending on congregation. The original
religion of Dukhhovnye
khristiane-molokane (Russian for: Spiritual
Christian Molokans, Духовные
христиане-молокане) as organized by Simeon Uklein
(many believe the religion preceded him), which separated
from Ikonoborsty
(image-wrestlers, iconoclasts) in the 1760s (some
relabeled Dukhobortsy,
“spirit-wrestlers”, in 1785). Molokane were named for their heresy of eating dairy products (molochnye) during the Great Fast (Lent) and splitting from the Orthodox faith. Though the Church created the hostile label as an insult, these Spiritual Christians embraced it with their own definition from the Bible (1 Peter 2:2). Molokane in Kars Oblast (now in Türkiye) fasted and held services for three days before each holiday — Thursday, Friday, Saturday — making each holiday a four-day event, with a feast on Sunday. The practce was continued by those who returned to Russia in the 1920s, and continues today. The scope of this three-day holiday-fast among all Molokane in all regions today is not yet known. The only international Molokan organization is the Souiz dukhovnykh khristiane—molokan (Russian for “Union of Spiritual Christian Molokans” (USCM), Союз духовных христиан—молокан (СДХМ), website: SDHM.ru), founded in Moscow in 1990, and transferred about 1994 to Kochubeevskoe, Stavropol' territory (krai), Russian Federation, after a plea to relocate to the Northern Caucasus to serve the thousands of refugees from the Caucasus. Today many still object to the transfer because to be effective in Russia a “Center” must be in Moscow. In 2007, the SDKM had about 45 dues-paying member congregations in the Russian Federation, and one in San Francisco, California — First Russian Christian Molokan Church : Molokanskii molitvanyi dom (Russian: Molokan prayer house/hall, Молоканcкий молитваный дом). People of all faiths are welcome to attend. ^ Contents ^
American Molokane celebrate 8 holidays. Molokane welcome visitors, photography, and conversion; have open communion; and celebrated 200 years of religious freedom in 2005. Molokane differ somewhat between congregations but agree they are all one unified religion, and rarely split over liturgy. One “Old-Constant” congregation (Russian: staro-postoyannie, старопостоянние) in central Stavropol territory still uses the Old Slavonic Bible and language for reading and singing; and claims the others have fallen away from their original Old Russian religious language. Molokane are somewhat critical, yet tolerant of Pryguny and Dukh-i-zhizniki for adapting non-Biblical versed songs during their services borrowed from other faiths. Molokane have little contact with the zealous and contradictory prophesies of the Dukh-i-zhizniki who use the label Molokan for themselves while avoiding, often condemning, authentic Molokane. About 224 congregations were counted world-wide since 1950.
^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————B. Pryguny, Dukhovnye — 10 holidays. Pryguny is Russian for “Jumpers” or “Leapers.” The full Russian label is dukhovnye khristiane-pryguny, духовные христиане-прыгуны, Spiritual Christian Jumpers. Today in Russia most call those in the same congregation who do not jump — dukhovnye (Russian for Spirituals, духовные), and those who jump — pryguny. In this taxonomy, the term Pryguny is used to categorically distinguish these congregations from Molokane and Dukh-i-zhizniki. Historically, other descriptive terms were used, translated as Bouncers, Dancers, Prancers, Noisy-nose-breathers (holotropic breathers) Molokan-Whips, etc. The current Russian Wikipedia article Прыгуны (сектa) (Jumper (sect)) uses the synonyms: трясуны (tryasuny : shakers ), сионцы (siontsy : zionists),and веденцы (vedentsy : visionaries). Pryguny are a hybrid, with origins and membership from Molokane, German Anabaptists, subbotniki (Sabbatarians : субботники), Russian Orthodox, Lyudi bozhii (People of God : Люди Божий), Novyy israil' (New Israel : Новый Израиль), Skoptsy (Castrates : Скопцы), Shaloputy (Шалопуты), and other non-Orthodox movements. (Zhuk, Sergei I. Russia's Lost Reformation: Peasants, Millennialism, and Radical Sects in Southern Russia and Ukraine, 1830-1917, (2004) page 126.) Before the label “prygun,” the most zealous Spiritual Christian faiths belittled original Molokane by saying we (Pryguny) are dukhovnye and they (Molokane) are postoyannie (Russian : постоянние, constant, steadfast, unchanged, original, genuine, authentic). This term is used by both sides. Non-Molokan zealots who wanted the Molokan label used it as an insult, and Molokane converted it semantically as a defensive modifier to clarify that their faith is the "unchanged original." See perspective points of view, above. In all the world, only in Iutsa town, Stavropol' territory (krai), does a Molokan assembly hall display a sign using the word postoyannie. The sign was placed by my wife's grandfather, Vasili Antonovich Serguiev, who immigrated from Turkey (now Türkiye) to Rostov in the 1920s, then to Stavropol in the 1950s and became presviter. Up to that time the Iutsa Molokane had no identity conflict with a smaller congregation of Pryguny who met in a house. In the 1960s large numbers of Dukh-i-zhizniki, who falsely called themselves Molokane, arrived from Turkey (Türkiye) and were resettled in neighboring towns, and one Prygun presbyter, originally from Tbilisi, which divided the Prygun congregation. To differentiate the 2 Prygun congregations from the Molokan congregation in Iutsa, and from all the Dukh-i-zhizniki in neighboring towns, this sign was probably placed in the 1960s (to be determined). In American marketing lingo, the sign announces; "famous original formula, accept no substitutes, the real deal." After 1992, visiting Dukh-i-zhiznik women from California (who arrived in Moscow with the Heritage Club) were seeking their relatives, which they called "our people," found the Prygun congregations in Iutsa, and gave them each a huge donation, enough to build and expand their prayer halls. The women missed Prygun congregations in other towns and had no close Dukh-i-zhiznik relatives in Russia. I have visited nearly all congregations in Russia, and only found one other sign, on the main assembly in Kochubeevskoe, which identifies it as a Molokan prayer hall. (Photos of signs to be posted.) Molokane-Subbotniki, who refused to worship on Sunday, were labeled “Saturday Molokans” in the Russian Empire Census of 1897, while the original believers remained “Sunday Molokans” (voskerseniki : воскресеники). Some Sunday Molokans, who in 1817 begin migrating to Tavria guberniia (now South Ukraine), adapted features from other Russian Spiritual Chirstians and from German Protestants (Russians' Secret) — a focus on the Apocalypse, prophesy, songs and mind altering spiritual acts like fasting (postnichestvo : постничество), ecstatic dances (radenie : радение), jumping, skipping, walking in the spirit / in joy (khozhdenie v dukhe : хожденин в духе), and actions (deistviia : действия). ^ Contents ^
The label pryguny first appeared in Russian print about 1854 (according to Dr. Breyfogle), though earlier reports described jumping, dancing, leaping, and rapid breathing. Many Saturday Molokane, mostly Subbotniki, in the Former Soviet Union merged with Adventists, and no longer use the label Molokan, yet associate with Molokan and Prygun friends and relatives. The 1897 Russian census counted Pryguny separate from Molokane in Transcaucasia; and we know they celebrate different holidays
Pryguny divide their holidays into “God's holidays” and “Christ's holidays” (Russian: Prazdniki Gospodni i Khristovy, Праздники Господни и Христовы). The 7 Christ's holidays were chosen from more than 40 Orthodox holidays as being the most worthy holidays. Of the 5 God's holidays 2 complimented Christ's holidays, so 3 were added probably by Subbotniki who joined Pryguny and insisted on adding their own Old Testament holidays. Song 181 of the American Dukh-i-zhiznik Songbook of Zion (Sionckii pesennik : Сионский песенник) documents these Prygun holidays. This songbook appears in about 10 progressive versions, after the second version each new book listed lyrics primarily composed and sung by the Dukh-i-zhizniki, but deleting very few as the versions grew. Most lyrics have fallen from common use. The lower numbered songs are the oldest, hence this was definitely a Prygun song that was brought to America.
** Скинопигия (Greek: σκηνοπηγία = skenopegia) : "the pitching of the tent" (John 7:2), Here translated as: "Feast of Tabernacles [Kushchei]" ^ Contents ^
^ Contents ^
———————————————————————————C. Dukh-i-zhizniki — 5-6 holidays. Dukh-i-zhizniki is a Russian term for “people who use the religious text, in short called the Dukh i zhizn'.” In English this could be translated as "Spirit-and-Lifers" which can easily be confused with other groups using similar names in English. For that reason, the most specific and unique universal term must be Dukh-i-zhizniki, transliterated from the Russian: Дух-и-жизники. Removing or deleting the hyphens, or replacing them with spaces, changes the Russian meaning. The Dukh-i-zhiznik family of faiths began in America among descendants of various (at least 12, up to 25) Spiritual Christian tribal faiths from Transcaucasia, Russia, who migrated to the western United States and Mexico from 1904 to about 1912. The most zealous were varieties of Maksimisty who insisted with religious zeal and eclecticism that their prophetic leader, Maksim G. Rudomyotkin, was, as he claimed, "King of the Spirits" (Цар духов : Tsar dukhov). Though Maksim reportedly died in 1877, some believe he did not die but rose to heaven, some say on a white horse, or chariot, and will soon return on the "right side" of Jesus Christ onto Mt. Ararat for the millennium, the thousand-year reign with Christ on earth. The secret contraband writings of Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) in Russia were secretly given few (2?) of his followers who visited him while he was in a monastery prison in Suzdal, north of Moscow Russia. The smugglers took this fobidden contraband to Rudomyotkin's home village of Nikitino (now Fioletovo, Armenia). Two bundles of tiny script were kept by a relative Mikhail E. Telegin and shared among a few of Rudomyotkins followers. For some reason, perhaps greed and jealousy, Aleskei S. Tolmachoff stole the small bundles of Rudomyotkin's notes from Telegin and smuggled them to Arizona, United States. The notes were again stolen (copied in secret) by Pivovaroff and Valoff and published in Los Angeles by Shanin and Kobsiv during the 3-year bride-selling scandal (1912-1915). The 1928 version of the Dukh i zhizn' (Spirit and Life) evolved from a publication in 1915 of selected handwritten notes smuggled to Arizona by a niece of the Prygun prophet and martyr in Russia, Maksim G. Rudomyotkin (1818~1877). A series of versions were created which added, deleted, rearranged, and edited spiritual writings from other men. The 1928 version was disputed for omitting a chapter submitted by Pivovaroff which he published as a pamphlet and which was often inserted into the book. When James Pivovaroff published the first nearly complete English translation in 1976 he included this missing chapter. Dukh-i-zhizniki evolved mostly from descendants of mixtures of non-Molokan Spiritual Christian congregations and faiths (Prygun, Khristovoverie, Stundisti, Sionist, Klubnikinist, Maksimisty, Noviy israil', etc.) mainly from what is now central Armenia, and far eastern Anatolia Türkiye. The most aggressive were followers of the Prygun presviter Maksim G. Rudomyotkin (often shortened to MGR), called Maksimisty, who instructed them to abandon half of their Prygun holidays — the holidays shared with Molokane (Christ's holidays) — because they were adapted from Orthodoxy, to keep only the Old Testament holidays (God's holidays) adapted from Subbotniki, and to shun Molokane and Subbotniki — forming a new sect. Followers of prophet Efim G. Klubnikin, and immigration organizer Filip M. Shubin initially joined in Los Angeles along with other zealots and non-zealots. When they began to established a new life in the city, from the late 1910 into the 1960s, more than 50 years, various individuals and factions confronted each other, most leaving the faiths, many splitting to form new congregations. Dukh-i-zhizniki somewhat solidified after 1928 when these diverse congregations in the U.S. allowed the book Dukh i zhizn' to be placed on their altar tables (prestol), as a Third Testament to the Bible, and used it for worship and rituals. The editors of the 1928 edition signed as Братскiй Союзъ Духовныхъ Прыгуновъ (Bratskii Soiuz Dukhovykh Prygunov : Fraternal Union of Spiritual Jumpers), but in the introductory pages the misnomer Molokan is used. The book was undoubtedly a spiritual victory by the Maksimisty to have their prophet dominate the book with 66% of the pages, and impose his "new rituals" (novye obryady) upon all congregations, though many members in all congregations did not believe in the divinity of Rudomyotkin. Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) also called his followers “Zionists” and “New Israel”, though they did not share communion with New Israel nor did they migrate to Palestine as did many Subbotniki. Molokane and Pryguny commonly call them Maksimisty (Russian for: “followers of Maksim G. Rudomyotkin”, maksimisty, максимисты), but not all Dukh-i-zhizniki are Maksimisty. Rudomyotkin was registered in a Suzdal monastery as a prygun, where his death was documented by Nikolai Ilyin in 1877, yet disputed by some followers who believe he rose to heaven like Jesus Christ (on a white horse, in a chariot) or returned to his home village in disguise. The precursors to the Dukh-i-zhiznik faith were transported to Los Angeles beginning in 1904, and begun to solidify in 1915 when a few Maksimisty who moved to the state of Arizona published in Los Angeles some of Rudomyotkin's notes in the Russian language in the book: Утренняя звезда (Utrennyaya zvezda : Morning Star), then published a Prayerbook (Russian: Molitvennik, Молитвенникъ), and a songbook. They ignored the prayer books used by Molokane ( a different faith) that began to settled in San Francisco in August 1906. In the Former Soviet Union the Dukh-i-zhiznik books are often collectively called obryadniki (обрядники : ritual, ceremony books). ^ Contents ^
After about half a dozen or more revisions, the final and current version of the Dukh i zhizn' was published in 1928 (758 pages) in Los Angeles by «Братскiй Союзъ Духовныхъ Прыгуновъ» (Bratskii Suiz Dukhhovnykh Prygunov : Fraternal Union of Spiritual Jumpers), not by "Molokans" as popularly assumed. About 66% of the pages are credited to Rudomyotkin (1818~1877), with debate, plus sections by 3 prophets (Klubnikin, Sokolov, Yesseivich), and a short history apparently by Pauline Young but not not credited to her. About 60 pages of controversial text by Rudomyotkin previously published in 1915 was omitted. Since 1928 the book has remained constant, unchanged (postoyannie). Another 60 pages by M.P. Pivovaroff were not included which enraged him such that he published his own prophetic writings, purchased several cases of the new book, and inserted his missing chapter, fabricating a second version in 1928. The book was disputed by some during every revision and printed version. The Dukh i zhizn' was placed “by the Holy Spirit” by the Prygun prophet Afanasy T. Beziaev (Bezayeff, Bezaieff), not by a democratic vote of members, on all Prygun altar tables in the U.S., except the Selimsky congregation in Arizona, and the Holy Jumper congregation in San Francisco. The book was allowed into the Guadalupe, Mexico, prayer house as a reference, not on the table. The two Molokan congregations in America (San Freancisco and Sheridan) were not approached or refused the book. Pressure to adopt the "new rituals" of Rudomyotkin took decades. Non-believers in the new book left the Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths. Before a failed migration back to the base of Mount Ararat in 1939, diaspora elders declared no need to translate their books into English. To continue the Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths in America, translations were needed to retain the youth. In 1944 John K. Berokoff in Los Angeles, conlcuded that migration to Russia is unlikely and began to re-publish the Arizona prayerbook translated in 1915 for Americans in Arizona, and his own translations. In 1947, a 3rd edition was edited and published by molodoe sobranie (the youth assembly) in the Flat(s) neighborhood, changing pages 747 to 758. (Research in-progress.) About 1964-66, John Wm. Volkov, while a graduate student in Slavic languages at the University of California Berkeley (U.C.B.), translated the entire book himself with some help from elder Russians in the San Francisco Bay area. Most difficult were numerous mystery "spiritual" words. In the summer of 1966 in Los Angeles, after Wednesday Night assembly, John Volkov, driven by Andrei A. Shubin, by uncle, arrived at the LA-UMCA (Gage Ave) after everyone left but 3 board members and me, Andrei Conovaloff. Volkov hand-delivered a typed carbon copy of a sample first section of his translation to LA-UMCA president Paul Lukianov, vice-president Mike Planin, and former president Alex Tolmas, with instructions to publish the book and donate all proceeds to the U.M.C.A. general fund. He said they could pass it around to anyone to proofread. That summer I was given a sample copy to take to Arizona elders to proofread, which I delivered to Alex L. Conovaloff. All groups apparently refused and/or were afraid to publish it. The project stagnated for more than a decade. I met John Volkov several times when he visited my maternal grandmother's house in Boyle Heights. He told me that the book title as printed on the cover in 1928 was inverted, and that the proper translated title is Book of the Sun, Spirit and Life, but in the triangular diagram, the words "Spirit and Life" appeared on top. This changed the commonly used short title, as published in 1915, from Дух и жизнь (Dukh i zhizn' ) to Книга солнце, дух и жизнь (Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' ). Volkov was respected by few Dukh-i-zhiznik elders. He was unmarried, college graduate, an alcoholic, and at times homeless. The late presbyter Harry Shubin often bought him to speak at the Wednesday night youth assembly at the U.M.C.A., always drunk. He had no permanent address or phone number that I could find in 1980. He was a friend of my late uncle Andy A. Shubin who told me none of Volkov's relatives knew where he was or if he died. If anyone knows, please reply. Though very few read Russian, the book was symbolically bought and given as a wedding gift, an icon of their faith. As in their meeting halls, this book must be placed next to the Bible, typically on the formal dining table (not in a kitchen) to symbolize their adherence to the Dukh-i-zhiznik faiths. To the most zealous, not displaying the book at home is near-heresy. ^ Contents ^
Efforts to publish the Volkov's translation was delayed about a decade, until 2 talented young men at the U.M.C.A. discovered that the translation existed (mostly in secret) and began the publication project, which was delayed nearly another decade by zealots. Credit for this project goes to buddies George G. Shubin and John Karnoff. John Karnoff died young in 2001. George G. Shubin edited the following (indented section) in July 2017. While getting married in 1969, George G. Shubin was told that he was lucky to get one of the last copies of the Russian "Spirit and Life" from the U.M.C.A. inventory. More were needed because Wm. Wm. Prohoroff had purchased all available books to distribute in the Soviet Union. At East Los Angeles College, Shubin was editor of the campus literary magazine, and later became editor of the U.M.C.A. newsletter The Molokan. He volunteered to organize a reprinting of the Russian Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn', with the help of his buddy John Karnoff. They spent a year estimating costs and soliciting funds. Elder publisher Paul I. Samarin provided much guidance and the printing facilities to reprint the original 1928 edition. They added a much needed 8-page index at the end and kept a 1-page insert Samarin added in 1958 to explain the various versions. The 1975 edition has 766 pages, 1500 copies were published. Their names did not appear, credit was given to Samarin. ^ Contents ^
Only Russian editions of Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn' are used by Dukh-i-zhizniki for singing. Occasionally the English versions are read when giving speeches, depending on the congregation, Russian literacy of speaker and guests present. Some claim the Dukh i zhizn' can only be understood in Russian by a few chosen with the gift of the Holy Spirit because many unknown mystical words appear in it. (Research in-progress.) Dukh-i-zhizniki in America apparently outwardly claimed the religious label Molokan for many reasons, including:
The largest cemetery in the U.S. operated by Dukh-i-zhizniki (Commerce CA) posts the label “Spiritual Jumper” only in Russian, not in English. (See image above.) The signs on the gate and street display “Russian Molokan Christian,” as does an internal sign in Russian and English, but the Russian words are not completely translated, hiding the embarrasing Prygun identity from descendants and Americans who cannot read Russian. The original historic label “Spiritual Christian” is also notably absent in English. ^ Contents ^
Wide Variety of Dukh-i-zhizniki A wide spectrum Dukh-i-zhizniki exist around the world in the 2000s. Divisions occur within and between congregations, and many remain irreversibly divided, by geography, by the extent of use and acceptance of the Dukh i zhizn', belief in and practice of various old Russian rituals and traditions, holidays, and after a dominate elder dies. See list of divisions below. All efforts to unify Spiritual Christians in the Americas into apocalyptic agricultural colonies failed. In 1933, an effort to unify all in Los Angeles into one “Big Meeting” (Bol'shoe sobranaie: often mistranslated as "Big church") failed mainly due to objections by zealous tribes against the komitet (the committee, and/or board of directors). Significant minor reasons involve the liberal attitudes of various presbyters and elders. A significant and persistent division indicator is that more members of the Bol'shoe sobranaie supported the U.M.C.A. (founded 1926) and Y.R.C.A. (founded 1939). Most members did not abandon all the "Christ's holidays" as commanded by Maksim G. Rudomyotkin (1818~1877) which is a sin to Maksimisty. Most of the minority of Molokan families in Los Angeles who wanted to attend meetings had to join the Bol'shoe sobranaie because they were not tolerated by the more zealous congregations. More Bol'shoe sobranaie families tolerated intermarriage, and some ne nash spouses joined. Drinking alcohol was more tolerated In short, Bol'shoe sobranaie was the most liberal of the congregations that tolerates the Kniga solntse, dukh i zhizn' on their altar table, next to the Russian Bible. By the 1950s, all Prygun congregations in the U.S.A. (not Mexico) were officially, though not intrinsically, converted to a Dukh-i-zhiznik faith. The adherence to a total Russian service with mystical ecstatic Spiritual jumping and prophesy caused thousands to not attend except for an important family event (primarily funerals then weddings) In 1950 many immigrant Pryguny who arrived in Los Angeles from Iran (Persia) were rejected by locally established zealot Dukh-i-zhizniki, until the immigrants placed the open Dukh i zhizn' on their altar table next to the open Russian bible and officially abandoned half of their holidays. This was a major cultural shock to the immigrants who were misled that they were being hosted by Spiritual Christian Molokane, people of identical faith. Until the immigrants were fully converted or left, American Dukh-i-zhizniki who attended the "Persian" Prygyn services were severely reprimanded for attending a heresy faith, even if only suspected of attending. See: Dukh-i-zhizniki in America: Chapter 8 — Aid to Brethren in Iran. In the 2000s, all Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations in Los Angeles County refused to attend any "Persian" event; official reason was lack of onsite parking, unofficial major reason was fear of Mexicans. About 2015 the "Persian" congregation property in East Los Angeles at 1135 S. Kern Ave was sold, and the funds put into a trust to pay for any member to join another (Dukh-i-zhiznik?) congregation. In his autobiography The Memiors of Paul John Orloff (2008, self published, 568 pages) the elder singer documented how he was falsely accused and extensively harassed for allegedly attending a "Persian" Prygun holiday in 1961. In "The Story of Why I avoided Big Church Since Sept. 14, 1965" (pages 427-456), Orloff (dob-dod) detailed the sequence of actions against him for allegedly attending a "Persian" Rozhdestvo service (Birth of Christ, Christmas). This false accusation was easy to verify because witnesses could testify that Orloff actually attended a Dukh-i-zhiznik pomenki (memorial service) that same day in Porterville, Central California, about 170 miles away. His accusers repeatedly refused to check the facts or talk with witnesses, and intensified their bullying until the Orloff family left to join another congregation (Akhtinskii, Samarin's, Percy St). For more than 50 years the "Big Church" board and prestol have refused to review this case and never apologized. (If they ever do, I'll post the date.) In the 1980s Dukh-i-zhiznik relatives of founders of the “Re-Formed” Prygun congregation in Oregon (above) were harassed. The elder lead singer John Alex Efseaff was terminated from his spiritual role, but allowed to sit in his place, at Novaya Romonovka sobranie (Beswick st) because his son Phillip co-founded an English Prygun congregation, not using the religious text Dukh i zhizn', and co-published the Besednyik (sic: Besednik, Беседник : talker, Old Russian) newsletter in the 1980s which critically examined Dukh-i-zhiznik history. The sin of the elder Efseaff was not publicly ostracizing his son for his heresy. In the 1990s descendants of the original core Klubnikin congregation (Gless st.) bought a property on Clark Street, City of Industry. In the 1970s, they were last congregation to move from the "Flats" because their building burned. They met house-to-house then rented a building in Norwald called "605" in the 19forced to move from the were the remnants soon nicknamed "Clarkies" in ridicule, and closed their doors to non-members for 10 years. ^ Contents ^
Ironically the oral history of these Spiritual Christians emphasizes religious freedom as a main reason for fleeing to America, yet many do not tolerate freedom of religion or speech, some to the extent of lying. They have bullied people based on allegations and actions of relatives, and threatened this website. Dukh-i-zhizniki around the world have divided for many reasons (not in rank order):
^ Contents
^
Pryguny around the world have divided for a few reasons:
Molokan divisions are very rare. Only one congregation of Molokane voluntarily divided, that I know of, in 2007 in Novokumskoe village (next to Levokumskoe), Stavropol territory, Russia. The division was about rituals and succession after the presviter Loskutov died, who lived nearby. The younger members wanted to eliminate some old rituals, so a minority who wanted to preserve their heritage rituals purchased a house across the street, which they converted to a meeting hall. The Novokumskoe congregation was much larger up to a few years earlier, about 2005, when Sunday bus service between Levokunskoe and Novokumskoe stopped, and the majority in Levokumskoe had to build a new hall, in which Vedat Akçayöz, historian from Türkiye of Prygun descent, recorded a "malakan" wedding on video. The minority isolated in Novokumskoe was stressed and reduced, which caused a leadership division. ^ Contents ^
Marriage In 1909 during the Pashka holiday in Los Angeles, Alex Kottoff 23 and Lana Sissoeff 18 attempted suicide because Lana's father forbid her marriage to Alex. From 1911 through the 1920s Prygun traditional parental control of free-unregistered marriage became a legal scandal in Los Angeles and near Glendale, Arizona. In contrast the San Francisco Molokane more quickly complied with American laws to register marriages, and allowed mixed marriages. For a century, Dukh-i-zhizniki controlled their families actions with punishments and rewards, ostracism and inheritance, for who they befriended and married. From 1905 through the 1930s in Los Angeles many Spiritual Christian immigrant families maintained their tradition of a customary "bride price" (kalym : калым) to compensate for their loss of a working daughter, and the expense of her wedding. In Russia the typical amount was 2 dairy cows, and in the U.S.A. it was $200-$500. In December 1911, Elsi Novikoff 17, fell in love with an American boy, though her father had already promised her to marry a Prygun boy for the highest price yet of $500 because she was very pretty and was earning money for her family. In 2016, the income relative value of $500 from 1911 is about $78,000, with a relative value range from about $10,000 to $268,000. (MeasuringWorth.com) She worked as a maid, and her boyfriend's family and employer advocated for her, hiring an attorney to defend her case in court. The story was national news and the investigation exposed more cases reported for neary 3 years. The court case correlates with mass hasty migrations of families to scattered rural colonies for a decade, until the depression after W.W.I. To maintain their old world parental controls (marriage, education, dress, language) many Spiritual Christian families fled in groups to other states (Arizona, Washington, Utah, New Mexico), a few went back home to Russia. Some reported that religious persecution in Los Angeles was their major reason for leaving to form remote farm colonies. Very fortunate for the Pryguny in Los Angeles, presiding Judge Curtis Wilbur was also on the board of directors of the Bethlehem Institutions, and intimately knew these immigrants from their other court cases and the work of Dr. Rev. Bartlett to assimilate them. The Spiritual Christians got off easy after agreeing to register all previous marriages and re-do the weddings which the Judge offered to perform for no fee. In Arizona in 1920, 2 presbyters (presvitery) were arrested and fined for the same crime. Mike P. Pivovaroff spent a night in jail, and Foma ("Homer") S. Bogdanoff turned himself in the next day before their trials. They were each fined $300 (nearly a year's wages each in 1920, bail paid by congregants) and ordered to re-do all marriages legally. In 2016, the relative value of $300.00 from 1920 ranges from $2,800 to $62,000. (MeasuringWorth.com) Within a few years most all the hastily formed farm colonies failed, and most Spiritual Christians decided to tollerate American laws and returned to their "kingdoms" in urban Los Angeles. Statistics on how many actually registered marriages is in-progress. In the 1930s after being denied mass emigration back to Russia, Dukh-i-zhizniki exported their newly organized faith to the Soviet Union. The ritual books (Dukh i zhizn', with prayer and song books) were mailed to Rostov (U.S.S.R.), Armenia (S.S.R.) and Kars (Türkiye), where all Maksimist and some Prygun congregations adopted them and transformed their faiths to somewhat conform with instructions from America, while retaining much of their historic differences of origin. Dukh-i-zhizniki now in the the North Caucasus, Russian Federation, arrived in two waves — in 1962 from Türkiye during a massive resettlement, and 1987-1990s from Armenia during perestroika. They are fractionated and sometimes claim to be the “true” Molokane due to propaganda from America, but avoid and scorn the orgnaized Molokane, S.D.K.M. (U.S.C.M.). The most zealous congregations in the Former Soviet Union (F.S.U.) reject all Dukh-i-zhizniki for abandoning their motherland, the prophesy to stay near Mount Ararat, other prophesies and communal traditions; living in cities; using yekrany (экраны : display screens, T.V., movies, computers). In opposition, many Dukh-i-zhizniki in the U.S.A. and Australia reject those in the F.S.U. for enlisting in the Soviet military (eating non-kosher-like), and because their grandparents did not obey their Klubnikinist prophesy to leave Russia, some calling them "Jerusalem," outsiders (ne nashi) and non-believers. Since perestoika, about 50 Dukh-i-zhiznik families were imported from Armenia, half to the U.S. and half to Australia, primarily to enhance the local congregations with Russian-speaking co-religionists. The immigrants found that their songs, rituals and a new holiday were not fully accepted. Those in Australia formed their own congregation. Those in the U.S. clustered among a few congregations which showed the most acceptance and need for Russian-speakers. Dukh-i-zhizniki rarely seek new affiliations with Molokane or Pryguny. Though 100s of Dukh-i-zhizniki work in Moscow, they do not hold prayer meetings and never attend Molokan services, even when personally invited by Molokane. When intermarriage occurs between these 3 denominations the couple must decide which to join, if any. Occasionally a Molokan marries a Dukh-i-zhiznik and joins the mate's congregation, only after conversion and scrutiny. No Dukh-i-zhiznik congregation joined the S.D.K.M. by 2007, or attended the 200th Anniversary in 2005, though some attended the diaspora 150th Anniversary held in San Francisco in 1955, and many Pryguny attended the 100th Anniversary held in 1905 in Vorontsovka, Tiflis governate (1844 Vorontsovka, 1935 Kalinino / Kalinin, 1992 Tashir, Armenia). Confusing to outsiders and to themselves, many Dukh-i-zhizniki today self-claim to be “true” Molokans by faith. Few welcome visitors, photography, or conversion; and most have closed communion. About 86 Dukh-i-zhiznik congregations, many are small, counted world-wide since 1950.
^ Contents ^
12. Other Classification Systems See Two Classification Systems for Spiritual Christian Molokane, Pryguny, and others, and Brandjacking the Dukhobortsy and Molokane. English version In-Progress Религиозные течения и секты. Справочник (Directory of religious denominations and sectarians) Discontinued Labels Though many labels have been used for the varieties of Spiritual Christians, most are now extinct or the labels no longer commonly used, for example: Knowers-Seers, True Spiritual Christians, Zionists, Akinfevs, Water Molokans, Sunday Molokans, Don group, Krylovs, Molokan-Sabbatarians (Molokan-Subbotniki), Saturday Molokans, Communalists, Noisy-nose-breathers, Bouncers, Molokan-Baptists, Molokan-Fasters, Clean, Stundist-Molokans, Evangelicals, Molokan-Presbyterians, New Molokans, Evangelical Christians, Springers (German translation of Pryguny) Shtundo-Evangelicals, New Israel, Tolstoyan, Nemolaky (non-prayers, non-worshipers)... |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
^ Contents
^
13. Research Methods In the 1950s my father explained why I found a cluster of artifacts in our cotton field when I chopped weeds — belt buckle, broken glass and pottery. He said that the Gozdiffs used to live there in the original colony. Now their son Mike and his family live a mile away. In the 1970s, I began to map our country road mile to show the location of our New Salem — Selimski — colony, named after the village in Russia (now Türkiye) were all the grandparents lived, and the other 3 colonies north of us. Since the 1960s, I recognized obvious differences among the 2 residual faith tribes in Arizona, but it was not until the 2000s that I realized they were so often confused because they lacked "scientific classification", like I learned in school. One name was missing, and needed to be created. I graduated in the life sciences where everything had a name, and if something did not have a name, a new name was made. The language of science is specific. My primary sources for this "Taxonomy" were gathered by visiting more than 100 Spiritual Christian congregations around the world, including 5 trips to the Former Soviet Union (1992, 1997, 2007, 2011, 2015) for more than a year total time. I visited the colonies in Baja California, Mexico, 3 times. My secondary sources were found around the world in libraries and archives, and from interested scholars. I toured California and up the Pacific Coast into Canada at least 10 times. During the 1970s I met 100s of Spiritual Christians as I coordinated and published in 1980 the most comprehensive directory of 4,500 households of non-Dukhobor Spiritual Christians from Russia in the Americas and Australia. In 1992, I attended and video taped the 2nd international congress of Spiritual Christians - Molokane, in Astrakhanka, Ukraine, where I met representatives from about 50 congregations across the Former Soviet Union. In 1996 I began posting on the Internet at Glendale Community College, Arizona, which recently built 2 buildings with 100s of desktop computers, easy to access. In 1997 my Prygun relatives in Stavropol province, Russia, conducted my wedding with Tatiana Nikolayevna, a local Molokan whom I met on my first trip. When she arrived in the U.S. we visited her Dukh-i-zhiznik cousins in Los Angeles County, whom I already knew. In 2000, Jonathan Kalmakoff launched the "Doukhobor Message Board" as a public genealogy database on RootsWeb, now hosted by Ancestry.com in the "Religions and Religious" section. Board information statement: " Welcome to the Doukhobor Message Board: This RootsWeb message board is for family researchers to post messages, share information and respond to others who are researching Doukhobor genealogy. .... Join the Doukhobor Mailing List ... Visit the Doukhobor Heritage Website" In 2002 I launched the "Molokan Message Board" as a public genealogy database, which is now hosted by Ancestry.com with "Religions and Religious" topics. Board information statement: "This board aims to limit information to Spiritual Christians from Russia and their families, primarily Dukh-i-zhizniki, Molokane, Pryguny, Subbotniki-Adventisty, Dukhobortsy, Baptisty and related groups." There is a list of links to more information. Many people began to post genealogy information, notably Nancy Popin-Umland who contributed about half of the messages. In the 2000s I met thousands of recently arrived Spiritual Christian Subbotniki and Adventisty (descended from Molokane) established in east Portland Oregon, and around Vancouver and Seattle Washington. Their elders sing many of the same hymns and melodies as the Spiritual Christians who arrived to North America more than 100 years earlier. In 2007 my wife coined the Russian word Dukh-i-zhizniki to precisely label the faiths that I called in English "Spirit and Lifers" and "S&L-users". The Russian term is a unique way to label the loosely organized network of congregations around the world that require the Kniga solnste, dukh i zhizn', and related song and prayer books for their liturgy. In 2008 I began a chronological database of relevant online references for our research, now with over 10,000 listings. My library consists of over 100 books about Spiritual Christians in and from Russia. I network with 4 Dukhobor scholars to compare notes, because their history inspired some of their Spiritual Christian neighbors in the Southern Caucasus to also move to North America, which is why most of you readers are not in Russia. To collect more data about the first rural migration from Los Angeles to Hawaii in 1906, we went there twice. In 2012 we went to Kauai to meet a local historian with whom I had been in contact, to locate the "Molokan Agricultural Colony" and sugar plantation that hosted them. In 2013 we focused on the state archives in Honolulu meeting up with the state archivist with whom I had been in contact with since about 1982. In 1906 before they left Los Angeles, local reporters recognized that they were at least 3 different groups in conflict. On our last day we located only two original published photographs of the Molokan group, with some Pryguny. In 1910, Demens published in Los Angeles a complete analysis about the failure of the Hawaii colonization. More later. In 2015 I visited my grandparents' village of Selim, Kars province, Türkiye. Several original houses remained, but the cemetery was covered by a parking lot for the new regional hospital. I also inspected the 3 Dukhobor 1895 burning of arms sites with historian Johnathan Kalmakoff and other Canadian Dukhobortsy on a heritage tour. I remained in Tbilisi, Georgia, where I located the last 3 Molokan congregations. In the past 25 years I have networked with historians — (alphabetical) Geroge Bolderoff*, Dr. Nicholas B. Breyfogle, Dr. Eugene Clay, Dr. Andrei Donskov, Ethel Dunn*and Dr. Stephen P. Dunn*, Larry Ewashen, Dr. Svetlana Inikova, Jonathan Kalmakoff, Joyce Keosababian-Bivin, Micheal P. Ledieav (died July), Jack MacIntosh*, Nancy Poppin-Umland, Mike Rudometkin, Koozma J. Tarasoff, USCC-Doukhobors, Dr. Sergei I. Zhuk, and many more around the world. In Russia I have relatives in all 3 of these groups, but most of my Conovaloff (Konovalov) ancestors, relatives and extended clans were Pryguny from Central Russia. They remained postoyannie (steadfast) Pryguny in the USA and Russia while tolerating Dukh-i-zhizniki. My Prygun relatives conducted our wedding in Essentuki, Stavropol krai, Russia, in 1997. We may be the only practicing Pryguny left in America because we can share holidays with both Molokane and Dukh-i-zhizniki. I hope some of you will be as thrilled as I am about the information we are collecting. Keep coming back for updates. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||